Table of Contents
What are Cycloalkanes?
Different organic molecules of organic compounds have different properties based upon their structure such as the Cycloalkanes. Did you know about the body fat present in the human body and also some food and hair products are made up of these hydrocarbons? Hence, these organic compounds exist in all the day-to-day examples of life.
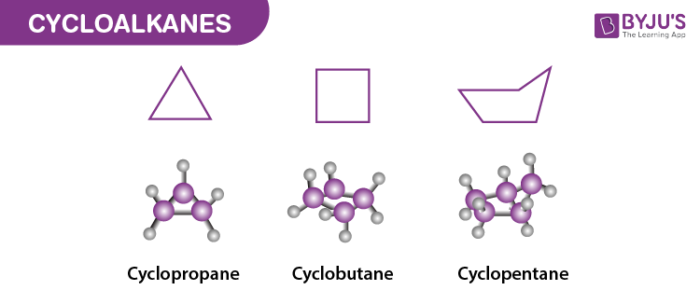
Cycloalkanes are the class of hydrocarbons having a ring-like structure. This ring is formed due to their saturated nature, and they have three compounds of alkane present in the structure which helps them in forming a ring. They have the general formula CnH2n ,Where n is said to be the number of carbon atoms present in the organic compound.
These consist of carbon-hydrogen bonds and also carbon to carbon single bonds where these carbon atoms join forming a ring or in the shape of a cyclic structure. Cyclopropane is considered to be one of the smallest cycloalkanes, and most of this class of members are said to be more stable in nature.
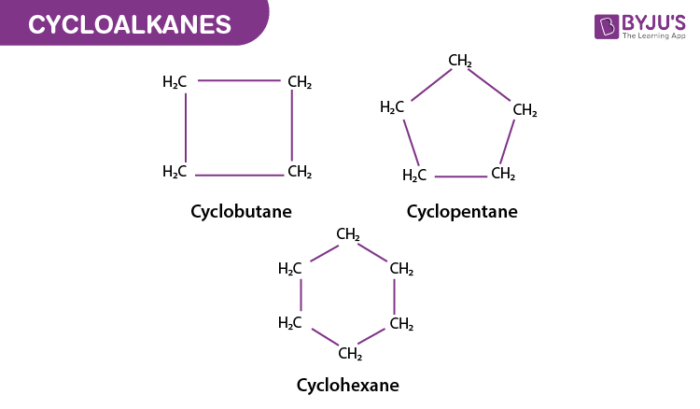
Some common examples of cycloalkanes are the cyclopentane, Cyclobutane, cyclohexane, and cycloheptane, cyclooctane, etc as shown below in the image. The number of carbon atoms present in the compound decides the structure of cycloalkane. For example, the saturated hydrocarbon with 4 numbers of carbon atoms is named Cyclobutane whereas the hydrocarbon with three carbon atoms present in the structure is given the name Cyclopropane.
Cycloalkanes- Properties
The various physical and chemical properties of Cycloalkanes are given below-
- The first four classes of cycloalkanes are said to be in gaseous state in the room temperature
- These saturated hydrocarbons are said to have their boiling points ranging between 10 – 20 K.
- These compounds are also reported exhibiting higher melting points and densities
- These are also called as saturated hydrocarbons since saturated compounds form ring structure
- Since the electronegativity between the carbon-hydrogen bonds is found to be too less for these compounds, they are said to be not having any polarity between the bonds.
- This class of saturated hydrocarbons is said to be insoluble in water, and the cycloalkanes in liquid form are said to be the good form of solvents for other organic compounds.
- The molecule of cycloalkane gets destroyed when burned
- Cyclopropane is said to be the most reactive compound when compared to other cycloalkanes.
Common Uses
Some uses are given below-
- In the medical applications, cycloalkanes are used as an organic solvent in the production of drugs
- These are utilised in the manufacture of hair products as well as in the food industries
- The cycloalkane called cyclopropane is used as an anaesthetic agent in the medical field
- Carboplatin which is derived from the cyclobutane is used to treat cancers
- They are also employed in the petroleum industries.
- Some classes of cycloalkanes are used for pigmentation purposes and also used as fragrances in the perfume manufacturing sector.
- Some of these saturated hydrocarbons are found in the tissues of plants and animals as steroids.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is a Cycloalkane in chemistry?
In organic chemistry, the monocyclic saturated hydrocarbons are cycloalkanes (also called naphthenes, but different from naphthalene). Analogous to their usual alkane equivalents, cycloalkanes have the same carbon count: cyclopropane, cyclobutane, cyclopentane, cyclohexane, etc.
Is benzene a Cycloalkene?
Ringed structures called cyclic hydrocarbons may be formed by hydrocarbons. Since they have the least ring pressure, cyclopentane and cyclohexane are the most popular cycloalkanes. Benzene has a ring of delocalized electrons, which gives the structure extra stability.
How do you count Cycloalkanes?
Cycloalkane numbering a When a cycloalkane’s carbons are counted, begin with a substituted carbon such that the lowest numbers (sum) are available for the substituted carbons. b. Number by alphabetical order, whether two or more related substituents are present.
Why is Benzene not called hexene?
Benzene is a molecule with a ring, but hexene is a chain. Alternative carbons in benzene have double bonds, but only one double bond is found in hexene. The benzene molecular formula is C6H6, but C6H12 is hexene.
Does benzene have double bonds?
We would imagine benzene to have reactions like ethene because of the three double bonds – just more so! Ethene undergoes further reactions in which the electrons are used to bind with additional atoms and one of the two bonds connecting the carbon atoms breaks.

Comments