Meaning of Economic Reforms
Economic reforms refer to the fundamental changes that were launched in 1991 with the plan of liberalising the economy and quickening its rate of economic growth. The Narasimha Rao Government, in 1991, started the economic reforms in order to rebuild internal and external faith in the Indian economy.
The reforms intended at bringing in larger cooperation of the private sector in the growth method of the Indian economy. Policy changes were proposed with regard to technology up-gradation, industrial licensing, removal of restrictions on the private sector, foreign investments, and foreign trade. The essential features of the economic reforms are – Liberalisation, Privatisation, and Globalisation, commonly known as LPG.
Quick link: Economic challenges in India
In other words, ‘“economic reforms’” normally indicate deregulation or at times, decrease in the size of government, to eliminate deformities caused by the management or the presence of administration, rather than current or raised regulations or government plans to lessen the perversions created by market failure.
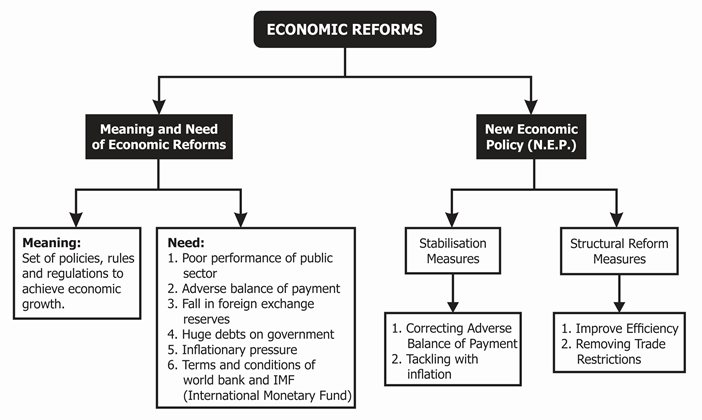
Need for Economic Reforms
- Poor performance of the industrial sector
- Adverse balance of payments
- Rise in fiscal deficit
- Inflation
- The Gulf War
Examples of Economic Reforms
Why were Economic reforms introduced in India?
Economic reforms were introduced in India because of the following reasons:
Poor performance of the public sector
- Public sector was given an important role in development policies during 1951–1990.
- However, the performance of the majority of public enterprises was disappointing.
- They were incurring huge losses because of inefficient management.
Adverse BoP or imports exceed exports
- Imports grew at a very high rate without matching the growth of exports.
- Government could not restrict imports even after imposing heavy tariffs and fixing quotas.
- On the other hand, exports were very less due to the low quality and high prices of our goods as compared to that of foreign goods.
Fall in foreign exchange reserves
- Foreign exchange (foreign currencies) reserves, which the government generally maintains to import petrol and other important items, dropped to the levels that were not sufficient for even a fortnight.
- The government was not able to repay its borrowings from abroad.
Huge debts on government
- Government expenditure on various developmental works was more than its revenue from taxation.
- As a result, the government borrowed money from banks, public and international financial institutions like the IMF, etc.
Inflationary pressure
- There was a consistent rise in the general price level of essential goods in the economy.
- To control inflation, a new set of policies were required.
Terms and conditions of the World Bank and the IMF
India received financial help of $7 billion from the World Bank and the IMF on an agreement to announce its New Economic Policy.
| Also, Explore: |
| Multiple Choice Questions: |
| Q.1 ___________mean change in a set of policies and rules and regulations from one period of time to another to achieve economic growth. |
| a. Tax reforms
b. Economic reforms c. Land reforms d. None of the above Answer: b |
| Important Topics in Economics: |
Explore more data on economics. Stay tuned for syllabus, relevant notifications, and sample papers on our website.
Frequently Asked Questions on Economic Reforms
What are the reasons for economic reforms in India?
The following are some of the reasons for economic reforms in India:
- Rise in prices due to inflation
- Rise in fiscal deficit
- Increase in adverse balance of payments
- Reduction in foreign exchange reserves
- Poor performance of Public Sector undertakings or PSUs
- Gulf war
Why is NEP called the policy of economic reforms?
NEP or New Economic policy is called policy of economic reforms as it seeks to remove the inefficiencies of the existing system and help in the growth of the economy.
Who is called the father of Indian economic reforms?
P.V. Narasimha Rao is known as the father of economic reforms in India
What are the three benefits of economic reforms in India?
The benefits of economic reforms in India are as follows:
- Economic growth was observed
- Foreign exchange reserves increased due to increase in foreign investment
- There was a reduction in the wholesale prices but increase in retail prices
nice information thank you