In physics, numerous kinds of forces exist, one of which is the normal force. The normal force is defined as the force that a surface employs on any other body. If that body is at rest, it means that the net force acting on the body is equal to zero. This means that the downward force, that is, the weight, must be similar to the upward force, which is the normal force.
| Table of Contents |
Concept of Normal Force
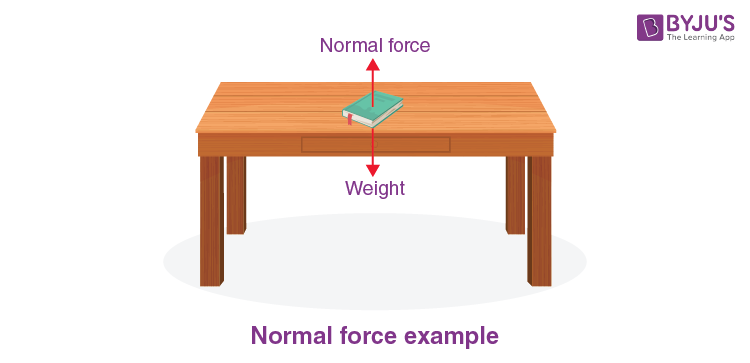
The normal force is a force that is felt every day. For example, when we place a book on a table, the typical reaction force resists the book from falling through the table, the strength of gravity is drawing the book downward, but the book isn’t falling. That means, there exists some force which must be pushing it up. That force is termed the normal force. The word ‘normal’ here means perpendicular to the surface.
One more example of normal force can be seen while bouncing a ball: as the normal force is a non-conservative force, it is also related to the friction force; both these forces are non-conservative forces.
If a ball is dropped from a certain height, it falls; gravity pulls the ball down, so it speeds up, while the drag from air slows down the fall. A massive normal force pushes the ball upwards when it hits the ground, which makes the ball bounce not as high as it bounced at the start. The normal force can also be perceived as non-conservative in the case of rolling resistance.
Normal Force Formula
Formula 1: When the force is acting on a body, dropping at an angle of θ, then the FN is larger than the articulated weight,
FN = F sin θ + mg
Where,
θ = the angle with which the body falls
FN = normal force
m represents the mass of the body
and g represents the force of gravity
Formula 2: When a body is pulled upwards by force, then FN is smaller than its weight
FN = mg – F sin θ
Where,
θ = angle with which body moves up
FN = normal force
m = the mass of the body
g = the force of gravity
Formula 3: When a body is resting on the flat surface, the normal force FN is
FN = mg
Where,
g = the force of gravity
m = mass
Formula 4: When the body is positioned on an inclined level, then normal force FN is given by
FN = mg cos θ
Where,
θ = the angle of the inclined surface
FN = normal force
m = mass of the body
g = the force of gravity

Watch the video to learn more about force and its types

Relation between Friction Force and Normal Force
When you try to move an object, then the force of Friction, Ffriction, acts opposite to the force you apply.
According to the laws of physics, friction is proportional to the force with which you are trying to slide the object on a surface.

You can see in the figure the force with which the gold bar presses against the ground is just its weight or mg.
Then in accordance with Newton’s third law of motion, the ground presses the bar back.
The force perpendicular to the surface pushing the gold bar is called the normal force, denoted by N.
In other words, the force pushing the two surfaces together is the normal force, and the stronger the normal force, the stronger the force due to Friction.
Both these forces, the normal force and the friction force are perpendicular components of the equal force—the force that a surface employs on an object! – The normal and friction forces increase proportionally; if the force exerted by the surface on an object increases.
Read More: Friction
Normal Force Examples
As per the definition and points mentioned above, you must have understood the exact meaning of force. Now, Let’s know more by Some real-life examples of normal force –
1. A Girl standing on a flat surface

The girl in the above picture is standing perpendicular on the flat surface; hence, a perpendicular force acts on the girl. This force will now be termed a Normal Force as it is acting perpendicularly to the girl.
2. Television resting on a table
When a television rests on a table, a perpendicular force exists on television. As this force is acting perpendicularly to the surface of television, this force will be none other than a Normal Force.

Conclusion: From the above examples, it is clear that when a force acts in a perpendicular direction, it will be termed a Normal Force.
| Related Articles |
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Define Normal Force.
Normal force is defined as the force that any surface employs on any other body.
What are the examples of Non-Contact Forces?
Gravitational Force, Magnetic Force, Electrostatic Force.
What type of force can be considered the force of attraction between the Earth and the Moon?
Non-Contact Force.
Which force is the strongest force?
Nuclear force is considered to be the strongest force, 100 times stronger than electromagnetic force.
Which force causes a charged balloon to attract another balloon?
Electrostatic Force.
Stay tuned to BYJU’S for more such interesting and informative articles. Also, register to “BYJU’S – The Learning App” for loads of interactive, engaging Physics-related videos and unlimited academic assistance.

Comments