Table of Contents
Introduction
We are all well aware of the importance of oxygen for survival. Hence, one must also be familiar with the transportation, exchange, and regulation of necessary gases. In very small organisms, there is no need to have a separate transportation system for gases as all its cells are directly involved in the exchange of gases by diffusion. This diffusion is caused due to the differential partial pressure of the respiratory gases. Gases tend to move from a high-pressure area to a low-pressure one. Towards the end of the process, oxygen passes from the blood to tissue fluid and carbon dioxide from tissue fluid into the blood. But larger, multicellular organisms will definitely need a mechanism for the transport of gases for their different organs and tissues. Human beings fall into this category and have a well-developed system for the transportation of gases.
Exchange and Regulation of Gases
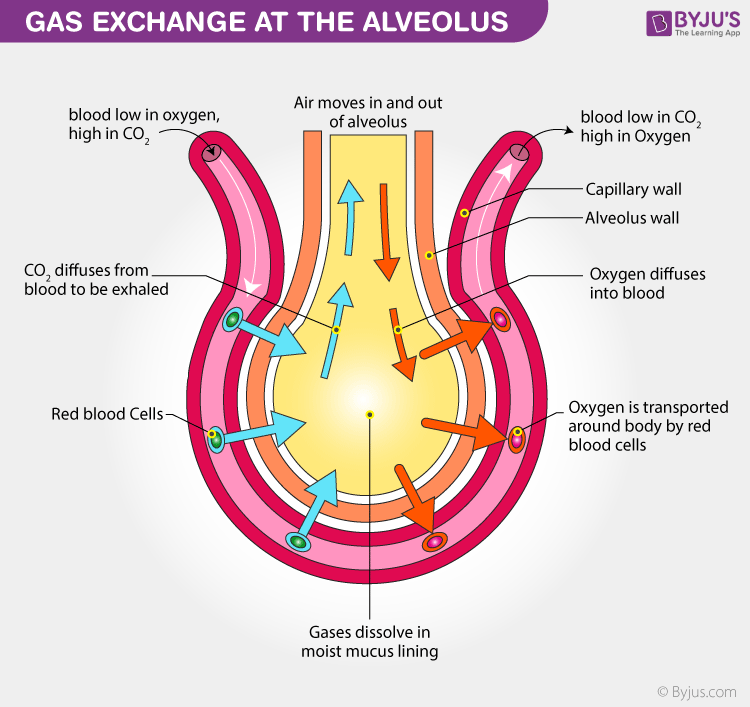
Exchange of gases in Humans
The transportation of gases is a very efficient process. Oxygen molecules get carried by the haemoglobin molecules of the red blood cells since it has a great affinity for oxygen. Each haemoglobin molecule binds to four molecules of oxygen. These oxygen molecules are picked up by haemoglobin and get transported by the blood to various tissues. As carbon dioxide is more soluble in water than oxygen, it is transported in the dissolved form in our blood, while some are also transported by haemoglobin. Not all of the carbon dioxide formed is expelled from the body as some of it reacts with water to form compounds useful for life processes.
Human bodies have mastered the art of catering to their needs. In other words, the human body knows when to increase the supply of oxygen and when to reduce it. To put this simply, it has learned the art of adaptation. This regulatory system that takes care of it is present in the medulla. The respiratory system happens to be extremely sensitive to the concentration of CO2 in the arterial blood. The decrease or increase of it is evident in the acceleration or slowing down of the respiration activity or in the change in rate and depth of breathing.
To know more about the Exchange of Gases in Tissues, watch the video given below:
To learn more about the exchange of gases in humans, or any other related topics, please log in to BYJU’s.

Comments