Pits
Pits are thin areas on the secondary cell walls of plants. They look like depressions on the walls. Also, they aid in the transport of minerals and water between the cells. Usually, a pit has a complementary depression in its neighbouring cell. These are termed ‘pit pairs’. The structure of a pit includes –
- Pit cavity
- Pit membrane
- Pit aperture
Types of Pits
The two major types of pits are – Simple pits and bordered pits. Bordered pits have a secondary wall thickening over the pit cavity, whereas simple pits do not have borders. A pit pair between a simple and bordered pit is called a half-bordered pit. A pit with no complementary pit is termed a blind pit.
Plasmodesmata
Plasmodesmata are fractions of the endoplasmic reticulum that connects the cells. They are usually lined by a plasma membrane. Also, it has a desmotubule and cytoplasmic sleeve. The space between the plasma membrane and desmotubules has a few microchannels.
The major role of plasmodesmata is to regulate the movement of molecules between the cells. Also, they help in short-distance movements. These plasmodesmata are abundantly seen in the pit membranes.
Also See: Transportation in Plants
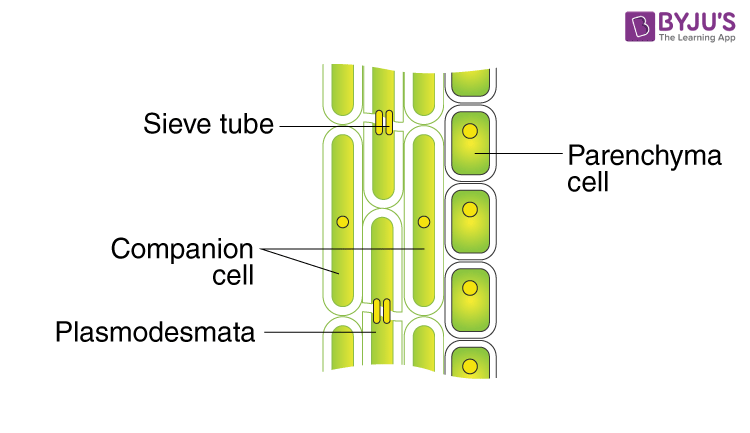
Difference between Pits and Plasmodesmata
Pits |
Plasmodesmata |
|
Pits are thin connections seen on the plant cell walls. |
Plasmodesmata are connections that are abundantly seen in the pits. |
|
The structure of a pit includes – pit membrane, pit cavity and pit aperture. |
The structure of plasmodesmata includes – cytoplasmic sleeve, plasma membrane and desmotubules. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the function of a pit and plasmodesmata?
What are torus and margo?
These are features seen in the border pits of gymnosperms. The torus and margo are parts of the pit membrane. The thick impermeable part is the torus, and the permeable one is the margo. It is the margo that surrounds the torus. They support the pit membrane and regulate its functions.
Where are pits found?
Pits are found in the walls of phloem parenchyma, sclerenchyma, xylem vessels, and tracheids. Bordered pits are found mostly in tracheids of gymnosperms and vessels of angiosperms.
Also Read: Difference between Tracheids and Vessels
Keep exploring BYJU’S Biology for more exciting topics.
Comments