The transition metals combine to form a large number of complex compounds in which metal atoms are bound to a number of anions or neutral molecules via electron sharing. Such compounds are known as coordination compounds in modern parlance. Coordination compound chemistry is an important and challenging area of modern inorganic chemistry.
Download Class 12 Chemistry Worksheet on Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds Set 1 PDF
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds Worksheet – Set 1
Q-1: In the complex [M(acac)(en)2]Cl, the coordination number and oxidation state of the element ‘M’ are respectively
- 6 and 2
- 4 and 2
- 4 and 3
- 6 and 3
Q-2: An example of double salt is
- Carnallite
- Potassium Ferricyanide
- Cuprammonium nitrate
- triglycinatocobalt(III)
Q-3: The characteristics shared by the species CN–, CO, and NO+ are
- Isoelectronic
- Bond order three
- All are sigma donor and pi acceptor
- All of these
Q-4: Which of the following is a didentate ligand?
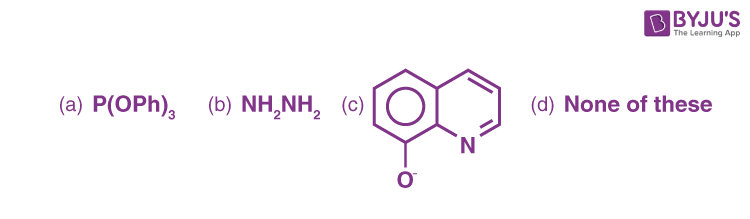
Q-5: Which of the following cannot act as a chelating agent?
- HC(CH2CH2NH2)3
- CH3NHCH2CH2CH3
- N(CH2CH2NH2)3
- H2NCH2CH2CH2NH2
Q-6: Which one of the following compounds will exhibit linkage isomerism?
- [Pt(NH3)2Cl NO2]
- [Co (NH3)2 NO2 ]Cl2
- [Co (NH3)4Cl2]Cl
- [Co (en)2Cl2]Cl
Q-7: Give the IUPAC name of the complex compound [Co(NH3)4 (H2O)Br](NO3)2
Q-8: The primary valency of Ag in Na3[Ag(S2O3)2] is
- +2
- -2
- 0
- +1
Q-9:Transition metal complexes’ CFSE can be calculated using
- Spectroscopy of UV-visible light
- Spectroscopy in the infrared
- Spectroscopy by NMR
- Spectroscopy of microwaves
Q-10: What is the order of magnitude of Δo values for Cr(III) octahedral complexes with sigma donor, pi donor, and pi acceptor ligands?
Q-11: Calculate the spin only magnetic moment of the compound Hg[Co(SCN)4].
Q-12: How many electrons are present in the eg set of d-orbital of sodium nitroprusside complex?
Q-13: When bis(ethane-1,2-diamine) copper (II) sulphate is dissolved in water, calculate the number of ions formed.
Q-14: a) Identify the dark blue complex formed when [Fe(CN)6]3- is treated with ferrous sulphate and account for the origin of its colour.
b) What is the common name for the formed complex?
Q-15: A coordination compound is made up of one Co(III), one chloride, one sulphate, and four ammonia molecules. When combined with aqueous BaCl2, the compound’s aqueous solution yields no precipitate, whereas a precipitate is formed when combined with aqueous AgNO3 solution. Draw its structure and use chemical equations to explain the observations.
Q-16: Define the following:
- Heteroleptic complex:
- Coordination Isomerism
Q-17: List two limitations of CFT.
Q-18: What is the synergic effect? How does it improve the bond between CO and metal?
Q-19: How will you account for ruby’s red colour?
Q-20: When potassium oxalate solution is added to a hot solution of potassium dichromate containing dilute sulfuric acid, effervescence occurs and potassium trisoxalatochromate(III) is formed.
i) Write the chemical formula of the formed chromium complex.
ii) Determine the complex’s room temperature spin only magnetic moment in B.M.
Download the PDF to access answers to the Chemistry Worksheet for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds Set -1.
Download PDF


Comments