We know that the conduction of heat takes place when the molecules of matter vibrate. Heat energy is transferred from a higher temperature area to a lower one. This process abides by Fourier’s law. Let us understand Fourier’s law through the article below. Fourier’s law is also called the law of thermal conduction equations or the law of thermal conductivity.
|
Table of Contents: |
What Is Fourier’s Law?
Fourier’s law states that the negative gradient of temperature and the time rate of heat transfer is proportional to the area at right angles of that gradient through which the heat flows. Fourier’s law is the other name of the law of heat conduction.
Newton’s law of cooling and Ohm’s law are a discrete and electrical analog of Fourier’s law.
Differential Form Of Fourier’s Law
Fourier’s law differential form is as follows:
\(\begin{array}{l}q=-k\bigtriangledown T\end{array} \) |
Where,
- q is the local heat flux density in W.m2
- k is the conductivity of the material in W.m-1.K-1
- ▽T is the temperature gradient in K.m-1
In one-dimensional form:
\(\begin{array}{l}q_{x}=-k\frac{\mathrm{d} T}{\mathrm{d} x}\end{array} \) |
Integral form
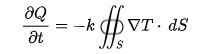
Where,
- \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{\partial Q}{\partial t}\end{array} \)is the amount of heat transferred per unit time
- dS is the surface area element
When the same equation is given in the differential form, which is the basis of heat equation derivation:
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{Q}{\bigtriangleup t}=-kA(\frac{\bigtriangleup T}{\bigtriangleup x})\end{array} \) |
Where,
- A is the area of the cross-sectional surface
- ΔT is the temperature difference between the endpoints
- Δx is the distance between two ends
Fourier’s law in terms of conductance
\(\begin{array}{l}\frac{\bigtriangleup Q}{\bigtriangleup t}=UA(-\bigtriangleup T)\end{array} \) |
Where,
- U is the conductance
Fourier’s Law Derivation
The derivation of Fourier’s law was explained with the help of an experiment which explained the Rate of heat transfer through a plane layer is proportional to the temperature gradient across the layer and heat transfer area.
Let T1 and T2 be the temperature difference across a small distance Δx of area A. k is the conductivity of the material. Therefore, in one dimensional, the following is the equation used:
When Δx → 0, the following is the equation in a reduced form to a differential form:
The three-dimensional form the Fourier’s law is given as:
Related Physics laws:
| Sound Waves | Ampere |
| Power of a Lens & Ray Optics | Force |

Comments