Malonic Acid
Malonic acid is a dicarboxylic acid with the chemical formula C3H4O4. Dicarboxylic acids are organic compounds containing two carboxylic acid functional groups. Dicarboxylic acids generally show the same chemical behaviour and reactivity as monocarboxylic acids. Malonic acid is a substance found in some fruits that occurs naturally. Fruits generated in organic farming contain greater concentrations of malonic acid in citrus compared to fruits generated in conventional farming.
The IUPAC name of malonic acid is propanedioic acid. Malonic acid is the archetypal instance of a competitive inhibitor: it functions in the respiratory electron transport chain against succinate dehydrogenase. Malonic acid is correlated with deficiency of malonyl-CoA decarboxylase, an inborn metabolism mistake.
Table of contents
- What Is Malonic Acid?
- Structure Of Malonic Acid
- Properties Of Malonic Acid – C3H4O4
- Synthesis Of Malonic Acid
- Uses Of Malonic Acid
- Health Risk Of Malonic Acid
- FAQs
What is Malonic acid?
Malonic acid is also known as Propanedioic acid or Dicarboxymethane. The name is derived from the Greek word Malon which means apple. Malonate is the ionized form of malonic acid, along with its esters and salt. It appears as a white crystal or crystalline powder. It dissolves in alcohol, pyridine, and ether.
Malonic acid was first prepared in the year, 1858 by the French chemist Victor Dessaignes by the oxidation of malic acid. Malonic acid is found in some fruits viz citrus fruits. Malonic acid can be produced through the fermentation of glucose.
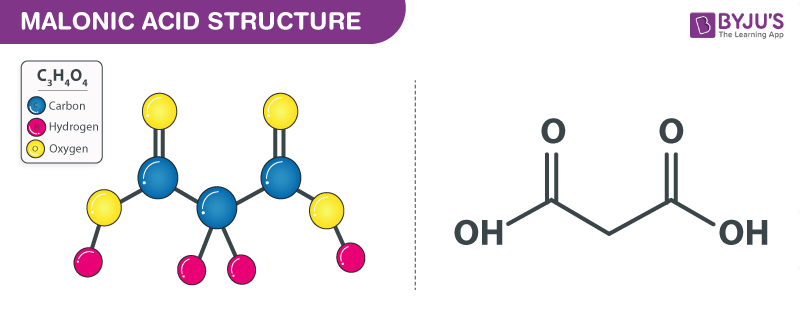
Malonic acid Structure – C3H4O4
Properties of Malonic acid – C3H4O4
| C3H4O4 | Malonic acid |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 104.061 g/mol |
| Density | 1.619 g/cm³ |
| Boiling Point | Decomposes |
| Melting Point | 135 to 137°C |
Malonic acid Synthesis – C3H4O4
Preparation of malonic acid starts with chloroacetic acid which is also known as MCA (monochloroacetic acid).
Step 1: Sodium carbonate produces sodium salt.
Step 2: It is made to react with sodium cyanide.
Step 3: cyanoacetic acid salt is generated through nucleophilic substitution.
Step 4: The nitrile group is hydrolyzed with sodium hydroxide to produce sodium malonate.
Step 5: The acidification results in malonic acid.

Industrially, malonic acid is produced by the hydrolysis of diethyl malonate or dimethyl malonate. Malonic acid is a forerunner to polyester specialities. Malonic acid is used to generate countless useful compounds as a construction block chemical.
Uses of Malonic acid – (C3H4O4)
The uses of malonic acid are listed below.
- Malonic acid is used as a precursor in polymers and polyester.
- It is used in flavours as well as in the fragrance industry.
- It is used to control acidity.
- It is used in pharmaceutical products.
- It is used as a cross-linking agent between potato starch and cornstarch to enhance its mechanical properties.
- It is used in the preparation of barbituric salt.
- It is used in electroplating.
- It is used to produce vitamin B1, vitamin B6, vitamin B2, and amino acids.
- It is used in chemical synthesis as a building block.
Malonic acid Health Risks
- It is a strong irritant and is harmful when inhaled, ingested or absorbed by the skin leading to skin damage and damage to mucous membranes.One has to consult doctor if breathing difficulty is observed
- A few laboratory animal toxicity studies of malonic acid are done but the studies are insufficient to define extra health impacts.
Frequently Asked Questions- FAQs
What happens when malonic acid is heated?
On heating malonic acid, acetic acid and carbon dioxide are produced.
Is malonic acid strong?
Malonic acid is a diprotic acid. pKa1 is 2.83, and pKa2 is 5.69 . Higher the pka value, weaker will be the acid. So that the malonic acid is a medium- strong acid.
What is the source of malonic acid?
Malonic acid is found in many fruits and vegetables. The calcium salt of malonic acid occurs in high concentrations in beetroot.
What is malonic acid soluble in?
Malonic acid is soluble in water. It is a polar molecule which forms H+ ion in an aqueous solution. It is also soluble in methyl alcohol but insoluble in hexane.
Is malonic acid optically active?
Malonic acid does not have any chiral center, so it does not exhibit optical isomerism.


Comments