What is a catalyst and what is catalysis?
Catalysts, by their definition, is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without changing themselves. The process by which a catalyst increases the rate of reaction is termed catalysis.
How do catalysts work?
For reactants to react and give a product the reactant molecules must have threshold energy and the number of molecules with this energy should also be above a threshold value. This particular energy is called Activation Energy. Only those molecules from the reactants will be able to form products that have energy above activation energy.
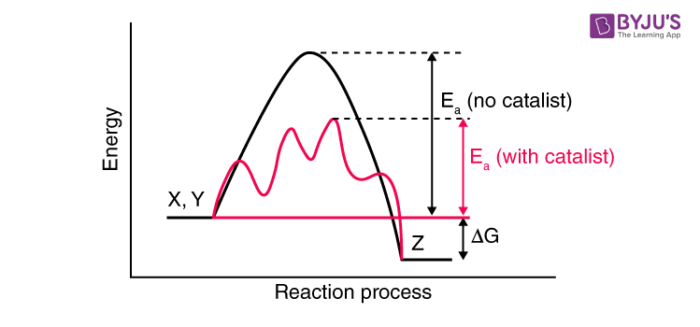
They alter this activation energy or provide a different reaction mechanism that has a requirement of lower activation energy to give products. The role of a catalyst in chemical reactions is best explained by intermediate-complex theory. According to intermediate-complex theory, it brings down the activation energy for a reaction or provides a different pathway for the reaction where activation energy is lower. It makes temporary bonds with the reactant molecules to form an intermediate complex. This intermediate complex then decomposes to give the products and the catalyst. The catalyst remains the same before and after the reaction. No change (chemical) is observed in them.
A catalyst can catalyze only spontaneous reactions as it cannot alter the Gibbs Free Energy, ΔG, and hence cannot catalyze a non-spontaneous reaction. A catalyst always increases the rate of a reaction; any substance that reduces the rate of a reaction is called an inhibitor. It has been observed that a catalyst does not change the equilibrium constant for a reaction but rather accelerates backwards as well as the forward reaction to attain equilibrium fast. A catalyst catalyzes the forward as well as the backward reaction to the same extent and hence the equilibrium point remains the same and is attained fast as compared to the reaction without it.
Conditions for catalysis:
Catalysts are highly efficient substances; a small amount of catalyst can catalyze a large number of reactants through catalysis. It is therefore important for the process designers to have ample information about the catalysts and the role they play in altering the reaction rates of various reactions. Catalysts have revolutionized the manufacturing industry. Most industries involved in manufacturing products and commodities use catalysts to reduce production costs and improve the rate of production. Even our body has various types of catalysts that play an important role in chemical reactions that occur inside our body, these are called enzymes. Catalysts play a very important role in today’s world and hence having some knowledge about them will always be helpful.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
How can a positive catalyst alter the reaction?
What is the role of catalyst poison in Rosenmund reaction?
What are the key factors in heterogeneous catalysis?
– Adsorption of reactant molecules activation centre.
– Formation of activation complex at the centre.
– This complex decomposes to give products.
– Desorption of products from the surface of the catalyst.
What is the role of promoters in Haber’s process?
What is the significance of autocatalysis?
To know more about catalysts and catalysis, register with BYJU’S.

Comments