Active and Passive Transport
“Active transport is the movement of molecules across a membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration against the concentration gradient, often assisted by enzymes and requires energy”
“Passive transport is the movement of ions and molecules across the cell membrane without requiring energy.”
Active and passive transport are the two main biological processes that play a crucial role in supplying nutrients, oxygen, water and other essential molecules to the cells along with the elimination of waste products. In essence, active and passive transport work for the same goals/ purposes, but with different movement.
Let us see how active and passive transport are different from each other.
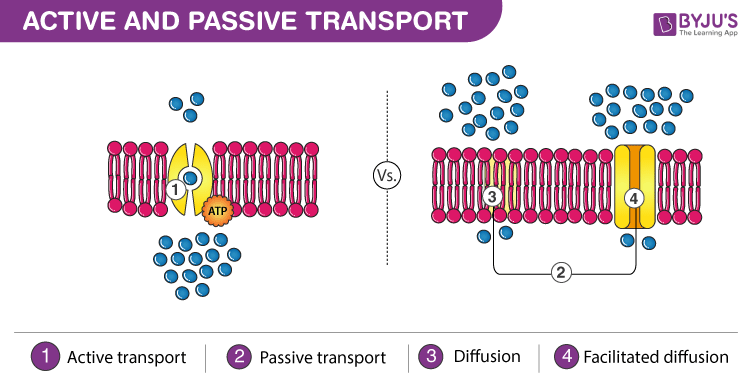
Difference Between Active And Passive Transport
Following are the important difference between active and passive transport:
| Active Transport | Passive Transport |
| Requires cellular energy. | Does not require cellular energy. |
| It circulates from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration | It circulates from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration |
| Required for the transportation of all the molecules such as proteins, large cells, complex sugars, ions, etc. | Required for the transportation of all soluble molecules, including oxygen, water, carbon dioxide, lipids, sex hormones, etc. |
| It transports various molecules in the cell. | It is involved in the maintenance of the equilibrium level inside the cell. |
| Active transport is a dynamic process. | Passive Transport is a physical process. |
| It is highly selective. | It is partly non-selective |
| Active transport is a rapid process. | Passive transport is a comparatively slow process. |
| Transpires in one direction. | Transpires bidirectionally. |
| Active transportation is influenced by temperature. | Passive transportation is not influenced by temperature. |
| In active transport, carrier proteins are required | In passive transport, carrier proteins are not required |
| This process reduces or halts as the oxygen content level is reduced. | This process is not affected by the level of oxygen content. |
| Metabolic inhibitors can influence and stop active transport. | Passive transportation is not influenced by metabolic inhibitors. |
| Different types of Active Transport are – Exocytosis, endocytosis, sodium-potassium pump |
Different types of Passive Transport are – Osmosis, diffusion, and facilitated diffusion |
Active Transport
This is the biological process in which molecules move against the concentration gradient and require chemical energy to move biochemical compounds from a lower region to the high region. Therefore, this process uses ATP – Adenosine triphosphate to pump molecules through a concentration gradient. Complex sugar, ions, large cells, proteins and other particles are transported in this process. There are two types of Active transport:
- Primary Active transport
- Secondary Active transport
Exocytosis, endocytosis and sodium-potassium pump are a few examples of active transport. The process of endocytosis and exocytosis are utilized by all the cells for transportation of molecules which cannot passively permeate via the membrane.
- Endocytosis is the process of active transportation of molecules into the cells by the action of engulfing it along with its membrane.
- Exocytosis produces a counter function thereby forcing molecules out of the cell. The process of homeostasis facilitates an equal flow of molecules in and out of a cell which confers that the number of molecules that enter the cell through endocytosis equates to the number of molecules that exits a cell through the process of exocytosis. Both the processes assure that nutrients and wastes are balanced for the smooth functioning of the cells.
Main Article: Active Transport.
Passive Transport
In this biological process, energy is not required for transporting the molecules, as the biochemicals move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. All particles which are easily soluble are transported through passive transport. This process is carried out to maintain the balance and the equilibrium level in a cell. All the waste molecules including, water and carbon dioxide is separated and moved out of the cell using passive transport. Meanwhile, nutrients like oxygen that are functional for the cell are diffused in this process. Osmosis, diffusion and facilitated diffusion are some of the examples of passive transport.
Main Article: Passive Transport
Key Points on Active and Passive Transport
- Active transport requires energy for the movement of molecules whereas passive transport does not require energy for the movement of molecules.
- In active transport, the molecules move against the concentration gradient whereas in passive transport, the molecules move along the concentration gradient.
- Uptake of glucose in the human intestine works on the principle of active transport.
- Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis and filtration are examples of passive transport.
Related Links:

Frequently Asked Questions
How is active transport different from passive transport?
Active transport moves molecules and ions from lower concentration to higher concentration with the help of energy in the form of ATP. On the other hand, passive transport moves molecules and ions from a higher concentration to lower concentration without any energy.
What is the role of ATP in active transport?
ATP hydrolysis provides energy for the movement of molecules and ions across a concentration gradient. The movement of molecules occurs either inside the cells (endocytosis) or out of the cells (exocytosis).
Mention two examples of active and passive transport.
Examples of active transport include sodium-potassium pump, uptake of mineral ions by the roots of the plants, etc. Whereas, the examples of passive transport include the exchange of gases in the alveoli of the lungs and the exchange of nutrients in the kidneys.
What is the importance of active and passive transport?
Active and passive transport regulate the entry and exit of ions and molecules in a cell. These processes allow only specific materials to cross spontaneously through the cell membrane. Rest need a carrier to pass through the membrane.
What are the different types of passive transport?
Passive transport can be of the following different types:
- Simple diffusion
- Osmosis
- Facilitated diffusion

Thank you so much
Thank you so much! The explanations are clear and concise. It saved me time and mental energies to understand.