MSBSHSE Class 8 Science textbook solutions of Chapter 13 works as a guide for students, showing them the correct approach to write a particular question. In order to score good marks in their exam, students should refer to the right study material available in the market. While preparing for their exam, it is always advisable to take help from the prescribed textbook of the subject. These solutions of Maharashtra Board Class 8 comprises all the questions mentioned in the Class 8 Science textbook.
The solutions provided are prepared by a team of subject experts who have a deep knowledge of the subject. Students can refer to these MSBSHSE Class 8 solutions of Science after they complete solving textbook questions to verify their answers and rectify their mistakes.
MSBSHSE Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Objective Questions: Textbook Important Questions and Solutions
MSBSHSE Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Textbook Exercise Questions
Q1. Complete the statement by filling the gaps using appropriate term from the terms given in the bracket. (slow, coloured, arrow, fast, smell, milky, physical, product, chemical, reactant, covalent, ionic, octet, duplet, exchange, sharing, equality sign)
a. An ……………. is drawn in between the reactants and products while writing the equation for a chemical reaction.
b. Rusting of iron is a ………………… chemical change.
c. The spoiling of food is a chemical change which is recognized from the generation of certain ………… due to it.
d. A colourless solution of calcium hydroxide in a test tube turns ….. on blowing in it through a blow tube for some time.
e. The white particles of baking soda disappear when put in lemon juice. This means that it is a ………. change.
f. Oxygen is a …………….. in respiration.
g. Sodium chloride is ……….. compound while hydrogen chloride is ……… compound.
h. Electron ……… is complete in each hydrogen in a hydrogen molecule.
i. Chlorine (Cl2) molecule is formed by …………… of electrons between two chlorine atoms.
Answer a: An arrow is drawn in between the reactants and products while writing the equation for a chemical reaction.
Answer b: Rusting of iron is a slow chemical change
Answer c: The spoiling of food is a chemical change which is recognized from the generation of certain smell due to it.
Answer d: A colourless solution of calcium hydroxide in a test tube turns milky on blowing in it through a blow tube for some time.
Answer e: The white particles of baking soda disappear when put in lemon juice. This means that it is a chemical change.
Answer f: Oxygen is a Reactant in respiration.
Answer g: Sodium chloride is ionic compound while hydrogen chloride is covalent compound.
Answer h: Electron shell is complete in each hydrogen in a hydrogen molecule.
Answer i: Chlorine (Cl2) molecule is formed by …………… of electrons between two chlorine atoms.
2. Explain by writing a word equation.
a. Respiration is a chemical change.
b. Hard water gets softened on mixing with a solution of washing soda.
c. Lime stone powder disappears on adding to dilute hydrochloric acids.
d. Bubbles are seen on adding lemon juice to baking soda.
Answer a: Respiration is a continuously occurring biological process. In this process, we inhale the air and exhale carbon dioxide and water vapour. After an in-depth study, it is learnt that glucose in the cells reacts with oxygen in the inhaled air to form carbon dioxide and water. The word equation and the chemical equation of this chemical reaction are as follows.
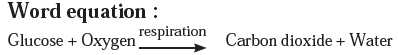
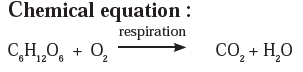
Answer b: Some wells or tube wells have hard water. It is brackish to taste and does not form lather with soap. This is because hard water contains the chloride and sulphate salts of calcium and magnesium in dissolved state. To soften the hard water, a solution of washing soda is added to it. This results in a chemical reaction to form a precipitate of insoluble carbonate salts of calcium and magnesium. As the dissolved salts of calcium and magnesium go out in the form of precipitate of the carbonate salts, the water is softened. The following equation can be written for this chemical change.
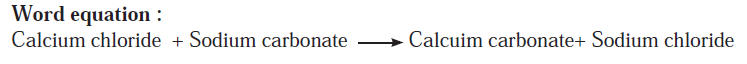
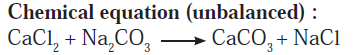
Answer c: The lime stone (calcium carbonate) reacts with hydrochloric acid and three products are formed. One of them is calcium chloride, which being soluble in water, gets washed away with water. The second product is carbon dioxide; its bubbles mix up in air. The third product, water mixes with water. The following equation can be written for this chemical change.
Word equation: Calcium carbonate + Hydrochloric acid → Calcium chloride + Carbon dioxide + water
Answer d: When baking soda is added to lemon juice a chemical change takes place in the citric acid present in the lemon juice and the gas formed is carbon dioxide. The word equation can be written for this chemical reaction as follows:

Q3. Match the pairs.
| Photosynthesis | Tendency to lose electrons |
| Water | Reactant in combustion process |
| Sodium chloride | Chemical change |
| Dissolution of salt in water | Covalent bond |
| Carbon | Ionic bond |
| Fluorine | Physical change |
| Magnesium | Tendency to form anion |
Answer:
| Photosynthesis | Chemical change |
| Water | Covalent bond |
| Sodium chloride | Ionic bond |
| Dissolution of salt in water | Physical change |
| Carbon | Reactant in combustion process |
| Fluorine | Tendency to form anion |
| Magnesium | Tendency to lose electrons |
4. Show with the help of diagram of electronic configuration how the following compounds are formed from the constituent atoms.
a. Sodium chloride
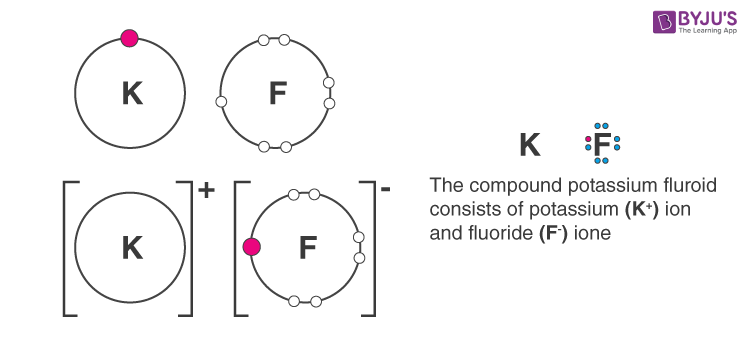
b. Potassium fluoride
c. Water
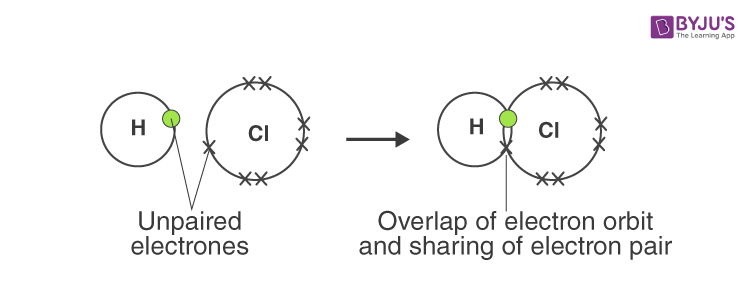
d. Hydrogen chloride
Answer a: Sodium chloride

Answer b: Potassium fluoride
Answer c: Water

Answer d: Hydrogen chloride
Q5. Define ionic bond and ionic compound
Answer: The chemical bond formed due to an electrostatic force of attraction between the
oppositely charged cation and anion is called an ionic bond or an electrovalent bond. The compound formed by means of one or more ionic bonds is called an ionic compound.
Q6. Define covalent bond.
Answer: A covalent bond is formed by equal sharing of electrons from both the participating atoms. The pair of electrons participating in this type of bonding is called shared pair or bonding pair. The covalent bonds are also termed as molecular bonds. Sharing of bonding pairs will ensure that the atoms achieve stability in their outer shell, which is similar to the atoms of noble gases.
Q7. What is chemical bonding?
Answer: Chemical Bonding refers to the formation of a chemical bond between two or more atoms, molecules, or ions to give rise to a chemical compound. These chemical bonds are what keep the atoms together in the resulting compound.
Q8. Explain combustion of fuels.
Answer: Wood, coal, petrol or cooking gas are burnt for getting energy. The common substance that burns in all these fuels is ‘Carbon’. During the combustion process carbon combine with oxygen in air and the product carbon dioxide is formed. A common equation can be written for all these combustion processes as follows.
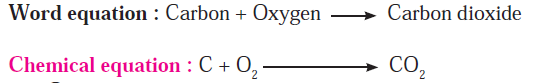
Combustion of fuel is a fast and irreversible chemical change.
Q9. What is the difference between physical and chemical change?
Answer: The difference between physical and chemical change are as follows:
| Sl. No. | Differentiating Property | Physical Change | Chemical Change |
| 1 | Explanation | In a physical change, the molecules are rearranged while their actual composition remains same. | In a chemical change, the molecular composition of a substance completely changes and a new substance is formed. |
| 2 | Example | Some examples of physical change are freezing of water, melting of wax, boiling of water, etc. | A few examples of chemical change are digestion of food, burning of coal, rusting, etc. |
| 3 | Reversibility | Physical change is easily reversible i.e original substance can be recovered. | Chemical change is irreversible i.e. original substance cannot be recovered. |
| 4 | Formation of new substance | In physical change, no new substance is formed. | A chemical change is always accompanied by one or more new substance(s). |
| 5 | Type of Change | Physical change is a temporary change. | Chemical change is a permanent change. |
| 6 | Energy Production | In a physical change, no energy is produced. | In a chemical change, energy is produced (heat, light, sound, etc.) |
| 7 | Absorption of Energy | Physical change involves very little to no absorption of energy. | During chemical reaction, absorption and evolution of energy takes place. |
| 8 | Affects | Physical change affects only physical properties i.e. shape, size, etc. | Chemical changes affect both physical and chemical properties of the substance including its composition. |
Q10. Define chemical change and word equation.
Answer: During a chemical change the chemical composition of the original matter changes
and new substances having different properties and different chemical composition are formed. A chemical equation can be written for a chemical change, if the exact change in chemical
composition is known. Names and chemical formulae of the original substance and newly formed substance are used while writing a chemical equation.
For example, when baking soda is added to lemon juice a chemical change takes place in the citric acid present in the lemon juice and the gas formed is carbon dioxide. The word equation can be written for this chemical reaction as follows.

This is neutralization reaction.
Q11. What is physical change and chemical change?
Answer: The change in which the molecular composition is completely altered and a new product is formed is called a chemical change. Chemical changes create a new product. The changes in chemical change are irreversible and permanent. It reveals that chemical change cannot be reversed by changing or altering the experimental changes. The mass of the substance is altered during a chemical change.
During the physical change, the arrangement of molecules is altered leading to change in state. No new products are formed, and the molecular composition remains totally the same. For example, the molecular composition of ice and water is not altered. No energy changes occur as a result of a physical change. The energy needed to bring a physical change is equal to the amount of energy required to reverse the change. There is no change in energy. The changes are reversible and temporary. The reaction gets reversed if the cause of producing the change is removed.
Q12. What is the Octet Rule?
Answer: All atoms except noble gases have less than eight electrons in their valence shell. In other words, the valence shells of these atoms do not have stable configurations. Therefore, they combine with each other or with other atoms to attain stable electronic configurations. Therefore, the tendency of atoms of various elements to attain stable configuration of eight electrons in their valence shells is the cause of chemical combination and the principle of attaining the maximum of eight electrons in the valence shell of atoms is called octet rule.
Q13. Discuss types of covalent bonds.
Answer: Depending upon the number of shared electron pairs, the covalent bond can be classified into:
- Single Covalent Bond
- Double Covalent Bond
- Triple Covalent Bond
Q14. Write the difference between Ionic and Covalent Bond
Answer: The difference between ionic and covalent bond are:
| Covalent Bonds | Ionic Bonds |
| A covalent bond is formed between two similar electronegative non-metals | This type of bond is formed between a metal and non-metal |
| Bonds formed from covalent bonding have a definite shape | Ionic Bonds have no definite shape |
| Low Melting Point and Boiling Point | High Melting Point and Boiling Point |
| Low Polarity and more Flammable | High Polarity and less Flammable |
| Covalent Bonds are in Liquid or gaseous state at room temperature | At room temperature, Ionic Bonds have Solid-state. |
| Examples: Methane, Hydrochloric acid | Examples: Sodium chloride, Sulfuric Acid |
Q15. Write the ionic bond properties.
Answer: Due to the presence of a strong force of attraction between cations and anions in ionic bonded molecules, the following properties are observed:
- The ionic bonds are the strongest of all the bonds.
- The ionic bond has charge separation and so they are the most reactive of all the bonds in the proper medium.
- The ionic bonded molecules have high melting and boiling point.
- The ionic bonded molecules in their aqueous solutions or in the molten state are good conductors of electricity. This is due to the presence of ions which act as charge carriers.
Q16. Define noble gases.
Answer: Group 18 of the modern periodic table consists of noble gases. Helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon are noble gases. These gases are monatomic and chemically inert under normal conditions and hence are also named as inert gases. These gases are present in very small quantities in the atmosphere and so they are also called rare gases.
Q17. Discuss chemical reactions in everyday life.
Answer: Following are the chemical reactions in everyday life.
Photosynthesis: The process of photosynthesis by which autotrophs manufacture their food is another chemical reaction. In the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll, plants manufacture glucose from carbon dioxide and water from the environment.
Rusting: The process of oxidation (reactions in the presence of oxygen) results in the formation of a brown flaky layer over the metal surfaces such as iron. This layer is formed due to the oxidation of the top most layer to form the metal oxide which we know as rust. Similar layers are formed on other metals such as silver where a green colored layer is formed.
Cellular Respiration: The process of respiration in humans also involves a chemical reaction. The glucose molecules undergo oxidation to produce carbon dioxide and water along with energy.
Combustion: The process of combustion involves the oxidation of a material in the presence of oxygen from the environment and heat to produce ash, smoke, and other gases.
Frequently Asked Questions on Maharashtra Board Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Chemical Change and Chemical Bond
Are these Maharashtra Board Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Chemical Change and Chemical Bond useful for the exams?
Yes, these solutions are very helpful. students are highly recommended practising these solutions because they lay the foundation for the questions that are asked often in the board exams. These questions act as the perfect guide for Class 8 students during their board exam preparation as it is set according to the latest Class 8 Science Syllabus by the subject experts. Students can discover various solved questions and exercises that will aid them to prepare well for board exams.
How to solve these Maharashtra Board Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 13?
Water is mainly water molecules and it reduces the concentration of ions in the solution by adding water to an acid or base. The concentration of H+ ions decreases when an acidic solution is mixed with water, and the solution pH increases towards 7. The acid is less acidic.
Where can we get the Maharashtra Board Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 13?
Students are advised to solve these questions and then to refer back to the solutions to identify the mistakes and rectify them early on so that they can avoid them in the exams. Timing the process helps with time management and this is also the perfect tool to measure one’s exam preparations.
Comments