What is Potassium acetate?
“CH3CO2K is a potassium salt of acetic acid with the chemical name Potassium acetate. It is also called Diuretic salt or Potassium ethanoate, or Acetic acid potassium salt. It is an essential macro-mineral and a potassium salt which consists of an equal numbers of acetate and potassium ions”.
Diuretic salt is a deliquescent white crystalline powder. It is soluble in water and has a pH value between 7.5-9.0. It is widely used to replenish electrolytes, and as well as a urinary and systemic alkaliser. Earlier it was used in expectorants and diuretics.
Potassium helps in maintaining intracellular tonicity, which is required for nerve conduction, smooth muscle contraction, normal renal function, and maintenance of blood pressure.
Table of Contents
- Properties of Potassium acetate – CH3CO2K
- Potassium acetate structure – CH3CO2K
- CH3CO2K Uses (Potassium acetate)
- Preparation of Potassium acetate
- History
Properties of Potassium acetate – CH3CO2K
| CH3CO2K | Potassium acetate |
| Molecular weight of CH3CO2K | 98.142 g/mol |
| Density of Potassium acetate | 1.8 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point of Potassium acetate | Decomposes |
| Melting Point of Potassium acetate | 292 °C |
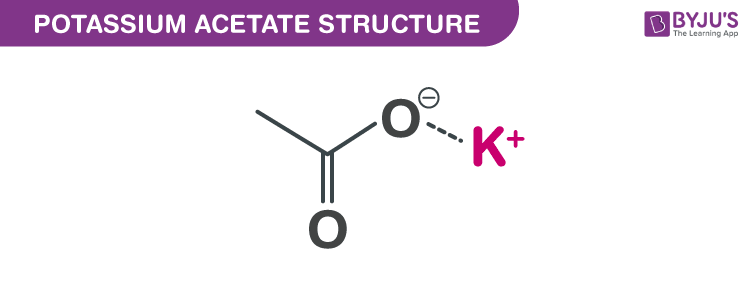
Potassium acetate structure – CH3CO2K
CH3CO2K Uses (Potassium acetate)
- Potassium acetate is used as a deicer to remove ice and stop its formation.
- Used as a food preservative.
- Used as a catalyst to produce polyurethanes.
- Used in molecular biology to precipitate dodecyl sulphate.
- Used in the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Used in the making of lubricants.
- Used as a food acidity regulator.
- Used in fire suppression.
- Used in laboratory chemicals.
- Used in agricultural chemicals.
Preparation of Potassium acetate
Potassium ethanoate can be generated by treating a potassium-containing base like potassium hydroxide (KOH) or potassium carbonate (K2CO3) with acetic acid (CH3COOH). The chemical equation for the same is given as follows:
CH3COOH + KOH → CH3COOK + H2O
The above reaction is termed as acid-base neutralisation reaction (An acid-base reaction in which an acid reacts with a base to form salt and water).
At around a temperature range of 41.3 °C, the sesquihydrate in water solution starts forming semi-hydrates.
History
Acetic acid potassium salt was initially used to prepare Cadet’s fuming liquid which is known to be the first organometallic compound produced. This compound was used as a urinary alkaliser and in a diuretic. It functions by changing the physical properties of body fluids.
Learn more about the Structure, physical and chemical properties of CH3CO2K from the experts at BYJU’S.

Comments