What is Artificial Sweetener (Sweetening Agents)?
Natural sweeteners like sucrose and fructose give sweetness to a substance, but they also contain calories which can be harmful to humans when taken in extra quantities.
Artificial sweeteners are substances that are used as substitutes for natural sugar (sucrose), they contain low calories. They are many times sweeter than regular sugar, so they are also referred to as intense sweeteners.
Table of Contents
- Sweetening Agents
- How does an Artificial Sweetening agent work?
- Common Artificial Sweetener
- Advantages of Artificial Sweeteners
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Sweetening agent
Some of them are so sweet that dextrose or maltodextrin is added to reduce the intense sweetness of artificial sweetening agents. These sweetening agents are generally obtained from the substitutes of synthetic sugar, but they can also be formed from natural substances, including herbs or sugar itself.
Artificial sweetener is one of the most attractive substitutes for sugar as it does not add many calories to our diet. It can be used directly in processed food such as puddings, dairy products, candy, soft drinks, baked goods, jams and many other foods and beverages. It can also be used after mixing it with starch-based sweeteners.
How does an artificial sweetening agent work?
For a sweetening agent to work properly, a sweetener should be soluble in water and it should readily bind with a receptor molecule present on the surface of the tongue. The receptor is actually connected with a G- protein and when the sweetener binds with the receptor, the G- protein starts dissociating which in turn activates a nearby enzyme and triggers a sequence of events in which the signals are transmitted to and are interpreted by the brain. The interaction between the receptor and sweetener accounts for the sweetness of an artificial sweetening agent.
Common Artificial Sweetener
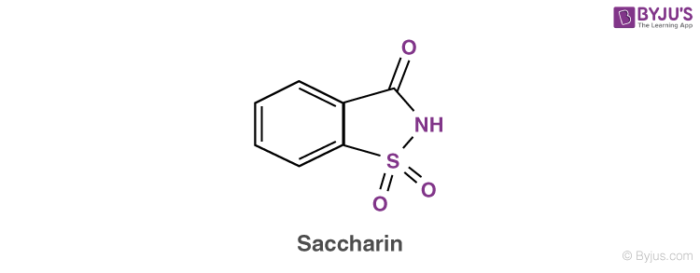
- Saccharin: It was discovered in 1879 and is considered the oldest non-nutritive sweetener. Sucrose is about 300 times less sweet than saccharin, but it has a bitter aftertaste. It cannot be used in products where baking of food is necessary as it becomes unstable when it is heated. But it can be used to sweeten candies, drinks, and toothpaste.
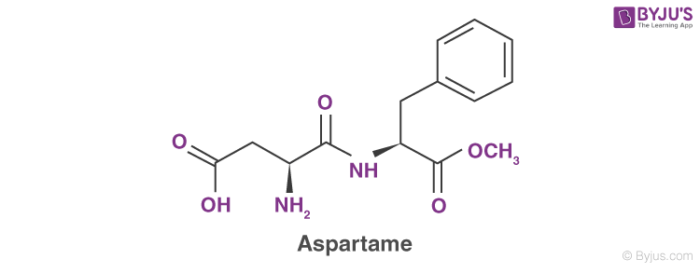
- Aspartame: In 1879 Aspartame was discovered and it was found that it is approximately 200 times sweeter than sugar. It is a dipeptide methyl ester and its name is aspartyl phenylalanine-1-methyl ester. It is commonly used as a tabletop sweetener and is also used in a variety of foods. When it is heated it breaks down into amino acids and loses its sweetness, so it cannot be used for baked foods. As it becomes unstable at cooking temperature, it is only used in soft drinks and cold foods.
Advantages of Artificial Sweeteners
- Weight Control: If someone wants to lose weight, then they should use an artificial sweetening agent as virtually it carries zero calories. One gram of sugar carries 4 calories, and one teaspoon of sugar contains about 4 grams of sugar. So by eating 1 teaspoon also we gain 16 calories. So in the case of weight control, an artificial sweetening agent is the best option.
- Diabetes: It also helps in controlling diabetes as it does not raise the blood sugar levels because it does not contain the carbohydrates in it.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Why artificial sweeteners are bad for you?
The subject of heated debate is always artificial sweeteners. They are said to increase the risk of cancer, on the one hand, and damage your blood sugar and intestinal health. On the other hand, they are considered healthy by most health officials, and many individuals use them to decrease their sugar consumption and lose weight.
What is the healthiest sugar substitute?
The most nutritious alternative is possibly stevia, followed by xylitol, erythritol, and yacon syrup. Natural sugars, such as maple syrup, molasses, and honey, are less unhealthy and also have health advantages over normal sugar.
What is the least harmful artificial sweetener?
Erythritol, xylitol, stevia leaf extracts and neotame are the easiest and healthier sugar alternatives, with a few caveats: Erythritol: Huge doses of this sugar alcohol (more than about 40 or 50 grams or 10 or 12 teaspoons) often induce nausea, however, smaller quantities are okay.
Is aspartame harmful to the body?
No serious health issues, other than for individuals with phenylketonuria (PKU), have been conclusively identified with aspartame. This is an unusual genetic condition (present at birth) in which phenylalanine, an amino acid that is found in many foods (and in aspartame), can not be broken down by the body.
Does aspartame cause inflammation?
Artificial ingredients can not be processed well by your body, so substances such as aspartame and mono-sodium glutamate can cause an immune response. Aspartame is a neurotoxin that is mostly “attacked” by the body, thereby causing inflammation.

It’s quite helpful.