What is Borax?
Borax is a compound consisting of an elementary substance called boron, united with oxygen and soda.
Borax is also known as sodium borate, sodium tetraborate or disodium tetraborate is explained in this article. Borax is a soft, colourless compound of Boron and can be dissolved in water. The main forms of borax are anhydrous and decahydrate salt and sometimes pentahydrate salt. This article focuses on the formula and structure of borax.
In regions like California’s Death Valley, where the water drained and left behind mineral deposits, borax is frequently discovered in dry lake beds. Borax and boric acid share the same chemical composition and even share a similar appearance. Borax is frequently used for cleaning, although boric acid is mostly employed as a pesticide. Insects are killed by boric acid by attacking their neurological and digestive systems.
Table of Contents
Borax Chemical Formula
The most common form of borax is Borax decahydrate which has 4 Boron atoms, 17 oxygen atoms, 2 sodium atoms, and 20 hydrogen atoms. The chemical and molecular formula of Borax is by-
| Chemical Formula of Borax | Molecular Formula of Borax |
| Na2B4O7• 10H2O
or,
Na2B4O5(OH)4•8H2O |
H20B4Na2O17 |
Recommended Videos

Natural Sources of Borax
- Borax is naturally found in evaporite deposits which are produced by the recurrent evaporation of seasonal lakes.
- Naturally occurring borax is purified by recrystallization.
- Borax can also be synthesized from boron compounds.
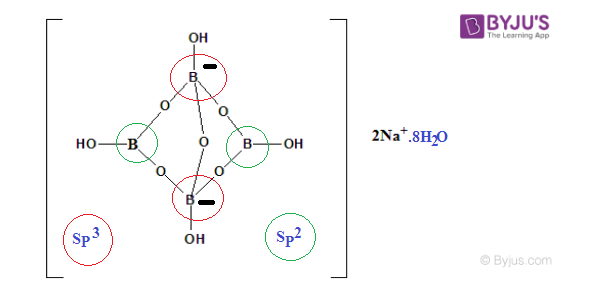
Borax Structural Formula
Borax Reaction
Borax is mainly used in laundry and other cleaning products. It is also used to prepare boric acid by reacting with hydrochloric acid, i.e. HCl. This process was first used by Wilhelm Homberg. Apart from this, borax is also used in the food, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries.
Borax reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce boric acid. The reaction is as follows:
Na2B4O7·10H2O + 2 HCl → 4 B(OH)3 + 2 NaCl + 5 H2O
Borax Reaction – Each of the sugar residues in the polymer has two hydroxyl groups positioned in the cis- form. This leads to an interesting and valuable reaction with dissociated borate ions that is characteristic of such polymers.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is Borax chemistry?
A major boron compound, a mineral, and a salt of boric acid is borax, also known as sodium borate, sodium tetraborate, or disodium tetraborate. Powdered borax, composed of soft, colourless crystals that readily dissolve in water, is white. Borax, sold commercially, is partly dehydrated.
Is Borax the same as baking soda?
Baking soda and borax are derivatives of numerous chemical compounds widely found. Borax is categorized as a white solid sodium borate, whereas baking soda is categorized as white crystal sodium bicarbonate.
What is Borax used for?
- Borax is mainly used in laundry and other cleaning products.
- Borax is also used in the food, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries.
Can Borax be used as a disinfectant?
Borax has many chemical characteristics that add to its cleaning ability. Borax and other borates clean and disinfect by converting some water molecules to hydrogen peroxide.
Is borax and boric powder the same?
Two different formulations of the same compound are Borax and Boric Acid. Borax is a mineral used in cleaning materials that is extracted straight from the earth (a type of the element Boron). The extracted, distilled and refined type of boric acid is used in a number of chemical products.
Is Borax safe for humans?
Borax can not be swallowed safely. Borax is quick for the body to break down when it is either inhaled or swallowed, according to the Toxicology Data Network of the NLM. However, both severe poisoning and organ injury will result if inhalation or absorption occurs.
Why is borax dangerous?
When penetration happens through the skin or eye touch, inhalation or swallowing, Borax can be irritating. Poison studies indicate that misuse of borax-based pesticides with symptoms such as vomiting, eye irritation, nausea, skin rash, oral irritation, and respiratory effects can result in acute toxicity.
To learn more about such chemistry topics, keep visiting BYJU’S.
Read more:

Thanks