What is Vaporization?
Vaporization can be defined as the process in which the liquid state changes into the vapour state. As a result of an increase in temperature, the kinetic energy of the molecules increases. Due to the increase in kinetic energy, the force of attraction between the molecules reduces. As a result, they escape into the surrounding in the form of vapours. This process involves the consumption of heat energy.
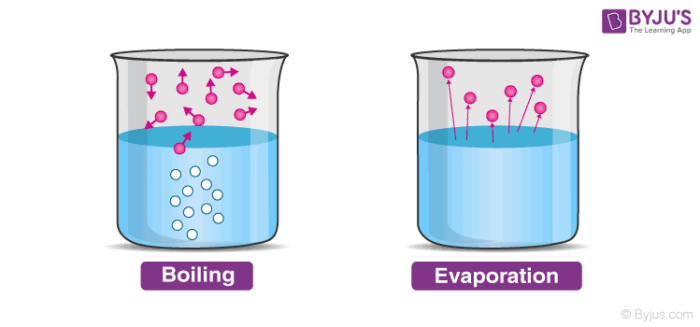
Table of Contents
- Recommended Videos
- Types of Vaporization
- Factors affecting the Rate of Vaporization
- Example of Vaporisation in Daily Life
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Recommended Videos

Types of Vaporization
Vaporization can be divided into two types.
- Evaporation
- Boiling
Evaporation is different from boiling on the basis that evaporation is a surface phenomenon, unlike boiling which is a bulk phenomenon.
Ever wondered why water is stored in earthen pots?

The science involved in this medieval practice is evaporation. Water is stored in earthen pots especially in summer to keep the water cool. Earthen pots are made up of clay particles and have pores in them. When water is poured into the pot, it gets evaporated from the pores by absorbing heat from the remaining water in the pot.
This causes the cooling of the remaining water in the pot due to heat loss. Hence, water is kept cool which makes it suitable for drinking during summers.
Factors affecting the Rate of Vaporization
- Temperature: Vaporization is directly proportional to temperature. As the temperature rises the kinetic energy of the molecules also increases. As a result, the force of attraction reduces. Hence, with an increase in temperature the rate of evaporation increases.
- Surface area: With the increase in surface area, the rate of vaporization also increases as more particles are exposed to the change in temperature.
- Pressure: Pressure is inversely proportional to evaporation. As pressure increases, it gets difficult for the particles to gain the required kinetic energy and escape.
- Wind speed: With an increase in wind speed, the rate of evaporation also increases as particles are driven away by the wind.
Examples of Vaporization in Our Daily Life
- Industrially, salt is recovered from sea water by the process of vaporization.
- Wet clothes are dried up due to the process of vaporization.
- The process is used in many industrial processes for separating the components of a mixture.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is boiling?
What is vaporization?
What is the main difference between boiling and vapourization?
Vaporization, conversion of a substance from the liquid or solid phase into the gaseous (vapour) phase.
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn interesting topics and for further queries please get in touch with the mentor support team at BYJU’S.


Comments