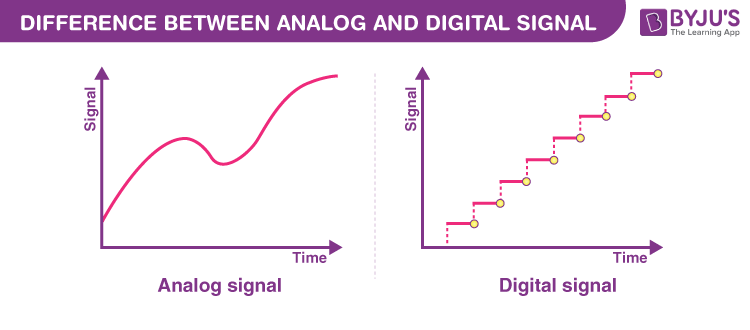
Analog and digital signals are the types of signals carrying information. The major difference between both signals is that the analog signals have continuous electrical signals, while digital signals have non-continuous electrical signals. The difference between analog and digital signal can be observed with the examples of different types of waves.
| Table of Contents: |
What Are Analog Signals?
Analog signals were used in many systems to produce signals to carry information. These signals are continuous in both values and time. The use of analog signals has declined with the arrival of digital signals. In short, to understand analog signals – all signals that are natural or come naturally are analog signals.
Read More: Waves.
What Are Digital Signals?
Unlike analog signals, digital signals are not continuous, but signals are discrete in value and time. These signals are represented by binary numbers and consist of different voltage values.
Difference between Analog and Digital Signals
To summarise, we have given the various differences between analog signal and digital signal in a tabular form below. Both these signals are used in electronic communication system to transfer information from one place to another.
| Difference between Analog and Digital Signal | |
We know that the major difference between an analog and a digital signal is that analog signals are continuous signals, while digital signals are discrete signals. In the video below, we have discussed more differences between them.

Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What are some examples of digital signals?
Digital signals do not produce noise. Digital computers and digital phones are some of the examples of digital signals.
What are the examples of analog signals?
A human voice, analog phones, and thermometer are some of the examples of analog signals.
How to convert analog signal into digital signal?
For the conversion of an analog signal into a digital signal, there are two steps that needs to be followed. The first step is a sampling. In this step, continuous electrical signals with varying time are considered. Both the axis that x-axis and y-axis are considered. Sampling is usually done along the x-axis and is classified into two categories, and they are sampling and downsampling. The second step is known as quantization. Quantization is done along the y-axis and it processes the image in which the continuous signals are divided into overlapping and non-overlapping signals.
What is sampling theorem?
The sampling theorem is defined as the continuous-time signal that can be represented in the form of samples and can be recovered back if the sampling frequency is greater than the maximum frequency of the signal.
What is undersampling?
Undersampling is defined as the sampling frequency which is less than the maximum frequency of the signal which results in overlapping of the successive cycles of the spectrum.
To learn more differences or other related topics, download BYJU’S – The Learning App.


Comments