In plants, pollination plays an important role in reproduction.
Pollination is the sexual method of reproducing in all plants by the process of transferring the pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the gynoecium and thereby permitting the fertilization process. In this process, the spermatophytes or the seed plants pass their genetic information to its next-generation, just like all other living organisms.
Christian Konrad Sprengel first identified the process of pollination in the 18th century. This is commonly known as an interaction between pollen vector and a flower. The significance is found in agriculture and horticulture.
There are two types of pollination -:
- Self-pollination
- Cross-pollination

Cross-Pollination
Cross-pollination is defined as the deposition of pollen grains from a flower to the stigma of another flower. Commonly, the process is done by insects and wind. By insects, the process takes place in several plants like strawberries, grapes, raspberries, tulips, apples, plums, pears, daffodils, and more. Pollination by the wind is observed in different grasses, maple trees, dandelions and catkins.
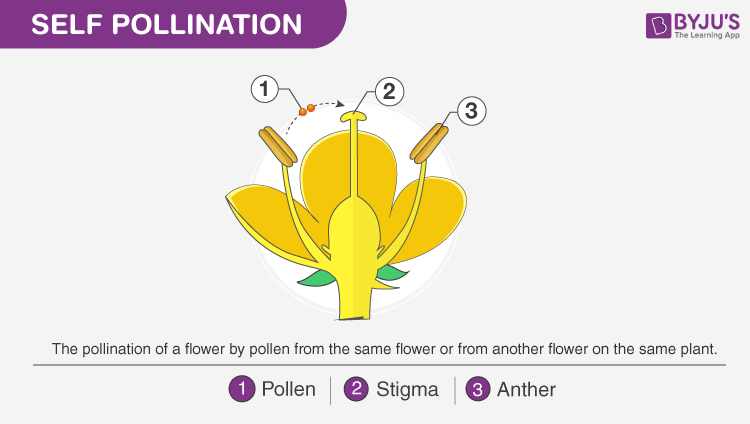
Self Pollination
In this process, the pollen grains transfer from the stigma of the same or genetically similar flower. Self-pollination can be observed in legumes such as orchids, sunflowers, peas, peanuts, oats, peaches, potatoes, wheat, and others.
Recommended Video:

Let us learn more in detail about the differences between the two types of pollination.
Difference Between Self-Pollination and Cross-Pollination
| Self-Pollination | Cross-Pollination |
| Transfer pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower. | Transfer pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a different flower. |
| This process can take place in the same flower or a different flower of the same plant. | This process can take place between two flowers present on different plants. |
| It occurs in the flowers which are genetically identical. | It occurs between flowers which are genetically different. |
| Few species that exhibit self-pollination – Paphiopedilum parishii, Arabidopsis thaliana | Few species that exhibit cross-pollination – apples, daffodils, pumpkins and grasses |
| Causes homogenous conditions in progenies. | Causes heterozygous condition in progenies. |
| Self-pollination increases genetic uniformity and decreases genetic variation. | Cross-pollination decreases genetic uniformity and increases genetic variation. |
| Causes inbreeding. | Causes outbreeding. |
| Reduces the gene pool. | Maintains the gene pool. |
| Produces limited amounts of pollen grains. | Produces large amounts of pollen grains. |
| In self-pollination, both the stigma and anther simultaneously mature | In cross-pollination, both the stigma and anther mature at different times. |
| Transfers a limited number of pollens. | Transfers large numbers of pollen. |
| This process is carried out even when the flowers are closed. | For cross-pollination to happen, the flower should be open. |
| No need for pollinators to transfer pollen grains. | Require pollinators to transfer pollen grains. |
| Pollen grains are transferred directly to a flower’s stigma. | Pollen grains are carried via wind, insects, animals, water, etc. |
Register with BYJU’S to learn more about pollinations, types and its differences.

So good it helps me to get the answer
Thank you so much😍
It help me a lot thanks
It help me alot
It’s very helpful 😊
Helpful to me
nice but points are of higher classes.
fantastic awsome answer😊
Thank you so much😍
Wow, it is great I got my question’s answer. Thank you very much Byjus 🙏🙏
Thanks to the team of Byju’s
Thank you so much very very helpful for the revision😇😇😇
Oh wow, thanks for it 😇🙌🙌🙏
good answer easily understandable ✌✌
Good. I like Byju’s learning and teaching method
Great job
was so much useful.
the differences were amazing.
very educating.
Thanks for this amazing work
It’s very helpful