Rajasthan Board Class 10 Social Science 2017 Question Papers With Solutions are solved by our subject professionals who have deep knowledge in the field of Social Science. By solving the Class 10th previous year question papers, students can understand the question paper pattern, weightage of marks, important questions, etc. It also helps students to review their preparation level and work on their weak points. Students should solve Rajasthan Board Class 10 Social Science 2017 Question Paper to get a real hand on the final exam paper. By referring to these RBSE Class 10 Social Science Previous Year Question Paper 2017 with Solutions, students can easily gauge their performance and preparation level for the board exams.
Previous year question papers are considered as the best resource while preparing for the board exam. The solutions provided in this article will help students to understand the correct methodology of answering any particular question. After they complete solving the previous year question paper students should refer to the solutions to rectify their mistakes and work on it. Students can download solutions from the highlighted link below.
Rajasthan Board Class 10 Social Science Question Paper 2017 with Answers – Free Download
Download RBSE Board 2017 Social Science Question Paper
Download RBSE Board Social Science Question Paper With Solutions
Rajasthan Board Class 10 Social Science Question Paper With Solution 2017
1. In which session congress demanded “Purna Swarajya”?
Answer: Lahore session on 26th December 1929.
2. Which form of government accommodates Social diversity?
Answer: Democratic form of government.
3. What is suitable measure for comparison of development between two or more countries?
Answer: The most basic comparison of development between two or more countries is between GDP per capita levels.
4. What is medium of exchange?
Answer: A medium of exchange is an intermediary instrument used to facilitate the sale, purchase or trade of goods between parties. For an instrument to function as a medium of exchange, it must represent a standard of value accepted by all parties. In modern economies, the medium of exchange is currency.
5. Write the meaning of investment.
Answer: Investment refers to the expenditure incurred by producers on the purchase of capital goods such as machinery, plant, etc.
6. Write any two ways of consumer exploitation.
Answer: Two ways of consumer exploitation are:
- Under weighing. Many dishonest shopkeepers weigh less than that they should.
- Adulteration. At times adulterated or defective goods are sold in the market.
7. Write a short note on the Jallianwala Bagh massacre.
Answer: In Jallianwala Bagh, which is a public garden enclosed from all sides except its narrow entrance, a group of Indians had gathered to protest peacefully against the Rowlatt Act and the arrest of their two leaders. They were unarmed and the crowd consisted of women and children too. On April 13, 1919, Brigadier General Reginald Dyer carried out one of the deadliest attacks in the history of India. Dyer’s troops closed the main entrance to the garden. Without warning, he ordered his troops to fire at the crowd of 15,000 to 20,000 people. Shooting continued for ten minutes until the ammunition was nearly exhausted. Official figures of the massacre reveal that only 379 people died, however, the Indian National Congress had then pegged the figure at least 1,000 people killed and 500 injured.
8. What are Rare Species?
Answer: A rare species is a group of organisms that are very uncommon, scarce, or infrequently encountered. This designation may be applied to either a plant or animal, and is distinct from the term endangered or threatened.
9. Write any four causes of declining biodiversity in India.
Answer: Four causes of declining biodiversity in India are:
- Climatic change
- Increasing Human Population
- Exploitation of Natural Resources
- Hunting and Poaching
10. Write any four demerits of multi-purpose river projects.
Answer: Four demerits of multi-purpose river projects are:
- The initial cost is considered as high.
- It adversely effects our environment and aquatic life.
- It also has adverse effects on the quality of soil and changes in cropping pattern.
- It creates disputes between different states and the displacement of local communities
11. Explain impact of Globalization on agriculture.
Answer: Impact of Globalization on agriculture are:
- Globalisation is an old phenomenon.
- It started at the time of colonisation.
- In the nineteenth century when European traders came to India, during that time as well the Indian spices were exported to different countries of the world and farmers of south India were encouraged and enhanced to grow these crops.
- Till today, it is one of the major items of export from India.
- Under globalisation, majorly after 1990, the farmers in India have been exposed to new challenges and tasks.
- Despite being an important and major producer of rice, cotton, rubber, tea, coffee, jute and spices, our agricultural products are not able to compete with the developed countries due to the highly subsidised agriculture in other foreign countries.
- Today, Indian agriculture marks itself at the crossroads.
- To make agriculture successful and profitable, proper and considerable amounts of thrust should be given to the improvement of the condition of marginal and small farmers.
12. Write any two uses of Copper mineral.
Answer: Two uses of Copper mineral are:
- It is used to conduct electricity
- It is used in cooking utensils
13. Explain any four causes of noise pollution.
Answer: Four causes of noise pollution are:
- Industrialisation: Industrialisation has led to an increase in noise pollution as the use of heavy machinery such as generators, mills, huge exhaust fans are used, resulting in the production of unwanted noise.
- Vehicles: Increased number of vehicles on the roads are the second reason for noise pollution.
- Events: Weddings, public gatherings involve loudspeakers to play music resulting in the production of unwanted noise in the neighbourhood.
- Construction sites: Mining, construction of buildings, etc add to the noise pollution.
14. What is the difference between International and local trade?
Answer: Difference between International and local trade are:
- Trade between two countries is called international trade whereas local trade is carried in cities, towns, and villages
- International Trade may take place through sea air or land routes whereas local trade is mainly carried through land routes
- In International trade volume of trade is more whereas in Local trade volume of trade is less.
- It brings change in national income whereas local trade doesn’t bring any change in national income
Note : Attempt any two questions from Q. No. 15 to 17:
15. Describe the technological changes in World Economy in 19th Century.
Answer: In the early nineteenth century, factories increasingly became an
intimate part of the English landscape. In the 1st phase of industrialisation, cotton was the leading sector. Later steel and iron industry led the way towards industrialisation. Due to higher demand for iron and steel, railways started expanding. Technological changes occurred gradually. The machines often broke down and the cost incurred to repair them was not cheap. When steam engines were invented, it was not accepted quickly. Although it improved productivity, industrialists were slow to accept them.
16. Explain the importance of Advertisement in goods market.
Answer: Advertising plays a very important role in today’s age of competition. Advertising is one thing which has become a necessity for everybody in today’s day-to-day life, be it the producer, the traders, or the customer.
Advertising plays a very important role in customers’ lives. Customers are the people who buy the product only after they are made aware of the products available in the market. If the product is not advertised, no customer will come to know what products are available and will not buy the product even if the product was for their benefit. One more thing is that advertising helps people find the best products for themselves, their kids, and their family. Thus, advertising is important for the customers.
17. Describe the Housing problem of Bombay in the mid-nineteenth century.
Answer: The city of Bombay quickly developed and its trade in cotton and opium developed. People from all over India migrated here in search of livelihood. But the life of migrants was not smooth. The three major problems faced by people who migrated to Bombay during the mid – 19th century are:
- Bombay became a crowded city. With the rapid expansion of the city, the crisis of housing became acute by the mid-19th century.
- The congested city life of Bombay developed the problem of water supply. Water was scarce and people often quarrelled every morning for a turn at the tap.
- Due to high rents, migrants were forced to share homes, either with relatives or caste fellows who were streaming into the cities.
18. Write a note on Vienna congress.
OR
Describe the Resistance to France colonial education in schools in Vietnam.
Answer: The Congress of Vienna was a meeting of ambassadors of European states chaired by Austrian statesman Klemens von Metternich. It was held in Vienna from November 1814 to June 1815, though the delegates had arrived and were already negotiating by late September 1814. The objective of the Congress was to provide a long-term peace plan for Europe by settling critical issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. The goal was not simply to restore old boundaries but to resize the main powers, so they could balance each other and remain at peace. The leaders were conservatives with little use for republicanism or revolution, both of which threatened to upset the status quo in Europe. France lost all its recent conquests while Prussia, Austria and Russia made major territorial gains. Prussia added smaller German states in the west, Swedish Pomerania and 60% of the Kingdom of Saxony; Austria gained Venice and much of northern Italy. Russia gained parts of Poland. The new Kingdom of the Netherlands had been created just months before, and included formerly Austrian territory that in 1830 became Belgium.
Answer: School textbooks disparaged the Vietnamese and glorified the French. It also provided justifications of French colonial rule. The textbooks portrayed that Vietnamese were primitive and lacked intelligence. However, the teachers did not follow the syllabus, they were taught what was happening on the ground. This resistance to follow and teach the school syllabus grew stronger when the number of Vietnamese teachers increased in the lower classes. Gradually with the forming of various groups by the students, schools became a vital spot of political battles.
19. “According to your view democracy is accountable, responsive and legitimate
government.” Give three arguments in favour of your view.
Answer: The most basic outcome of democracy should be that it produces a government that is
accountable to the citizens, and responsive to the needs and expectations of the citizens.
- People have control over their rulers and have a right to choose their rulers.
- The democratic government will take more time to follow procedures before arriving at a decision. But because it has followed procedures, its decisions may be both more acceptable to the people and more effective.
- Democratic Governments are legitimate governments because they are elected by the citizens of the country through electoral processes, unlike a country ruled by dictators.
20. Which desirable reforms can be done in the present context in Indian democracy?
Describe any three possible reforms.
Answer: Democratic reforms initiatives need to be taken by politically conscious citizens, political parties, movements.
- There needs to be political reforms. The best way to bring in political reforms is to encourage greater political participation by ordinary citizens.
- Just framing laws to ban something need not necessarily bring in the necessary democratic reforms. Instead laws need to be framed which will provide incentives to political actors and empower people to carry out democratic reforms. Right to information (RTI) is an excellent example of empowering people and maybe some similar laws could be explored to empower people in democracy.
- Any democratic reforms need to take into consideration on how to implement and who is going to implement it.
Democratic reforms cannot be the same in all democracies. Democratic reforms will keep changing based on time and new challenges that will keep cropping up. Hence one needs to keep in mind the broad consensus based on which democratic reforms need to be carried out.
21. Write any six public facilities.
Answer: Six public facilities are:
- Educational facilities that the government provides such as chairs, books, etc for the use of the public.
- Government provides hospitals, vaccine programmes to maintain the quality of life.
- Law and order security for people so that people can live peacefully.
- Banking facilities provided to make our money safe and to get loans from the banks.
- Roads and highways constructed so that people can commute easily without any hurdles.
- Government provides basic food items like rice, dal, oil, etc to below poverty line people with the help of Public Distribution System.
22. Give any two differences between formal and informal sector credit.
Answer: Two differences between formal and informal sector credit are:
Formal sectors:
- Formal sectors provide cheap and affordable loans and their rate of interest is monitored by the Reserve Bank of India.
- Formal sector strictly follows the terms of credit, which includes interest rate, collateral, documentation and the mode of repayment.
Informal sectors:
- Include loans from moneylenders, traders, employers, relatives, friends, etc. Features for informal sector loans are:
- Their credit activities are not governed by any organisation, therefore they charge a higher rate of interest.
23. Write any two benefits of Multinational Corporations.
Answer: Two benefits of Multinational Corporations are:
Cheaper Labour – One of the advantages of multinational corporations is the opportunity to operate in countries where labour is not as expensive. Multinationals can set up their offices in several countries where demand for their services and products are high while cheaper labour is available.
Job Creation – When international companies set up branches in other countries, employees and members of the team are locals. That said, more people are given employment opportunities especially in developing countries.
24. Explain the Judicial machinery for redressal of consumer disputes.
Answer: The law has enabled consumers the right to represent in the consumer courts.
There is a three tier quasi judicial machinery at the national, state and district levels for redressal of consumer disputes. The National level court deals with cases involving claims exceeding Rs 1 crore. The state level courts deal with cases involving claims between Rs 20 lakhs and Rs 1 crore. The district level courts deal with cases involving claims upto Rs 20 lakhs. There are consumer protection councils or consumer forums to give guidance to the consumers on how to file cases in the consumer court. These organisations also receive financial support from the Government for creating awareness among people.
25. Discuss the Religious effects of the Print Revolution.
OR
The novel is a modern form of literature. Explain it.
Answer: The religious effects of the Print Revolution are:
- Fear of spread of irreligious thoughts – Many were apprehensive of the effects that the easier access to the printed word and the wider circulation of books, could have on people’s minds. It was feared that if there is no control over what was printed and read, then rebellious and irreligious thoughts might spread.
- Division of church – In 1517, the religious reformer Martin Luther wrote Ninety Five Theses criticising many of the practices and rituals of the Roman Catholic Church. This led to a division within the Church and to the beginning of the Protestant Reformation.
- Index of prohibited books – The Roman Church, troubled by such effects of popular readings and questionings of faith, imposed severe controls over publishers and booksellers and began to maintain an Index of Prohibited Books from 1558.
- Print and Muslims – To check conversion or fear of change of laws Muslims used cheap lithographic presses, published Persian and Urdu translations of holy scriptures, and printed religious newspapers and tracts.
- Print and Hindus – Among Hindus, too, print encouraged the reading of religious texts, especially in the vernacular languages. The first printed edition of the Ramcharitmanas of Tulsidas, a sixteenth-century text, came out from Calcutta in 1810. Religious texts, therefore, reached a very wide circle of people, encouraging discussions, debates and controversies within and among different religions.
Answer: Nineteenth-century periodicals serialised important novels, which gave birth to a particular way of writing novels. In the 1920s in England, popular works were sold in cheap series, called the Shilling Series. Since social reforms and novels had already created a great interest in women’s lives and emotions, there was also an interest in what women would have to say about their own lives. From the 1860s, a few Bengali women like Kailashbashini Debi wrote books highlighting the experiences of women. A woman in a Tamil novel expressed what reading meant to women who were so greatly confined by social regulations.
26. What are resources ? Describe biotic and abiotic resources.
OR
´
Write causes and methods of conservation of soil erosion.
Answer: Resources is a vast concept. Resources are everything that is useful and contributes value to society. A resource is a water, air, food, animals, plants, metals, minerals, and anything else that exists in nature and also has usefulness to human civilization.
- Biotic resources – The term “biotic” is formed by the combination of two terms, “bio” meaning life and “ic” meaning like. Thus, the term means life-like and is related to all the living entities present in an ecosystem.
- Abiotic resources – The term abiotic refers to all the non-living factors present in an ecosystem. Sunlight, water, land, all constitute the abiotic factors.
Answer: The causes of soil erosion are:
1. Rainfall and Flooding – Higher intensity of rainstorm is the main cause of soil erosion. Four types of soil erosion are caused by rainfall:
- Rill erosion
- Gully erosion
- Sheet erosion
- Splash erosion
The raindrops disperse the soil, which is then washed away into the nearby streams and rivers. Regions with very heavy and frequent rainfall face a large amount of soil loss. The flowing water during floods also erodes a lot of soil by creating potholes, rock-cut basins, etc.
2. Agriculture – The farming practices are the major cause of soil erosion. The agricultural activities disturb the ground. The trees are cleared and the land is ploughed to sow new seeds. Since most of the crops are grown during spring, the land lies fallow during winters. Most of the soil is eroded during winters.
Also, the tyres of tractors make grooves on the land, making a natural pathway for water. Fine soil particles are eroded by wind.
3. Grazing – The grazing animals feed on the grasses and remove the vegetation from the land. Their hooves churn up the soil. They also pull out plants by their roots. This loosens the soil and makes it more prone to erosion.
4. Logging and Mining – A large number of trees are cut down to carry out the logging process. Trees hold the soil firmly. The canopy of the trees protects the soil from heavy rainfall. The leaf litter that protects the soil from erosion, is also lost during logging. Mining activities also disturb the land and leave the soil more prone to erosion.
5. Construction – The construction of roads and buildings exposes the soil to erosion. The forests and grasslands are cleared for construction purposes, which exposes the soil making it vulnerable to erosion.
6. Rivers and Streams – The flowing rivers and streams carry away the soil particles leading to a V-shaped erosion activity.
7. Heavy Winds – During dry weather or in the semi-arid regions, the minute soil particles are carried away by the wind to faraway lands. This degrades the soil and results in desertification.
Methods of conservation of soil erosion.
- Afforestation
- Checking Overgrazing
- Constructing Dams
- Changing Agricultural Practices
- Crop Rotation
- Strip Cropping
- Use of Early Maturing Varieties
- Contour Ploughing
- Terracing and Contour Bunding
- Checking Shifting Cultivation
- Ploughing the Land in Right Direction
27. ‘Communalism can take various forms in politics.’ Explain any four forms.
OR
“Even today, women face many discriminations.” Explain the statement with examples.
Answer: Four forms are:
- The common form of communalism are practised on every day customarily beliefs. It can be in the form of religious prejudices, stereotypes of religions communities, supremacy of one religion over the other religions. These beliefs are so common that we often fail to detect even when we believe in it.
- It leads to a search for political dominance of religious community over others. It takes the form of majoritarian dominance for the majority community, for minority community, it can take the form of a desire to form a separate political unit.
- The most frequent form of communalism is political enlistment on the religious guidelines. It involves the usage of sacred symbols, religious leaders, emotional appeal and creating fear in order to accumulate followers of one religious community in the political arena. It is materialized to gain advantage in electoral politics.
- It often takes the form of communal violence, riots and massacre.
Answer: Women face disadvantage, discrimination and oppression in various ways:
- Literacy rate among women is much lesser than the literacy rate of men.
- The proportion of girls going for higher studies is much lesser than boys, because parents prefer to spend their resources for boys education instead of girls education.
- On an average it has been found that women work more than men, yet the proportion of women in high paid jobs is less than men. Women are paid less in almost all fields ranging from cinemas, sports, factories etc.
- Child sex ration is skewed since parents prefer boy child and abortion of girl child.
- Women face domestic violence, harassment.
- Proportion of women in Indian legislature is very low.
28. Discuss Nepal’s “Second Movement for Democracy”.
OR
Explain the challenges which are faced by the political parties in democracy.
Answer: In April 2006, Nepal witnessed an extraordinary movement to restore democracy. The features of this movement were as follows.
1) The movement aimed to reverse King Gyanendra’s orders of dismissing the Parliament and restore democracy in Nepal.
2) All the major political parties in the Parliament came together and formed an alliance called the Seven Party Alliance (SPA), which announced a four-day strike in Kathmandu.
3) They were joined by Maoist insurgents and various other organisations, as their protest developed into an indefinite strike. Millions of people resisted curfew and gathered on the streets every day demanding the restoration of democracy. Ultimately, the King was forced to concede all the demands of the people, i.e. restoration of democracy, power to an all party government and the formation of a new constituent assembly in the country.
This movement is known as Nepal’s second movement of democracy.
Answer: The challenges which are faced by the political parties in democracy are:
- The lack of internal democracy – If there is a concentration of power in the hands of one or only a few ministers in the party, it gives space to internal conflicts.
- The dynastic succession – This has been in the political parties from time immemorial. The leader of the party sets a lineage and one after another, a dynastic succession keeps taking place, which affects the chances of other ministers in the party to gauge an effective position in the party.
- Money and muscle power – The participation of smaller regional parties is lesser due to growing prominence of muscle and money power. These powers can mostly be seen during the election period where parties’ rich candidates can gain more votes using both of these.
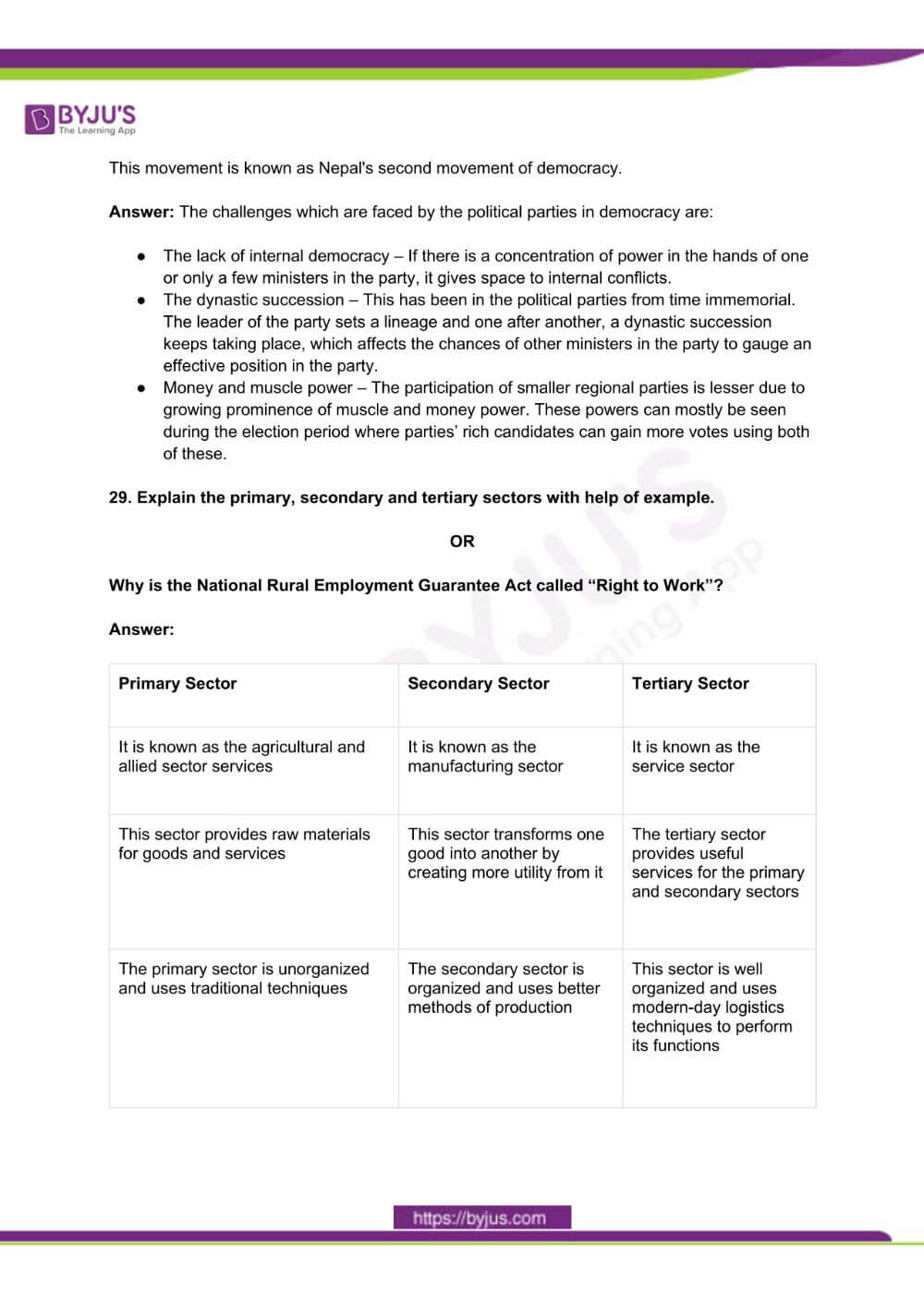
29. Explain the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors with help of example.
OR
Why is the National Rural Employment Guarantee Act called “Right to Work”?
Answer:
| Primary Sector | Secondary Sector | Tertiary Sector |
| It is known as the agricultural and allied sector services | It is known as the manufacturing sector | It is known as the service sector |
| This sector provides raw materials for goods and services | This sector transforms one good into another by creating more utility from it | The tertiary sector provides useful services for the primary and secondary sectors |
| The primary sector is unorganized and uses traditional techniques | The secondary sector is organized and uses better methods of production | This sector is well organized and uses modern-day logistics techniques to perform its functions |
| Activities in this sector consist of agriculture, forestry and mining | It includes manufacturing units, small scale units, large firms and multinational corporations | Banking, insurance trade and communications come under this sector |
| In most developing nations such as India, this sector is where a large section of the workforce is employed, in comparison to developed nations | The employment rate is in equilibrium as a specialized set of skills is required to find employment in this sector | This sector’s employment share has increased in the ensuing years |
Answer: National Rural Employment Guarantee Act called “Right to Work” because it provided 100 days work and wage to every person below poverty line.
Objectives of NREGA are:-
- It provided 100 days work and wage to every person below poverty line(BPL).
- It provided 150 days work and wage to people of disaster prone regions.
- Ration shops were opened to provide ration at low rates to people BPL (below poverty line).
- Deepening democracy at the grass-roots by strengthening Panchayati Raj Institutions.
- Effecting greater transparency and accountability in governance.
30. (A) Mark the following in the given outline Map of India :
(i) Salem
(ii) Durgapur
(B) Mark the following in the given outline map of India.
(i) Chauri-Chaura
(ii) Calcutta
Answer A and B: Activity to be done by yourself.
31. (A) “The Constitution of India clearly provided a three-fold distribution of legislative
powers between the Union and States. ” Explain the statement with examples.
Answer: Power is shared among different organs of government, such as the legislature, executive and judiciary. Such a separation ensures that none of the organs can exercise unlimited power.
The powers between Central and State Governments are divided based on 3 lists named union list, state list and concurrent list. Important subjects of national importance such as foreign affairs, defence, communication, banking etc comes under union list. It means the Central Government alone can make laws on such subjects. Commerce, agriculture, trade, irrigation comes under state list. Only state governments alone can make laws related to state subjects. Both central and state governments can make laws on subjects that come under concurrent list.
(B) (i) Write one medium for maximum promotion of Public Transport facilities.
(ii) Write any one reason of road accidents.
(iii) Which right of the citizens can be protected by imparting knowledge to them
about traffic rules and road safety.
Answer i: One medium for maximum promotion of Public Transport facilities is:
- Improving accessibility of services by providing targeted information to passengers.
Answer ii: One reason of road accidents:
Multitasking while driving a vehicle: While driving a vehicle on the road, the concentration of the driver should be 100%. Multitasking while driving like talking on the mobile phone or listening to music on earphones can cause road accidents as the concentration of the driver is not 100% on the road.
Answer iii: Right to Life













Comments