What is Acetylsalicylic acid?
Acetylsalicylic acid commonly known as Aspirin is a prototypical analgesic with the chemical formula C9H8O4.
It is also known as aspirin or 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid. It appears as a crystalline powder which is colourless to white. Generally, it has no smell but when in moist air it acquires a smell of acetic acid. It has a flashpoint of 482° F. It is most widely used in medication to treat pain, inflammation, and fever.
Aspirin is one of the safest and most effective medicines and is an extensively used medication globally, which is displayed on the WHO’s List of Essential Medicines.
Table of Content
- Structure of Aspirin /Acetylsalicylic acid
- Properties of Aspirin /Acetylsalicylic acid
- Synthesis of Aspirin/Acetylsalicylic acid
- Uses of Aspirin/Acetylsalicylic acid
- Health Risks Associated with Aspirin/Acetylsalicylic Acid
- FAQs
Acetylsalicylic Acid – C9H8O4
Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) is a potent, irreversible inhibitor of platelet aggregation but loses its action after first-pass deacetylation to salicylic acid ( SA). Acetylsalicylic acid was launched into the pharmacy industry more than 100 years ago. While initially conceived as an analgesic, doctors soon discovered that it had many other medicinal benefits. The German chemist Felix Hoffman entered the Bayer Pharmaceutical Company in 1894. In pursuit of a drug to ease the discomfort of his father’s arthritis, he looked again at Brugnatelli and Fontana’s salicin, which had been further modified by chemists to create pure salicylic acid.
By adding a buffer to the salicylic acid to produce acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), Hoffman developed a compound that was better tolerated and had fewer gastrointestinal side effects. In 1899, acetylsalicylic acid was released on the market and sold as “aspirin.”
Structure of Aspirin/Acetylsalicylic acid – C9H8O4
The structure of an acetylsalicylic acid molecule is illustrated below.
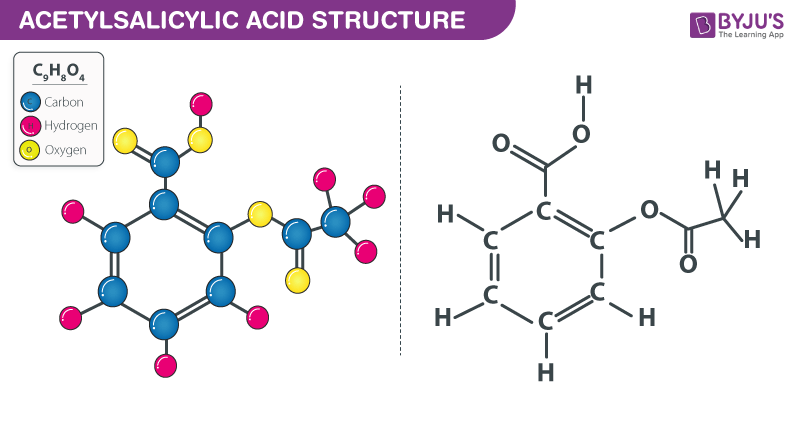
Acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin) – C₉H₈O₄
Properties of Aspirin/Acetylsalicylic acid – C9H8O4
| C9H8O4 | Acetylsalicylic acid |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 180.159 g/mol |
| Density | 1.40 g/cm³ |
| Boiling Point | 140°C |
| Melting Point | 136°C |
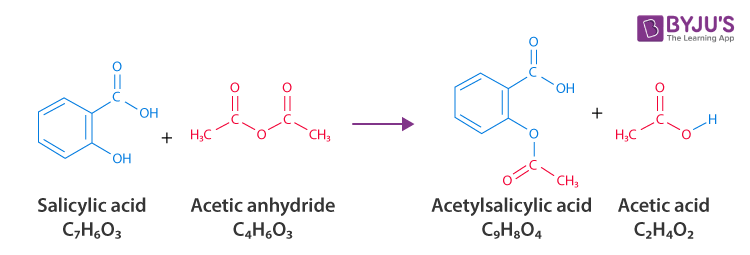
Synthesis of Aspirin/Acetylsalicylic acid (C9H8O4)
Step 1: Dry an Erlenmeyer flask and add 3 grams of salicylic acid to it.
Step 2: Put 5 to 8 drops of 85% phosphoric acid along with 6 mL of acetic anhydride into the flask.
Step 3: Mix the solution and keep the flask in warm water for 15 minutes.
Step 4: To the warm solution, add 20 drops of cold water dropwise. (this destroys the excess acetic anhydride)
Step 5: Keep the flask in an ice bath to cool the mixture as well as for speed crystallization.
Step 6: On completing the crystallization process, pour the mixture with the help of a Buckner funnel.
Step 7: Use ice-cold water to wash the crystals to minimize the loss of the product.
Step 8: To purify the product perform recrystallization. Put the crystals in 10 ml of ethanol. Stir the mixture to dissolve the crystals.
Step 9: 25ml of warm alcohol is poured into it and covered to form crystals as the solution cools. Once the crystallization process begins, keep the beaker in an ice bath for recrystallization.
Step 10: The contents of the beaker are poured out and suction filtration is applied.
Step 11: The excess water is removed from the crystals by keeping them on dry paper.
Step 12: To confirm acetylsalicylic acid, verify a melting point of 135°C.
- For detailed mechanism you may visit Mechanism of Acetylsalicylic acid
Uses of Aspirin/Acetylsalicylic acid-(C9H8O4)
- Acetylsalicylic acid acts as an inhibitor of cyclooxygenase.
- It is used to prevent venous and arterial thrombosis.
- It is used in the treatment of different types of headaches.
- It is used as an anti-inflammatory agent for long-term as well as acute inflammation.
- It is thought to reduce the overall risk of getting cancer, and dying from cancer.
- Aspirin is an important part of the treatment of those who have had a heart attack.
- It is a first-line treatment for the fever and joint pain symptoms of acute rheumatic fever.
Also read:
Health Risks Associated with Acetylsalicylic Acid
- Exposure pathways – Skin or eye contact, ingestion, and inhalation.
- Symptoms – Irritation in eyes, upper respiratory system, skin, increased blood clotting time, vomiting, and nausea.
- Aspirin, or acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is widely used as a pain relief for mild aches and pains and to alleviate fever. It is also an anti-inflammatory drug that can be used as a blood thinner.
- Aspirin is not typically recommended for children aged under 16 years, since it can raise the likelihood of Reye’s syndrome, which can arise with an infection, such as a cough, flu, or chickenpox. It may lead to permanent damage to the brain or death.
Practice Question
- Why is it necessary to wash aspirin with cold water?
- When acetic acid is added to the salicylic acid what happens to the OH group of the salicylic acid?
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is the use of acetylsalicylic acid?
Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) is used to treat discomfort, nausea, and swelling of various symptoms such as lower back and neck discomfort, measles, chronic colds, burns, menstrual pain, depression, migraines, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, sprains and strains, joint damage, toothache, shoulder pain and bursitis.
How does acetylsalicylic acid work?
In addition to chemically suppressing the body’s pain receptors, aspirin can also reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Aspirin helps to keep platelets in your blood from shrinking and clotting your arteries, thus reducing these dangers and increasing blood supply to the heart and brain.
What are the benefits of aspirin?
Aspirin or acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) is widely used as a pain relief for mild aches and discomfort and to alleviate fever. This is also an anti-inflammatory drug that can be used as a blood thinner. People with a high risk of blood clots, stroke, and heart disease can use aspirin at low doses in the long term.
What is aspirin’s chemical name?
Aspirin’s chemical name is 2-Acetoxybenzoic acid. Aspirin, a chemical called acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is widely used worldwide as an anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drug. Formula and structure: the molecular formula for acetylsalicylic acid is C9H8O4 and the expanded formula is CH3COOC6H4COOH.
Is acetylsalicylic acid soluble in ethanol?
Aspirin is soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, DMSO, and dimethylformamide, which are to be purged with inert gas. Aspirin solubility in these solvents is approximately 80, 41 and 30 mg/ml respectively.
What is acetylsalicylic acid used to treat?
Aspirin is used to alleviate fever and relieve mild to moderate discomfort from conditions such as stomach aches, toothaches, chronic colds and headaches. This may also be used to reduce discomfort and inflammation in conditions such as arthritis. Aspirin is known as a salicylate and a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
Who Cannot take aspirin?
Most people over 16 years of age can take aspirin safely. Nonetheless, aspirin is not suitable for certain individuals. Never give aspirin to a child younger than 16 years of age unless recommended by their doctor. There is a potential connection between aspirin and Reye Syndrome in infants.
How does aspirin work as an anticoagulant?
Anticoagulants such as heparin or warfarin (also called Coumadin) slow down the process of clotting your body. Antiplatelet medications, such as aspirin, prevent blood cells or platelets from folding together to form a clot. You may need daily blood checks to confirm how good the blood clots.
To learn more about the chemical reactions and structural details of Acetylsalicylic acid or aspirin (C9H8O4) from the expert faculties at BYJU’S register now!
Other important links:
| Salicylic acid | Types of Alcohols |


Comments