The First Law of Thermodynamics states that heat is a form of energy, and thermodynamic processes are therefore subject to the principle of conservation of energy. This means that heat energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can, however, be transferred from one location to another and converted to and from other forms of energy.
| Table of Contents |
Introducing State Variables
Thermodynamic state variables are the macroscopic quantities that determine a system’s thermodynamic equilibrium state. A system not in equilibrium cannot be described by state variables. State variables can further be classified as intensive or extensive variables. Intensive variables are independent of the dimensions of the system like pressure and temperature, while extensive variables depend on dimensions of the system like volume, mass, internal energy etc.
Explaining the first law of thermodynamics
The first law of thermodynamics relates to heat, internal energy, and work.
The first law of thermodynamics, also known as the law of conservation of energy, states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but it can be changed from one form to another.
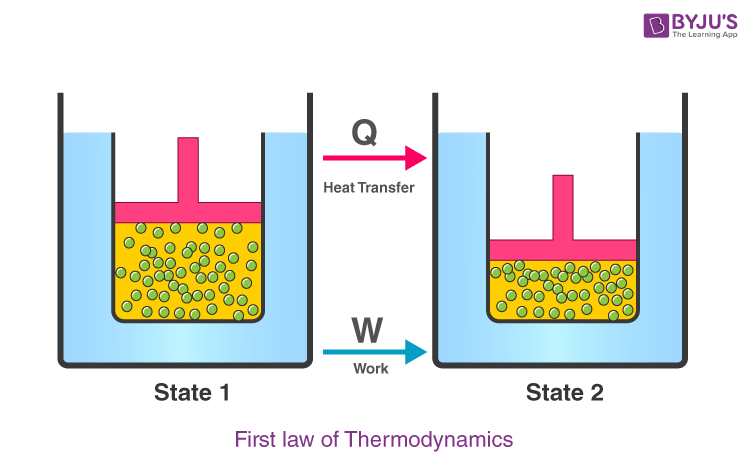
According to this law, some heat given to the system is used to change the internal energy while the rest is used in doing work by the system.
It can be represented mathematically as
\(\begin{array}{l}\Delta Q=\Delta U+W\end{array} \) |
Where,
- ΔQ is the heat given or lost
- ΔU is the change in internal energy
- W is the work done
We can also represent the above equation as follows,
\(\begin{array}{l}\Delta U=\Delta Q-W\end{array} \) |
So we can infer from the above equation that the quantity (ΔQ – W) is independent of the path taken to change the state. Further, we can say that internal energy increases when the heat is given to the system and vice versa.
Sign Conventions
The table below shows the appropriate sign conventions for all three quantities under different conditions:
| ΔU (change in internal energy) | Q (heat) | W (work done on the gas) |
| is “+” if temperature increases | is “+” if heat enters gas | is “+” if gas is compressed |
| is “-” if temperature decreases | is “-” if heat exits gas | is “-” if gas expands |
| is “0” if temperature is constant | is “0” if no heat is exchanged | is “0” if volume is constant |
Recommended Video
First Law of Thermodynamics Solved Examples
1. Calculate the change in the system’s internal energy if 3000 J of heat is added to a system and a work of 2500 J is done.
Solution:
The following sign conventions are followed in the numerical:
Solution:
The following sign conventions are followed in the numerical:
- Q is positive as heat is added to the system
- W is positive if work is done on the system
Hence, the change in internal energy is given as:
2. What is the change in the internal energy of the system if 2000 J of heat leaves the system and 2500 J of work is done on the system?
Solution:
The change in the internal energy of the system can be identified using the formula:
ΔU = Q-W
Substituting the values in the following equation, we get
ΔU = -2000-(-3000)
ΔU = -2000+3000
ΔU = 1000 Joule
Internal energy increases by 4500 Joules.

Suggested Reading
| Thermodynamics | Thermodynamic Processes & Types |
| Thermal Equilibrium & Zeroth Law Of Thermodynamics | Kelvin-Planck Statement |
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What does the first law of thermodynamics state?
Who stated the first law of thermodynamics?
Can the first law of thermodynamics be violated?
Why is the first law of thermodynamics important to the environment?
What are the limitations of the first law of thermodynamics
Stay tuned with BYJU’S for more such interesting articles. Also, register to “BYJU’S – The Learning App” for loads of interactive, engaging Physics-related videos and unlimited academic assistance.

it is important notes