
Centripetal acceleration is the rate of change of tangential velocity. The net force causing the centripetal acceleration of an object in a circular motion is defined as centripetal force. The derivation of centripetal acceleration is very important for students who want to learn the concept in-depth. The direction of the centripetal force is towards the centre, which is perpendicular to the velocity of the body.
The centripetal acceleration derivation will help students to retain the concept for a longer period of time. The derivation of centripetal acceleration is given in a detailed manner so that students can understand the topic with ease.
The centripetal force keeps a body constantly moving with the same velocity in a curved path. The mathematical explanation of centripetal acceleration was first provided by Christian Huygens in the year 1659. The derivation of centripetal acceleration is provided below.
Centripetal Acceleration Derivation
The force of a moving object can be written as
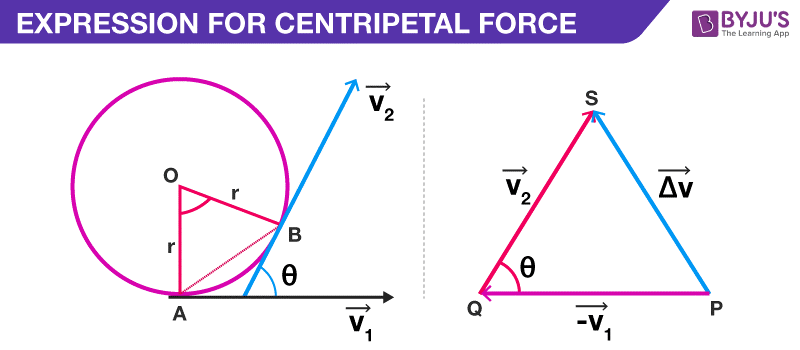
From the diagram given above, we can say that,
The triangle PQS and AOB are similar. Therefore,
Thus, we derive the formula of centripetal acceleration. Students can follow the steps given above to learn the derivation of centripetal acceleration.
Read More: Centripetal Acceleration
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What do you mean by centripetal acceleration?
Give the formula for finding centripetal acceleration.
Let r be the radius of the circular path
Then centripetal acceleration,
a=v2/r
Which force is responsible for producing centripetal acceleration?
Centripetal force is responsible for producing centripetal acceleration./div>
Is centripetal acceleration a constant or a variable vector?
What is the unit of centripetal acceleration?
From the video learn the concept of centripetal acceleration in detail

Stay tuned with BYJU’S and learn various other derivation of physics formulas.

nice way to study physics
when we form the triangle why is the v1 vector negative?
QP is the direction of the +v vector. The derivation uses PQ, and hence -v.
Its because in order to add v1 and v2 vectors vectorially using triangle method ,v1 vector has to attach its head to tail so as to obtain resultant vector delta v
simple tricks to study the physics
Nice and easy way to understand and memorise
How is del v/AB equal to v/r?
Thank you so much It’s very helpful 🥰
Very understandable