What are Oxoacids?
If the acid contains oxygen (called an oxoacid), then the suffixes –ous and –ic can be used which represent the lower and higher number of oxygens in the acid formula. Oxoacids contain hydrogen, oxygen, and other elements Acids that contain hydrogen, oxygen, plus another element are called oxoacids.
Table of Contents
- Oxoacids of Halogens
- Suggested Videos
- Properties of Halogen Oxoacids
- Structures of the Oxoacids of Halogens
Oxoacids of Halogens
This topic explains the Oxoacids of the Halogen Family. Group 17 includes fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine. They are collectively known as halogens, meaning salt producers. The members of this group highly resemble each other. There is a regular gradation in physical and chemical properties as we move down the group.
Astatine is the only radioactive element in the group. There are seven electrons in their valence shell (ns2np5), one electron short from the nearest noble gas configuration. Halogens have a small size due to their effective nuclear charge.
Hence, they do not have a tendency to lose electrons, rather they readily gain an electron to complete their octet. Halogens form several oxoacids (they are acids which contain oxygen in the acidic group).
Suggested Videos
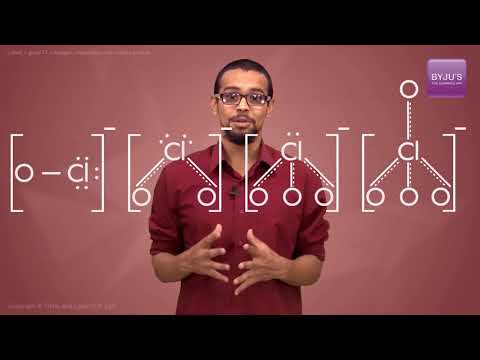
Properties of Halogen Oxoacids
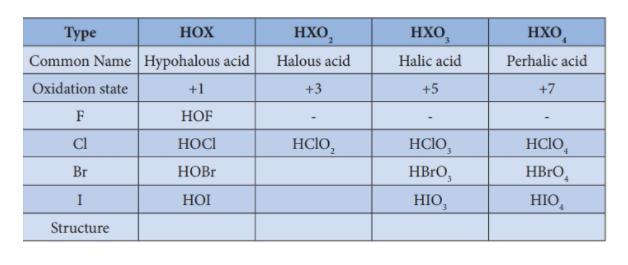
Fluorine has a very small size and high electronegativity. Therefore, it forms only one oxoacid, HOF which is known as fluoric(I) acid or hypofluorous acid. The other elements of the halogen family form several oxoacids. They cannot be isolated in a pure state. They are stable in an aqueous solution or in the form of salts.
Halogens generally form four series of oxoacids namely hypohalous acids (+1 oxidation state), halous acids (+3 oxidation state), halic acids (+5 oxidation state) and perhalic acids (+7 oxidation state).
- Chlorine forms four types of oxoacids. That is HOCl (hypochlorous acid), HOClO (chlorous acid), HOClO2(chloric acid) and lastly HOClO3 (perchloric acid).
- Bromine forms HOBr (hypobromous acid), HOBrO2(bromic acid) and HOBrO3 (perbromic acid). Iodine forms HOI (hypoiodous acid), HOIO2 (iodic acid) and HOIO3 (periodic acid).
Structures of the Oxoacids of Halogens
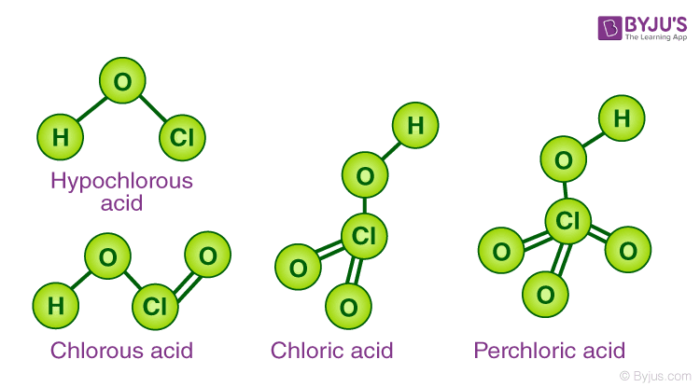
The central atom in the oxoacids is sp3 hybridized. Every oxoacid has essentially one X-OH bond. Whereas most oxoacids have X=O bonds present in them. This double bond between oxygen and halogen is d pi-pi in nature. In the series of oxoacids, the first member possesses high acidic strength. This is only due to the high electronegativity and small size of the halogen atom. The acidic strength increases with an increase in the oxidation number of halogens.
This article explains the oxoacids of halogens. For any further detail on this topic please install BYJU’S the learning app.

Comments