We have learnt what velocity is. Now, we will learn about the Velocity-Time Graphs.
| Table of Contents |
Velocity-Time Graphs
To draw velocity-time graphs, we will use the three equations of motion.
Case 1: Velocity-time graphs with constant velocity (zero acceleration)
When the velocity is constant, the velocity-time graph, with Y-axis denoting velocity and the X-axis denoting time, will be like:
- As the graph shows, the velocity is constant (c) throughout the interval.
- No particles of matter how much the time changes, the velocity will be c at every instant. In this case, we have taken the initial velocity to be positive.
- The graph will be different if the initial velocity is negative.
- Example: If the acceleration of a particle is zero (0), and velocity is constantly said 5 m/s at t =0, then it will remain constant throughout the time.
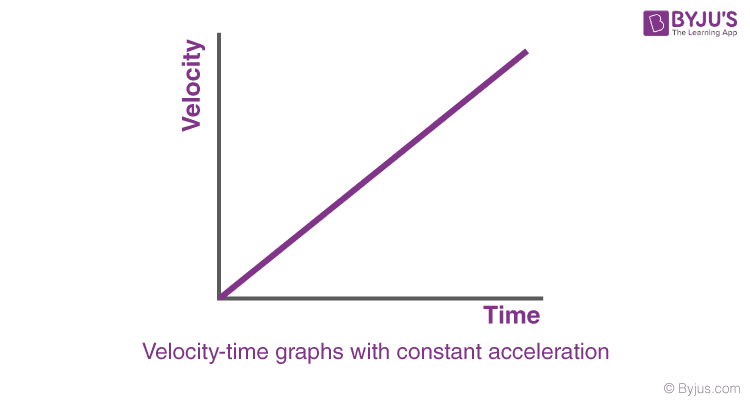
Case 2: Velocity-time graphs with constant acceleration
- When the acceleration is constant (positive), and the initial velocity of the particle is zero, the velocity of the particle will increase linearly as predicted by the equation:
- v = u + at
- Since u = 0
- v = at
- As shown in the figure, the velocity of the particle will increase linearly with respect to time. The slope of the graph will give the magnitude of acceleration.
- Example: If the acceleration of a particle is constant (k) and is positive, the initial velocity is zero, and then the velocity increases linearly. The slope of the velocity-time graph will give the acceleration.
Case 3: Velocity-time graphs with increasing acceleration
W
- When the acceleration is increasing with time, the velocity-time graph will be a curve as predicted from the equation:
- v = u + at
- Since u = 0
- v= at
- Since acceleration is a function of time, the velocity-time graph will be a curve.
- Note: Since the acceleration continuously increases with time, the magnitude of the slope will also continuously increase with time.
- Example: If the acceleration of a particle is a function of time and the initial velocity is zero, the velocity-time graph will be a curve. The slope of the velocity-time graph at any instant (at a certain time) will give the acceleration at that time.
- Case 3 was just the case of increasing acceleration. There will be a different graph when the acceleration decreases with time. To learn more about velocity-time graphs, join BYJU’S.
Complete quiz of the chapter Motion Class 9 Science

Top 10 NTSE Important Questions on Motion Class 9

To learn more about velocity-time graphs, join BYJU’S.
Test Your Knowledge On Vt Graphs!



Comments