Physics is a scientific subject that aims to create and practically test theories of the observable Universe. These theories change in scope and can be organised into many distinct branches. In this article, let’s go into the world of particle physics.
| Table of Contents |
What is Particle Physics?
- It is a branch of physics that studies the basic elements of matter and radiation and the interaction between them. The word particle can refer to various types of very small objects, but this branch usually investigates the irreducibly smallest detectable particles.
- It is also called “high energy physics” as many elementary particles don’t come under normal circumstances in nature. But, it can be identified during the energetic collision of other particles.
Modern Particle Physics
Modern particle physics research is focused on subatomic particles with less structure than atoms. These atomic constituents, like particles of protons, electrons and neutrons, are produced by radioactive and scattering processes.
Standard Model
- The standard model of particle physics is a theory related to the electromagnetic, nuclear interactions and also classifying the subatomic particles.
- This model was developed in the latter half of the 20th century, as a collaborative effort of scientists around the world. The development of the Standard Model was driven by a theoretical and experimental particle.
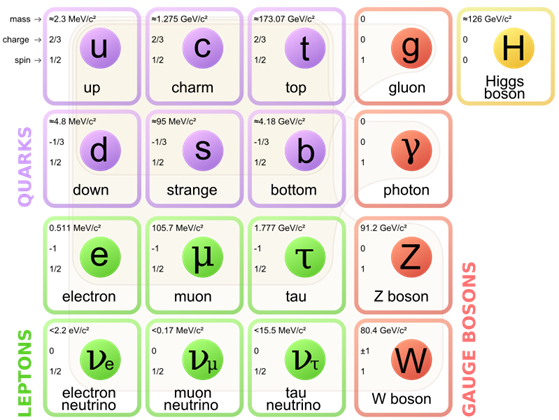
Standard Model of Particle Physics
- As currently formulated, the Standard Model has 61 elementary particles. The standard model contains 24 fundamental fermions, includes 12 particles and their associated antiparticles, which are the constituents of matter. Back in 2012, the standard model predicted the existence of Higgs Boson, which was known as the last piece.
- However, recently a particle named God’s particle was found that is consistent with the Higgs Boson particle and has stepped forward in the completion of the standard model of particle physics.
Theoretical Particle Physics
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics which employs mathematical models and abstractions of physical objects and systems to rationalise, explain and predict natural phenomena. There are several efforts being made in theoretical particle physics, in an attempt to develop the models, theoretical framework, and mathematical tools to understand current experiments and make predictions for future experiments.
Uses
- Particle physics is used to produce medical isotopes which are used in PET imaging and external beam radiotherapy.
- Helps to achieve the concept of a superconductor.
- Touchscreen technologies and the World Wide Web were developed at CERN institute for particle physics.
- Some other fields that use particle physics are workforce development, medicine, industries, science, and national security etc.
Particle Physics Formulas
Following is the table explaining the formulas used in particle physics with their symbols:
| Quantity | Defining equation | Symbols used |
| Number of atoms | N0=N+ND |
|
| Mass number | A=Z+N |
|
| Radioactive decay | \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{dN}{dt}=-\lambda N\end{array} \) \(\begin{array}{l}N=N_{0}e^{-\lambda t}\end{array} \) |
|
For interactive visuals and explanations for the same, kindly visit our site or download our BYJU’S Learning app from the Play Store.
The video explaining the spaces between particles



Comments