The eye is an important and one of the most complex sensory organs that we humans are endowed with. It helps us in visualizing objects and also helps us in light perception, colour and depth perception. Besides, these sense organs are pretty much similar to cameras, and they help us see objects when light coming from outside enters them. That being said, it is quite interesting to understand the structure and working of the human eye. It also helps us in understanding how a camera actually functions. Let’s have a glance at the human eye – its structure and functions.
| Table of Contents: |
Structure of Human Eye
A human eye is roughly 2.3 cm in diameter and is almost a spherical ball filled with some fluid. It consists of the following parts:
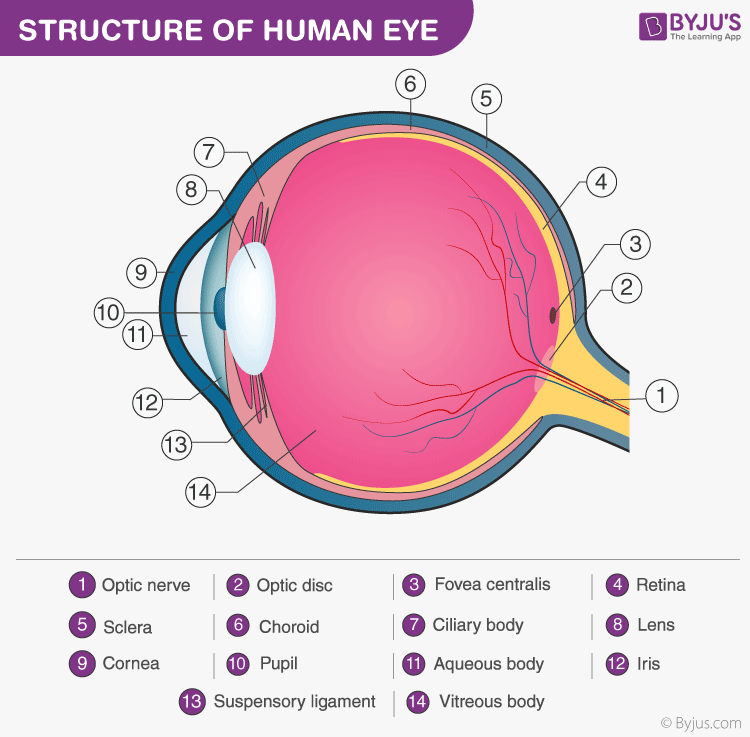
- Sclera: It is the outer covering, a protective tough white layer called the sclera (white part of the eye).
- Cornea: The front transparent part of the sclera is called the cornea. Light enters the eye through the cornea.
- Iris: A dark muscular tissue and ring-like structure behind the cornea is known as the iris. The colour of the iris actually indicates the colour of the eye. The iris also helps regulate or adjust exposure by adjusting the iris.
- Pupil: A small opening in the iris is known as a pupil. Its size is controlled with the help of iris. It controls the amount of light that enters the eye.
- Lens: Behind the pupil, there is a transparent structure called a lens. By the action of ciliary muscles, it changes its shape to focus light on the retina. It becomes thinner to focus on distant objects and becomes thicker to focus on the nearby objects.
- Retina: It is a light-sensitive layer that consists of numerous nerve cells. It converts images formed by the lens into electrical impulses. These electrical impulses are then transmitted to the brain through optic nerves.
- Optic nerves: Optic nerves are of two types. These include cones and rods.
- Cones: Cones are the nerve cells that are more sensitive to bright light. They help in detailed central and colour vision.
- Rods: Rods are the optic nerve cells that are more sensitive to dim lights. They help in peripheral vision.
At the junction of the optic nerve and retina, there are no sensory nerve cells. So no vision is possible at that point and is known as a blind spot.
An eye also consists of six muscles. It includes the medial rectus, lateral rectus, superior rectus, inferior rectus, inferior oblique, and superior oblique. The basic function of these muscles is to provide different tensions and torques that further control the movement of the eye.
Watch and learn about the structure of an eye

Function of the Human Eye
As we mentioned earlier, the eye of a human being is like a camera. Much like the electronic device, the human eye also focuses and lets in light to produce images. So basically, light rays that are deflected from or by distant objects land on the retina after they pass through various mediums like the cornea, crystalline lens, aqueous humor, the lens, and vitreous humor.

The concept here though is that as the light rays move through the various mediums, they experience refraction of light. Well, to put it in simple terms, refraction is nothing but the change in direction of the rays of light as they pass between different mediums. The table below shows the refractive indices of the various parts of the eye.

Having different refractive indexes is what bends the rays to form an image. The light rays finally are received and focused on the retina. The retina contains photoreceptor cells called rods and cones and these basically detect the intensity and the frequency of the light. Further, the image that is formed is processed by millions of these cells, and they also relay the signal or nerve impulses to the brain via the optic nerve. The image formed is usually inverted but the brain corrects this phenomenon. This process is also similar to that of a convex lens.
In any case, now that we have learned something about the human eye, each eye is very important, and they play a distinct part in helping humans to see.
Read More: Convex Lens
Watch the video and solve previous year questions in the chapter The Human Eye and Colorful World Class 10

Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Name some sensory organs.
What are the parts of the human eye?
Parts of the human eye are:
- Sclera
- Cornea
- Iris
- Pupil
- Lens
- Retina
- Optic nerves
What is blind spot?
Define lens.
What are the types of optic nerves?
Recommended Videos
The Human Eye and Colourful World Class 10 Science (Physics) NCERT Questions |
The Human Eye and Colourful World Class 10 Science (Physics Theory and Questions) |
Optical Phenomena Class 10 Science (Physics) |
Human Eye Class 10 Science (Physics) |
Atmospheric Refraction Class 10 Science (Physics) |
Human Eye and The Colourful World CBSE – Class 10 Exams 2023 |
The Human Eye and Colorful World Class 10 Science Previous Year Questions |
The Human Eye and Colourful World Class 10 Science Chapter Summary |
Structure and Functions of Human Eye – Class 10 Science (Physics) |
Defects of Vision and their Corrections – Class 10 Science (Physics) |
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more about other concepts of Physics with interactive videos.

Tq so much byjus this article is so useful for us we are so happy and our friends also happy we all are byjus users only tq so much for thinking about us and helping us
Nice app I love this app
I love this app
Really exactly perfect explaination without any wrong
This was very helpful thanks but i have some questions of my own 😉
Nice
I like this
most valuable lesson we must need this topic
This was really very helpful!
😀
It’s a perfect way to understand this ..because it’s language is easy and could ne understood easily..thankyou so much byjus….
nice ❤️. excellent
Thanks,This app is very good, you have helped me and my friends a lot, I have answered the question easily, that too without any mistake.
It was very helpful
Thanku so much
NICE NOTES
Great app ever🥰😌
Best notes 👌🏻
Got to know a lot of facts about human eyes, and I am really thankful to BYJU’S for this.
i just love your explanations and teaching pattern.
I love the way of teaching and explanation