Natural resources are materials found in nature that cannot be completely depleted. Natural resources can be used for a variety of purposes, the most important of which is energy production.
Natural resources are naturally occurring materials that are useful to man or could be useful in conceivable technological, economic, or social circumstances, as well as supplies are drawn from the earth, such as food, building and clothing materials, fertilisers, metals, water, and geothermal power. Natural resources have long been the domain of the natural sciences.
|
Definition: Natural resources are resources that exist (on the planet) independently of human activity. These are resources found in the environment and developed without the intervention of humans. Air, sunlight, water, soil, stone, plants, animals, and fossil fuels are all examples of natural resources. |
Natural Resources Chemistry Questions with Solutions
Q1. What is the best benefit of wind power?
a) Some say it is an eyesore
b) Some say it hurts birds and bats
c) It creates electricity that is safe for the environment
d) It takes up too much space
Correct Answer. (c) It creates electricity that is safe for the environment
Q2. What 2 gases produce acid rain?
a) Nitrogen and sulfur
b) Sulfur and magnesium
c) Magnesium and nitrogen
d) Nitrogen and oxygen
Correct Answer. (a) Nitrogen and sulfur
Q3. What is a source of energy that is formed from the remains of plants and animals that lived millions of years ago?
a) Solar Power
b) Hydroelectricity
c) Biofuels
d) Fossil Fuels
Correct Answer. (d) Fossil Fuels
Q4. How can lichen help in indicating the pollutants in air?
Answer. Since lichens are sensitive to sulphur dioxide (SO2) and do not grow in polluted areas, they are regarded as pollution indicators. Their presence indicates that an area is free of pollution, while their absence indicates that the area is polluted.
Q5. What is bad ozone and good ozone?
Answer. When present on Earth’s surface, ozone is a highly toxic gas. As a result, it is referred to as “bad ozone.” When present in the stratosphere, ozone is extremely protective because it prevents harmful ultraviolet rays from entering the Earth’s atmosphere. As a result, it is known as good ozone.
Q6. Explain overgrazing. What are the changes caused due to overgrazing?
Answer. Overgrazing is the process of consuming forests without allowing them to regenerate. Overgrazing causes biodiversity loss, mineral loss, soil erosion, and desertification.
Q7. Give existence of carbon.
Answer. Carbon exists in two states: free and combined.
- Carbon occurs free in nature in two forms: crystalline i.e. crystal form, as seen in diamond and graphite, and amorphous impure form, as coal formed beneath the earth’s crust.
- Carbon exists in the atmosphere as carbon dioxide (about 0.03 % by volume). It can also be found in natural gas and petroleum as hydrocarbons. In the solid-state, it can be found in wood (as cellulose), plants and animals as carbohydrates, and minerals such as limestone (CaCO3).
Q8. How does oxygen occur in nature?
Answer. In nature, oxygen exists in two forms. These forms are found in the earth’s crust, atmosphere, and water as oxygen gas (21%), and in combined form as oxides of metals and nonmetals. It can also be found in carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
Q9. What is air pollution? How it is caused? Give any two harmful effects.
Answer. Air pollution is the contamination of air with unwanted substances that can harm both living and non-living things.
Air pollution causes include:
- The combustion of fossil fuels emits O2, CO2, and NO2 gases, which contribute to acid rain. They also emit smoke and unburned carbon particles.
- Air pollution is also caused by chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) emitted by refrigerators, air conditioners, and aerosol sprays.
- Smoke from factories.
Air pollution is harmful because-
- It causes respiratory problems.
- Allergies, cancer, and heart disease are all caused as a result.
- Acid rain is also caused by air pollution.
Q10. Explain the oxygen cycle in nature.
Answer. The oxygen cycle is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the movement of oxygen within three major reservoirs: the atmosphere (air), the total content of biological matter within the biosphere (the global sum of all ecosystems), and the lithosphere (Earth’s crust). Failures in the oxygen cycle within the hydrosphere (the combined mass of water found on, beneath, and above the Earth’s surface) can result in the formation of hypoxic zones. Photosynthesis, which is responsible for the modern Earth’s atmosphere and life on Earth, is the primary driving force of the oxygen cycle.
Q11. What is humus?
Answer. Humus is a dark, organic material formed in soil by the decay of plant and animal matter.
Plants drop leaves, twigs, and other material to the ground, which accumulates. This substance is known as leaf litter. When animals die, their skeletons are added to the litter. All of this litter decomposes over time. This means that it degrades or decomposes into its most basic chemical elements. Many of these chemicals are essential nutrients for soil and organisms that rely on soil for survival, such as plants.
Q12. Write a note on how forests influence the quality of our air, soil and water resources.
Answer. Forests have the following effects on the quality of air, soil, and water resources:
- The role of forests in controlling air quality:
(a) Forests help to prevent the greenhouse effect and global warming.
(b) Forests increase the rate of photosynthesis in surrounding plants.
(c) Some trees are capable of absorbing harmful gases in the atmosphere.
- Forest influence on soil quality:
(a) The roots of massive trees prevent topsoil erosion.
(b) Forests also play a role in regulating biogeochemical cycles.
(c) Many decomposing bacteria and nitrogen-fixing bacteria live in close proximity to tree roots.
- (iii) The role of forests in water quality control:
(a) Forests aid in the return of pure water to the earth’s surface through rains.
(b) Forests contribute to the preservation of the water cycle and the earth’s water resources.
Q13. List any three human activities which would lead to an increase in the carbon dioxide content of air.
Answer. Three human activities that would result in an increase in the CO2 content of the air are as follows:
- Respiration is the natural process by which plants and animals release CO2. However, this release is neither dangerous nor harmful to our environment.
- Fuel combustion: Different types of fuels are burned to provide energy for various –, needs such as heating, cooking, transportation, and industrial fuels.
- Deforestation: Through the process of photosynthesis, trees aid in the conversion of CO2 into organic compounds such as glucose, starch, and others. When these trees are cut down irresponsibly, the level of CO2 in our environment rises.
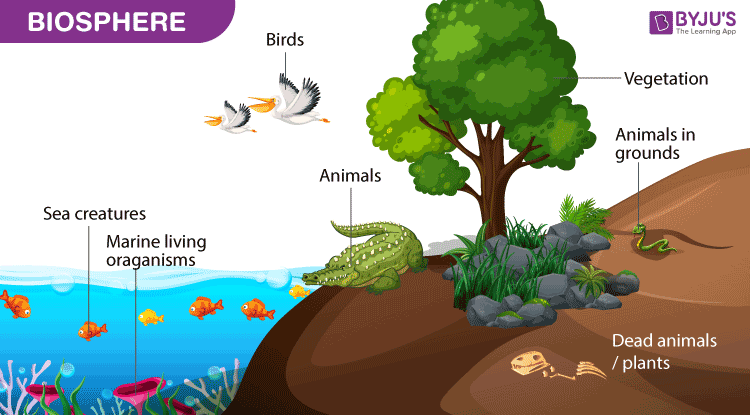
Q14. Explain the biosphere.
Answer. The biosphere, which includes both the ground and the atmosphere, is defined as the area of the planet where organisms live. The biosphere is defined as the region of the Earth’s surface where life exists on, above, and below the surface.
The biosphere is a narrow zone on the earth’s surface where soil, water, and air come together to support life. Only in this zone can life exist. There are many different types of life, ranging from fungi and bacteria to large animals.
The biosphere is defined as an area that contains all living organisms and their byproducts. As a result, it is critical for ecosystem maintenance, and the biosphere is critical for climate regulation.
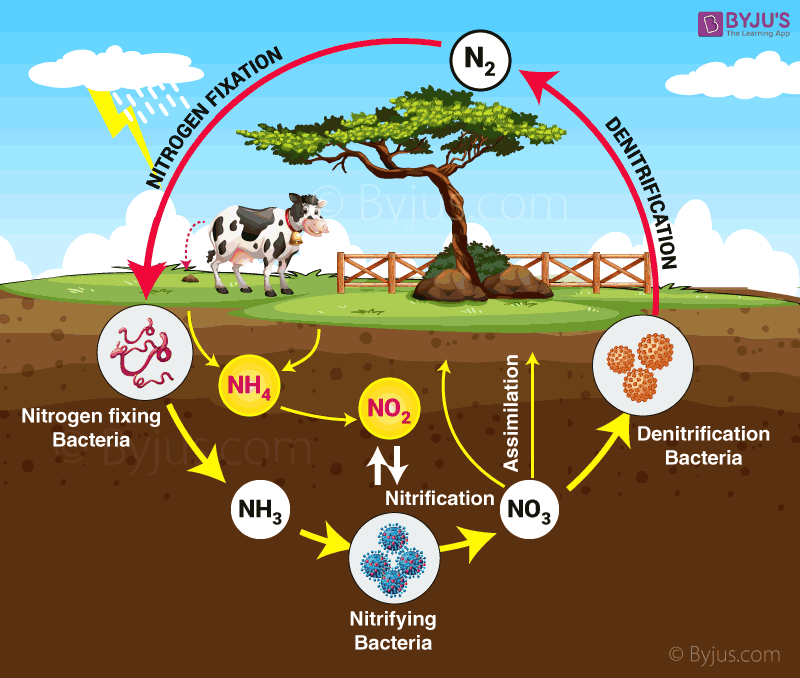
Q15. Explain the nitrogen cycle in detail and define all the terms involved in it.
Answer. Nitrogen cycle:
- Bacteria or lightning convert free nitrogen from the atmosphere into nitrates.
- Nitrates combine with soil and are absorbed by plants to produce proteins.
- Plant and animal proteins are converted into amino acids and ammonia.
- Ammonia is converted into nitrates, and these nitrates and nitrites in the soil are then acted upon by another group of bacteria known as denitrifying bacteria. Denitrification is the process by which nitrates are converted into free nitrogen and released back into the atmosphere.
The nitrogen cycle is comprised of the following terms:
1. Nitrogen fixation: Plants cannot use free nitrogen present in the air. This nitrogen molecule is broken down into nitrates and nitrites, which can then be taken up and used to create the necessary molecule. This is known as nitrogen fixation, and it can be accomplished by bacteria that live in the root nodules of leguminous plants. During the physical process of lightning, high temperatures and pressures are created in the air, converting nitrogen into oxides of nitrogen, which dissolve in water and fall as rain. This is also known as nitrification.
2. Ammonization Plants use the nitrogen compounds formed to form proteins, which are then converted into ammonia.
3. Nitrification Nitrogen nitrates and nitrites are acted upon by other microbes, such as Pseudomonas bacteria, which convert these compounds into free nitrogen gas.
Practise Questions on Natural Resources
Q1. To reuse something means what?
a) To use over and over
b) To use less of
c) To make into something new
d) To throw away
Q2. The micro-organisms which help in the formation of soil is-
a) Bacteria
b) Moss
c) Lichen
d) b and c
Q3. State the reasons for overexploitation of forests.
Q4. List any three human activities that you think would lead to air pollution.
Q5. Explain why is there a change in the wind direction in coastal areas during the day and at night.
Click the PDF to check the answers for Practice Questions.
Download PDF
Formation of Soil

Conservation of Natural Resources

Comments