A reverberatory furnace is a furnace that is mainly used for the extraction of tin, copper, aluminium and nickel metals as well as in the production of certain concretes and cements. The furnace is mostly used for smelting and refining these materials.
History
The early record of the reverberatory furnaces being used is in the medieval period mainly for melting bronze. In the late 17th century they were largely used for smelting of copper and lead. However, with each passing decade, the construction materials changed yielding better production capacities and the furnace was used for smelting a number of metals apart from just copper.
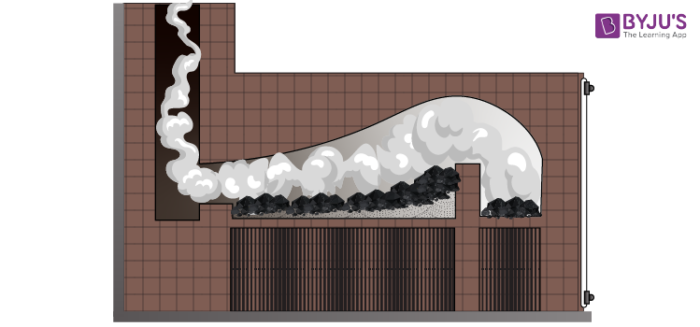
Construction And Operation
Today, the reverberatory furnace mostly consists of a rectangular steel box which is lined with castables processing non-wetting properties or refractory bricks. There is a vertically lifting door at one end and burners are placed usually on the other side of the furnace. Opposite the burners, there is a pouring spout and the exhaust gas duct. Roofs are also made of the same refractory brick which is durable and it further helps generate higher temperatures which lead to faster refining. However, as new technological innovations continue to be forged, they are changing and improving not only the basic construction materials but also the production capacity of this furnace.
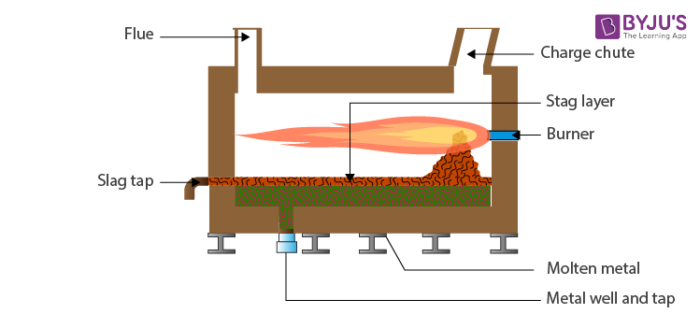
As for the operation, in a reverberatory furnace, heat is generally passed over the hearth which consists the ore mixture. The main method of heat transfer is through the radiation from the refractory bricks present in the walls and the roof. Additional heating is supplied from the burner to the ore. The roof of the furnace is also slightly arched and remains slanted towards the bridge of flues that deflects the flame for reverberation. The mixture is heated constantly until it melts. Meanwhile, the molten impure metal is collected in the hearth which is thick and made of a strong material that can also resist any disintegration by the slag. The process is repeated in the furnace until the ore concentrate is tapped at regular intervals. The collected material is then sent to a converter for further refinement.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Some prominent advantages of a reverberatory furnace are a high volume processing rate and low operating as well as maintenance costs. Whereas, the disadvantages include low efficiencies, high metal oxidation rates and usually a large space required.
How Is It Different From Blast Furnace?
We have already read that in a reverberatory furnace, the fuel apart from combustion gauges is actually separated from the material being processed. Here heat is supplied via convection of hot gases as well as reflection from the roof and sides of the furnace which are made of refractory bricks. However, when a blast furnace is there is no separation of the burning fuel (coke) and the subject material.

good