What is photooxidation?
As the name denotes, photooxidation is the oxidation reaction happening in the presence of light energy. When high-intensity light hits the plant, there is an excitation of energy that leads to the oxidation process. The accumulation of reactive oxygen harms the plants. This process happens in the chloroplast, and might destroy the plant pigments.
What is photorespiration?
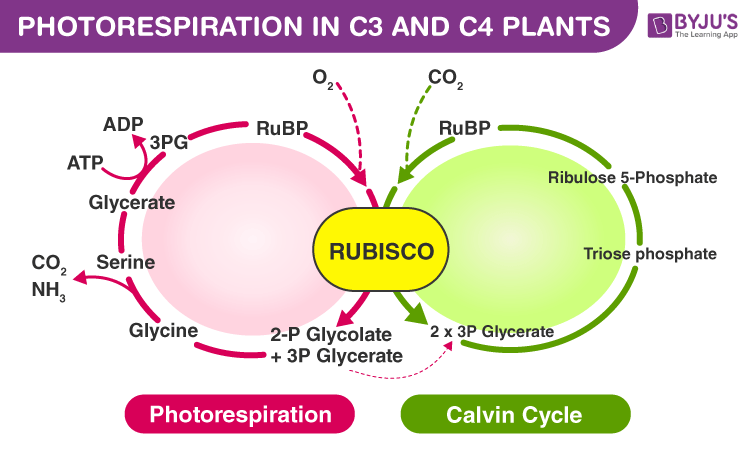
Photorespiration is a plant metabolic process where the RuBisCo enzyme oxygenates the RuBP molecule. It is considered a wasteful process, as the final product (3-phosphoglycerate) is produced at a reduced rate with a high metabolic cost.
The RuBP binds with O2 to form phosphoglycerate and a two-carbon molecule called phosphoglycolate. This pathway is known as photorespiration. This process is seen in C3 plants. Whereas, the C4 plants lack this photorespiration. The actual biological function of this pathway is not yet known.
Difference between Photooxidation and Photorespiration
Photooxidation |
Photorespiration |
| In the presence of high-intensity sunlight, the oxidation of chlorophyll happens. | In the presence of sunlight, uptake of oxygen and synthesis of CO2 takes place. |
| This leads to the accumulation of reactive oxygen. | The CO2 obtained through photosynthesis is lost here. |
| It is seen as a harmful process in plants. | It is an energy-wasting process. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What are C3 and C4 plants?
Examples of C3 plants – Wheat, oats, etc.
Examples of C4 plants – Sugarcane, Pineapple, etc.
What is RuBisCo?
RuBisCo is an enzyme found in the chloroplast of plants. This enzyme can bind to the active site of both O2 and CO2. Thus, the name RuBisCo. It has a higher affinity for CO2 when the ratio of O2 and CO2 are almost equal. If their concentration is not equal, their binding will be solely competitive.
How does photooxidation help in crude oil breakdown?
When sunlight acts on the oil, the oxidation process occurs. The photooxidation results in the change in the composition of the oil. This easily breaks the oil molecules. Thus, oil spills can be easily removed by photooxidation.
Also Read:
- Photorespiration
- Photorespiration in C3 and C4 plants
- Difference between C3 and C4 plants
- Calvin Cycle
Keep exploring BYJU’S Biology for more exciting topics.
Comments