Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Types of Invertebrates
- Characteristics of Invertebrates
- Phylum Arthropods
- Phylum Mollusca
- Phylum Annelida
- Phylum Coelenterata

Introduction
Invertebrates are animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column, derived from the notochord. These include all animals apart from the subphylum Vertebrata.
Invertebrates are animals with no backbone. 97% of the animals are invertebrates among the estimated 2.16 million animal species. Invertebrates exist about anywhere. These have been found in the driest of deserts, high reaches of the atmosphere and canopies of wettest rainforests. They also exist in the frozen Antarctic or under the deepest oceans.
Whether batting away irritating flies, unearthing a worm or admiring the complexity of a spider’s web and much more, all these animals are invertebrates.
Invertebrates are so many that it is almost impossible to count them all. There are so many invertebrate animal species of different shapes and sizes that help us in many ways and are vital to our survival.
Types of Invertebrates
Terrestrial invertebrates involve these groups and many also have members that live in marine environments and freshwater.
- Insects
- Spiders
- Worms
- Slaters
- Landhoppers
- Centipedes
- Millipedes
- Velvet worms
Freshwater and marine invertebrates involve the following groups and some of them also have land-dwelling members.
- Sea stars and sea urchins
- Anemones and corals
- Snails and slugs
- Sponges
- Bluebottles and jellies
- Crabs, prawns, crayfish & lobsters
Characteristics of Invertebrates
By now as you know what invertebrates are, let’s get to know about their characteristics.
- All invertebrates do not have a spinal cord or vertebral column, instead, most of them possess an exoskeleton that encompasses the entire body.
- Normally, these are tiny and don’t grow very large.
- Do not possess lungs since they respire through their skin.
- Since they cannot produce their own food, Invertebrates are heterotrophic.
- Reproduction occurs through fission.
Invertebrates involve all the animals that do not come under vertebrates group. There are mainly four kinds of invertebrates as listed below by Phylum.
- Phylum Mollusca
- Phylum Annelida
- Phylum Arthropods
- Phylum Coelenterata
Every group has its own characteristics and adaptations.
Phylum Arthropods
Arthropods are animals that have a segmented body. Their bodies are bilaterally symmetrical with a strong exoskeleton made up of chitin. Arthropods are capable of adapting to different environments quickly. Examples of Arthropods are Scorpions, Honey Bees, and Spiders.
A beetle’s shell is called an exoskeleton and it makes up for the lack of a backbone by providing rigidity and form.

Phylum Mollusca
These animals have an unsegmented body, unlike arthropods. Mollusca skin consists of a mantle that releases a shell. Their skin is soft and mostly found in seawater and fresh water. Examples of Mollusca are Octopus, Snail, and Oyster.
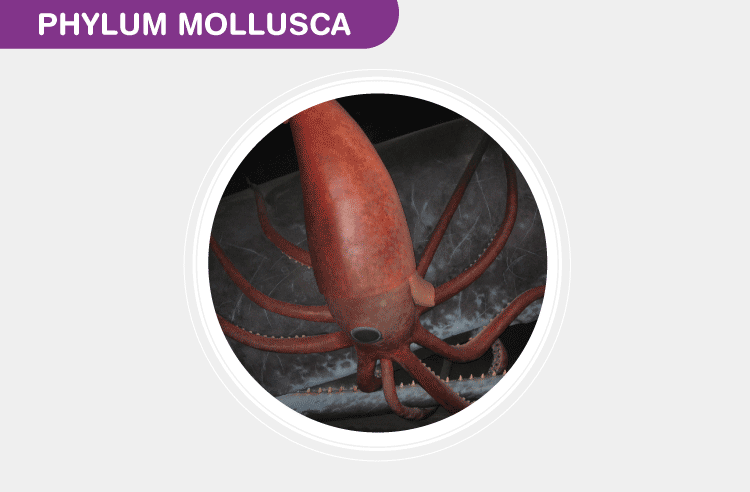
The largest invertebrate ever: An artist’s render of a colossal squid battling a sperm whale. Throughout history, there are just a handful of dead specimens found throughout the world and they still remain elusive to this day.
Phylum Annelida
The group of Annelids has many worms. Their bodies are segmented and consist of 3 layers and hence are called Triploblastic animals. Triploblastic refers to having 3 layers ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
Examples of Annelida involve Earthworm, Sandworm, and Leech.

The biggest leech in the world: The Giant Amazon Leech
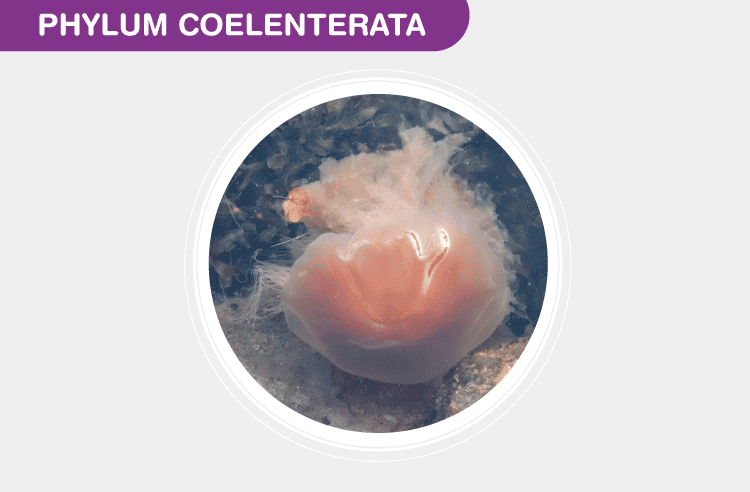
Phylum Coelenterata
The bodies of Coelenterates are radially symmetrical. These animals are diploblastic which means that their bodies comprise 2 layers known as ectoderm and endoderm. Examples of Coelenterates are Hydra, Jellyfish, and Coral.

I want to learn more about the alimenrary canals
Alimentary canal: https://byjus.com/biology/alimentary-canal-anatomy/
Very useful materials
I love biology! Thank you for helping with this article!!! 😊😇😍☺
Wow! I didn’t know that there are many types of invertebrates!
I wanna know about all the phylums of invertebrates