Assays are analytical or investigative procedures that aim at assessing a molecule quantitatively and qualitatively. ELISA (Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) and ELISpot (Enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent spot) are two widely used assays in diagnostic and molecular biology.
ELISA
ELISA is a biochemical assay that is used to detect the presence of a protein or ligand by directing antibodies against the molecule.
In the most simple form, an ELISA is performed by attaching the sample antigens to a solid surface, antibodies against the antigen are linked to an enzyme, a substrate for the enzyme is added, and the antibodies and antigens are allowed to hybridise. On binding, the substrate produces a signal that is mostly a colour change.
The four types of ELISA are Direct ELISA, Sandwich ELISA, Competitive ELISA and Reverse ELISA.
It is used in HIV tests, detecting food allergens and screening drugs in toxicology reports.
Read more: ELISA Technique
ELISpot
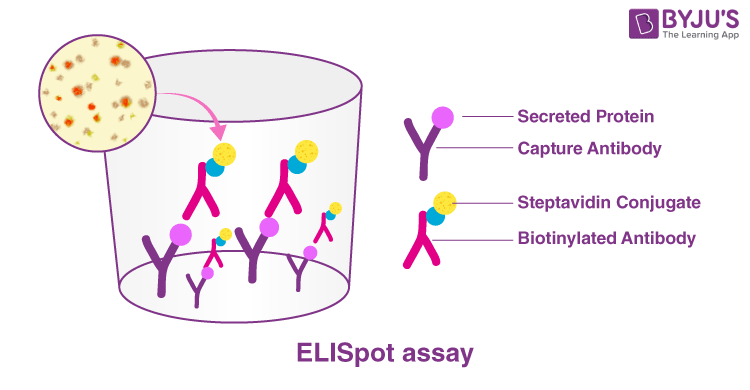
ELISpot is a technique that focuses on measuring the quantity of cytokine-secreting or antigen-specific cells. It is an immunostaining technique that uses antibodies to detect the protein analyte.
FluoroSpot is a variation of ELISpot that uses fluorescence to analyse multiple analytes at once.
Mechanism of ELISpot
- Antibody coating: A lab plate with 16-100 wells is taken and the first coating to be put in it is the monoclonal antibodies that are cytokine specific.
- Cell Incubation: The cells to be tested are added to the wells and allowed to secrete the cytokine.
- Cytokine capture: The cytokines secreted by the cell start to bind with the monoclonal antibodies.
- Detection antibody: The wells are rinsed to wash away the cell debris, and only the cytokines bound to the antibodies remain. Biotinylated cytokine-specific detection antibodies are added to detect the cytokine-bound antibodies.
- Streptavidin-enzyme conjugate: Streptavidin-enzyme conjugates are added to the well to detect the detection antibody.
- Addition of substrate: A substrate is added to the well that is catalysed by the enzyme conjugate. The reaction forms an insoluble precipitate that forms a spot in the well.
- Analysis: The spots formed can be read on an automated ELISpot reader, and then the frequency of cytokine secretion can be calculated.
ELISA vs ELISpot
| ELISA is a biochemical assay that is used to detect the presence of a ligand (mostly protein) by directing an antibody against it. | ELISpot is a technique that is used to measure cytokine-secreting cells. |
| It was discovered by Engvall and Perlmann in 1971. | It was discovered by Cecil Czerkinsky in 1983. |
| Antigens are first immobilised in the wells. | Antibodies are first immobilised in the wells. |
| It detects the total concentration of signalling proteins. | It identifies the frequency of cytokine secretion. |
| It is less sensitive than ELISpot. | It is more sensitive than ELISA. |
|
FluoroSpot is not a type but an alternative form of ELISpot. |
| It is used widely as a diagnostic tool to detect diseases such as HIV, Covid-19, dengue, malaria, etc. | It is not used individually in diagnostics but in addition to ELISA to detect pathogens. |
| It detects pathogens, food allergens and drugs during toxicological screening. | It is useful in vaccine development, cancer and allergy detection, monocyte cell characterisation and veterinary research. |
Explore BYJU’S Biology for more interesting topics.
Also Read:
- What Is Sandwich ELISA?
- What is ELISA and its types?
- What are the 4 steps of an ELISA protocol?
- Which diagnostic tests are most commonly used to determine the type and cause of respiratory system disorders?
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is ELISA used instead of radioimmunoassay?
ELISA tests are more accurate and sensitive, which is why they are preferred over radioimmunoassays (RIA).
What is the principle of radioimmunoassay?
RIA is a technique where a radioactive antigen competes with binding with a non-radioactive antigen, i.e. a phenomenon of competitive binding.
What is the difference between ELISA and Western Blot?
ELISA is a biochemical assay that is used to identify the presence of antigens and antibodies, whereas western blot is a molecular technique that is used to detect a particular protein in a tissue or blood sample.
Which cells can be analysed by ELISpot assay?
Monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, cytotoxic lymphocytes, and natural killer cells can be analysed by ELISpot assay.
Comments