Mendelian Disorder Definition
“Mendelian disorders are the genetic disorders caused at a single genetic locus.”
What are Mendelian Disorders?
In humans, Mendelian disorder is a type of genetic disorder primarily resulting due to alterations in one gene or as a result of abnormalities in the genome. Such a condition can be seen since birth and be deduced on the basis of family history using the family tree. The analysis hence carried out is known as pedigree analysis.
These genetic disorders are quite rare and may affect one person in every thousand or a million. Genetic disorders may or may not be inherited. Inheritable genetic disorders usually occur in the germline cells, whereas in non-inheritable genetic disorders the defects are generally caused by new mutations or due to some changes in the DNA. For instance, cancer may either be caused by an inherited genetic condition, or by a new mutation caused by the environmental causes or otherwise.
Also Read: Genetic Disorders
Types of Mendelian Genetic disorders
According to Mendel’s’ laws of inheritance, the different types of Mendelian disorders include:
- Autosomal dominant.
- Autosomal recessive.
- Sex-linked dominant.
- Sex-linked recessive.
- Mitochondrial.
The various types of Mendelian disorders can be identified easily from the pedigree analysis.
Examples of Mendelian Disorders
Few examples of the Mendelian disorder in humans are
- Sickle cell anaemia
- Muscular dystrophy
- Cystic fibrosis
- Thalassemia
- Phenylketonuria
- Colour blindness
- Skeletal dysplasia
- Haemophilia
Haemophilia
- This is a type of sex-linked recessive disorders. According to the genetic inheritance pattern, the unaffected carrier mother passes on the haemophilic genes to sons.
- It is a very rare type of disease among females because for a female to get the disease, the mother should either be hemophilic or a carrier but the father should be haemophilic.
- This is a disorder in which blood doesn’t clot normally as the protein which helps in clotting of blood is affected. Therefore, a person suffering from this disease usually has symptoms of unexplained and excessive bleeding from cuts or injuries.
- This type of genetic disorder is caused when the affected gene is located on the X chromosomes. Therefore, males are more frequently affected.
Sickle-cell anaemia
- This is a type of autosomal recessive genetic disorder.
- According to Mendelian genetics, its inheritance pattern follows inheritance from two carrying parents.
- It is caused when the glutamic acid in the sixth position of the beta-globin chain of haemoglobin molecule is replaced by valine. The mutant haemoglobin molecule undergoes a physical change which changes the biconcave shape into the sickle shape.
- This reduces the oxygen-binding capacity of the haemoglobin molecule.
Phenylketonuria
- This genetic disorder is autosomal recessive in nature.
- It is an inborn error caused due to the decreased metabolism level of the amino acid phenylalanine.
- In this disorder, the affected person does not have the enzyme that converts phenylalanine to tyrosine. As a result, phenylalanine accumulation takes place in the body and is converted into many derivatives which result in mental retardation.
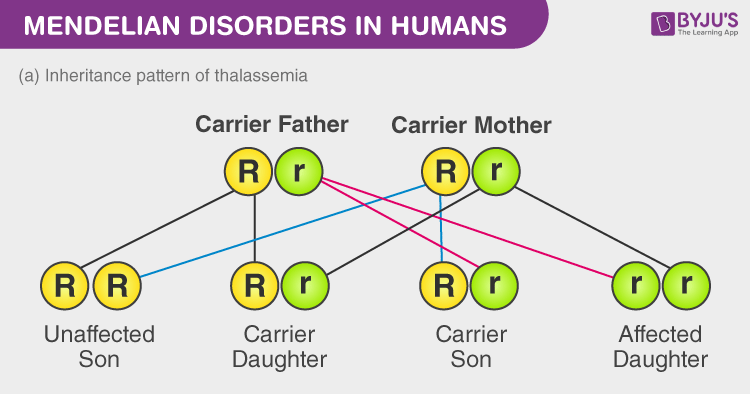
Thalassemia
- This is a type of disorder in which the body makes an abnormal amount of haemoglobin. As a result, a large number of red blood cells are destroyed that leads to anaemia.
- It is an autosomal recessive disease.
- Facial bone deformities, abdominal swelling, dark urine are some of the symptoms of thalassemia.
Cystic Fibrosis
- This is an autosomal recessive disorder.
- This disease affects the lungs and the digestive system and the body produces thick and sticky mucus that blocks the lungs and pancreas.
- People suffering from this disorder have a very short life-span.
Also Read: Chromosomal Abnormalities
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more about Mendelian Disorders in Humans.

Comments