DNA is negatively charged because of the presence of phosphate groups in nucleotides.
The phosphate backbone of DNA is negatively charged, which is due to the presence of bonds created between the phosphorus and oxygen atoms.
In DNA structure, a phosphate group comprises one negatively charged oxygen atom, which is responsible for the entire strand of DNA to be negatively charged.
Let’s explore more about DNA and its structure.
What is DNA?
DNA- Deoxyribonucleic Acid is an inherited material, which is found in every single living species from unicellular amoeba to multicellular organisms – plants, animals, birds, mammals and humans.
DNA – Deoxyribonucleic Acid is an organic compound that has a unique molecular structure and is found in both prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. These hereditary materials are made up of nucleotides molecules.
DNA was first identified and discovered by Johannes Friedrich Miescher, a Swiss Biologist in the year 1869, during his examination of white blood cells.
The structure of a DNA molecule is a double helix, which was later discovered by James Watson and Francis Crick and later proved that DNA molecules are mainly responsible for collecting and preserving genetic information in all living organisms.
Structure of DNA
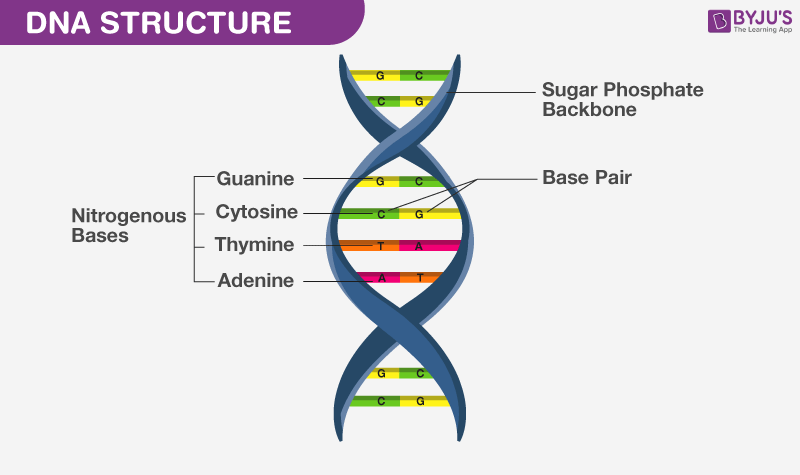
The structure of DNA defines the basic genetic makeup of all lives on the planet earth. Deoxyribonucleic acid is a molecule composed of nitrogenous bases, sugar molecules and phosphate groups.
The structure of DNA is double helix. DNA comprises two strands, which are found coiled or wrapped around each other and form quite similar structures to a twisted ladder. Each strand possesses a backbone, which is made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups.
DNA is composed of nucleotides, which contain:
- A phosphate group
- A sugar group
- Four different types of nitrogen bases – Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Guanine (G) and Cytosine (C).
Types of DNA
There are three different DNA types:
- A-DNA — Right-handed helix
- B-DNA — Right-handed helix
- Z-DNA — Left-handed helix
We humans have B-DNA, right-handed double-helical structure.
Functions of DNA
DNA is mainly involved in:
- Mutation
- Translation
- Replication
- Transcription
- Gene expression
Explore more: DNA Structure
Learn more in detail about DNA, their significance, why is DNA negatively charged and any other related topics at BYJU’S Biology


Comments