
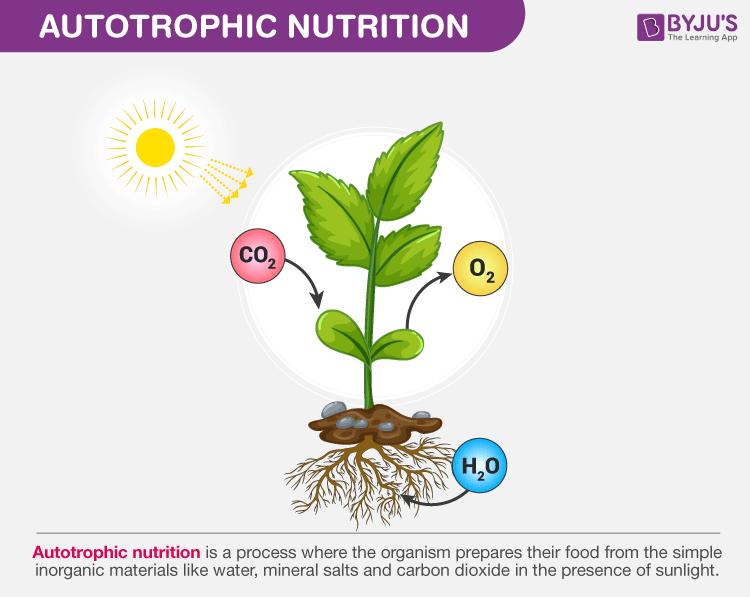
“Autotrophic nutrition is a process where an organism prepares its own food from a simple inorganic material like water, mineral salts and carbon dioxide in the presence of sunlight.”
The term “autotrophic” is formed by the combination of two terms, “auto” meaning self, and “trophic” meaning nutrition. The literal meaning of this term is self-nutrition.
The autotrophic organisms contain a green coloured pigment called chlorophyll which helps in trapping energy from the sun. All green plants possess an autotrophic mode of nutrition. They prepare their own food by utilizing solar energy, water, and carbon dioxide by the process of photosynthesis. This results in the formation of glucose.
Plants like blue-green algae and bacteria such as cyanobacteria are considered to be examples of autotrophs.
Also Read: Heterotrophic Nutrition
Photosynthesis
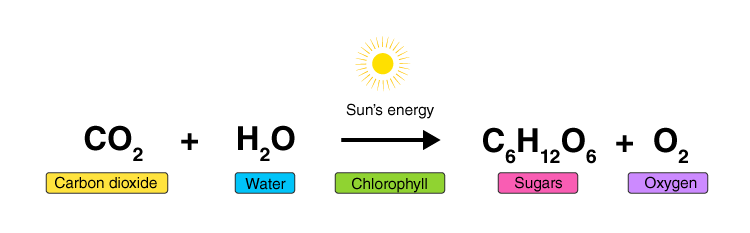
Photosynthesis is a process to convert solar energy into chemical energy to synthesize starch. Different parts of a plant play different roles to complete this process.
- Leaves – They are considered as the food factories of the plant.
- Stomata– It is present in the lower epidermis of the leaf which uses carbon dioxide from the air.
- Roots – They absorb minerals and water from the soil and transport it to different parts of the plant.
Leaves of the vascular plants have a special structure known as chloroplast which possesses chlorophyll. Plants synthesize glucose with the help of carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight. The stomata present in the leaf releases oxygen as a by-product during the daytime. The synthesized food is transported to different parts of the plant for storage and utilization. These green plants, prepare proteins using nitrogen, which could be obtained from the soil.
All the minerals which are dissolved in water are used to convert sugar into proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. These food components act as the source of energy for other heterotrophic animals and plants. Glucose is synthesized by this process and converted into different compounds like cellulose and starch, which is stored in different parts of the plant.
Autotroph Examples
Following are the important examples of autotrophs:
- Plants
- Algae- Green algae and red algae
- Bacteria such as cyanobacteria
Also Read: Difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs
To know more about autotrophic nutrition, and autotroph examples, keep visiting BYJU’S.

Thanks ! it was very helpful !☺️
Give two examples of Autotrophic plants.
Grass, wheat, maize.
Nice
Algae on stagnate water , plant which have chlorophyll
Nice explanation well done
I really found it very helpful.
Thank you, BYJU’s
give 10 examples of autotroph plants.