What is an Electrocardiograph?
An electrocardiograph or ECG is a test used to measure the electrical activity of the heart. The test takes only about a few minutes and is devoid of any pain.
The electrical activity of the heart causes the heart muscles to contract that results in the pumping of the heart. The ECG is in the form of spikes and dips known as waves. The wave pattern helps in assessing the rate and rhythm of our heartbeat.
The human heart produces an electrical impulse by itself. As this electrical impulse passes through our heart, it generates an electrical current that spreads over our body and reaches the skin.
The patient is connected to the Electrocardiograph (ECG) machine with three electrical leads (one each to both wrists and the third to the left ankle of the patient), that is used to monitor the activity of the heart. This is standard ECG testing.
Also Read: Human Circulatory System
Electrocardiograph
Process
The process of electrocardiograph includes:
- Small sticky electrodes are attached to the arms, chest and legs.
- These electrodes are connected to the ECG machine through wires that help in detecting the electrical impulses occurring at each heartbeat.
- These electrodes usually detect the very minute form of changes in an electrical path on the skin which arises from the heart muscles and the electrophysiologic patterns of the depolarizing during every heartbeat.
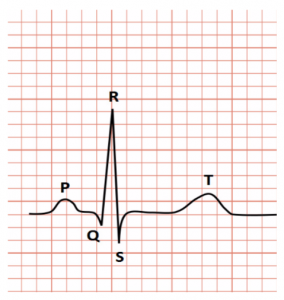
Explanation of the Electrocardiograph
P to T in the graph represents a specific activity of the heart. Let’s break it down.
- The P wave is the electrical excitation of the atria, or depolarization, initiating atrial contraction.
- The QRS complex is the depolarization of ventricles, initiating ventricular contraction. Marking the beginning of the systole.
- T wave means the return of ventricles to the normal state (repolarization). Marking the end of the systole.
By counting the number of QRS complexes we can evaluate the heartbeat rate of the patient. Any deviations in this shape results in heart diseases or an abnormal heart rhythm which can either be slow, irregular or very fast heartbeats. Hence it is essential equipment in the field of medicine.
Types of ECG Test
There are three main types of ECG tests:
Resting ECG
This type of ECG is used to examine the electrical activity of the heart at rest. While performing this test, the patient is asked to relax and then, their heartbeat is recorded.
Exercise ECG
This type of ECG is used to examine the electrical activity of the heart during stress or exercise. In this test, a patient is asked to run or walk on the treadmill or a cycle while the heartbeat is recorded.
24-hour ECG
As the name suggests, this type of ECG is conducted for 24 hours. The heart’s electrical impulses are measured by a device called the Holter Monitor.
Medical Uses of ECG
The main goal of electrocardiography is to obtain information regarding the heart’s electrical impulses. This means it can find evidence of past heart attacks or even any undiagnosed heart disease. The medical uses of such information are very valuable and grant a deeper insight into conditions like :
- Seizures
- Fainting
- Pulmonary embolism
- Cardiac dysrhythmias
- Myocardial infarction or heart attack
- Arrhythmia
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Ventricular hypertrophy
It also proves itself useful in applications such as:
- Biotelemetry of the patient
- The testing of Cardiac stress
- Diagnosis of structural heart diseases
- Monitoring the effects of heart medication
- Assessing the severity of the abnormalities in the electrolyte
- The monitoring of the form of anaesthesia that is involved
- CTA- Computed tomography angiography and also the MRA- Magnetic resonance angiography of the heart
- The screening of Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in adolescents as a part of the sports-related deaths, such as sudden cardiac death.
Why is an ECG done?
An electrocardiograph is done for the following reasons:
- To check the heart health in case of other diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, etc.
- To check the thickness of the chambers of the heart wall.
- To monitor if the medicines are causing any side-effects.
- To check if the mechanical devices implanted in the heart are working properly or not.
For more detailed information on Electrocardiograph (ECG), ECG tests, and its process, keep visiting BYJU’S website or download BYJU’S app for further reference.


what are those electrodes used in ecg??
Electrodes of ECG help in recording the electrical activity of the heart. The electrodes used in ECG do not produce any electricity. Hence, they do not pose any risk of shocks.