Genomic DNA and plasmid DNA are two sorts of DNA present in living entities. They are double-stranded structures containing deoxyribonucleotides. Genomic DNA is chromosomal DNA, whereas plasmid DNA is extrachromosomal. Let’s know the other notable differences between them.
What is Genomic DNA?
Most living beings have genomic DNA in each cell. The genomic DNA encodes genetic information that is passed from one generation to the next. Also, they are commonly termed as gDNA.
What is Plasmid DNA?
It is an extrachromosomal DNA that is separated from the genomic DNA. Its remarkable property of self-replication makes it exceptional. Thus, they are used as vectors in recombinant DNA technology. Some plasmids are also artificially created to serve this purpose.
Difference between Genomic DNA and Plasmid DNA
Genomic DNA |
Plasmid DNA |
| Genomic DNA is found in both prokaryotes as well as eukaryotes. | Plasmid DNA is found only in prokaryotes like bacteria, and also in a few eukaryotes. |
| It is a chromosomal DNA larger than the plasmid DNA. | It is extrachromosomal DNA that is comparatively smaller. |
| It is essential for the growth, survival and reproduction of the cell. | It is not very essential for the functioning of the cell. |
| Lower rate of replication. | Higher rate of replication. |
| It is not used as a vector in recombinant DNA technology. | The plasmid is a popular cloning vector in recombinant DNA technology. |
Also Refer: Difference between Plasmid DNA and Chromosomal DNA
Frequently Asked Questions
What are artificial plasmids?
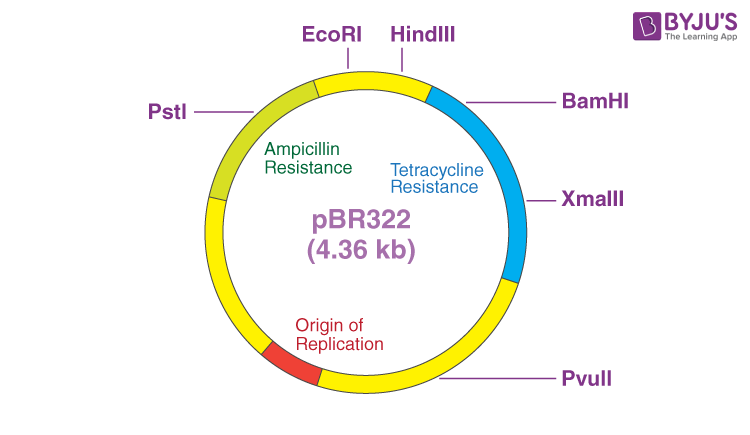
Some plasmids are artificially designed in laboratories. Their sole purpose is to act as vectors in introducing foreign DNA to the host cell. They have a higher rate of replication than the naturally occurring plasmids. Examples are – pBR322, pUC19, pUC18, etc.
What is recombinant DNA technology?
This technology modifies the phenotype of the host cell. The desired DNA is fragmented using a restriction enzyme and then ligated with the DNA of the cloning vector. Now the desired DNA replicates inside the genome of the host cell. This technology is widely used in the agriculture field to produce GMOs (Genetically Modified Organisms).
What is a plasmid vector?
The recombinant DNA is carried to the host cell via a plasmid vector. Some plasmids are naturally obtained, like the Ti plasmid from Agrobacterium tumifecians (plant bacterium). Whereas, some plasmids are artificially created to act as vectors (pBR322 and pUC19). Artificial vectors have a better replication rate than natural cloning vectors.
Also Read: Cloning vector

Keep exploring BYJU’S Biology for more exciting topics.
Comments