What is Monosodium Glutamate?
Monosodium glutamate, often abbreviated to MSG, is a sodium salt of glutamic acid. The chemical formula of MSG is C5H8NO4Na and its IUPAC name is sodium 2-aminopentanedioate. Since it is known to intensify meaty flavours in food, monosodium glutamate is widely used as a flavour enhancer in the food industry.
This compound was first produced by the Japanese chemist Kikunae Ikeda in 1908. At room temperature, MSG exists as a crystalline solid which is white in colour. It does not have any distinct odour.

Among the sodium, magnesium, potassium, and calcium salts of glutamic acid, MSG is the most soluble in water. Monosodium glutamate dissociates into sodium cations (Na+) and glutamate anions (C5H8NO4–) when dissolved in water.
Table of Contents
- Monosodium Glutamate Structure
- Preparation of Monosodium Glutamate
- Properties of MSG
- Physical Properties
- Chemical Properties
- What are the Uses of Monosodium Glutamate?
- Frequently Asked Questions
Monosodium Glutamate Structure
MSG molecules feature an ionic bond between Na+ and C5H8NO4–. The structure of a monosodium glutamate molecule is illustrated below.
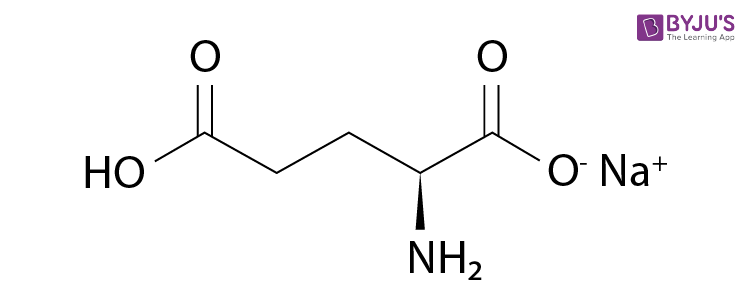
In solid MSG, the glutamate ion exists in its zwitterion form – –O(C=O)CH(NH3+)(CH2)2(C=O)O–.
Preparation of Monosodium Glutamate
The three most common methods of producing monosodium glutamate are listed below.
- Hydrolysis of some vegetable proteins in the presence of hydrochloric acid.
- Chemical synthesis with the help of acrylonitrile (CH2CHCN).
- A bacterial fermentation process involving starch or molasses.
The majority of MSG production is done through bacterial fermentation. Commercial samples of this compound are usually in the monohydrate form.
Properties of MSG
| Monosodium Glutamate | C5H8NO4Na |
| Molar Mass | Anhydrous: 169.11 grams/mole; Monohydrate: 187.12 grams/mole |
| Melting Point | 232oC |
| Boiling Point | Decomposes |
Physical Properties
- This compound is solid at room temperature and has a white, crystalline appearance.
- Monosodium glutamate is odourless.
- A saturated solution of MSG in water has a density of 26.2 grams per cubic centimetre at a temperature of 20o
- MSG is highly soluble in water; its solubility in water corresponds to 740 grams/litre.
Chemical Properties
- When heated to temperatures above 232oC, this compound decomposes to release toxic fumes containing oxides of nitrogen and sodium.
- Solutions of monosodium glutamate have pH values ranging from 6.7 to 7.2.
- When cooled to temperatures below -8oC, this compound crystallises as a pentahydrate.
What are the Uses of Monosodium Glutamate?
Monosodium glutamate has an umami taste and it intensifies meaty flavours when added to certain foods. Therefore, one of its primary applications is in the food industry. Some other important uses of MSG are listed below.
- This compound is used in several canned food products and spice blends.
- MSG is often added to tobacco in order to enhance its taste.
- It also finds use in the treatment of hepatic coma.
- MSG is an important component of several instant ramen noodle products.
Monosodium glutamate has been associated with several symptoms such as headaches, tingling sensations, and burning sensations. These symptoms are collectively referred to as the “Chinese restaurant syndrome”. However, the data from several studies suggest that there is no link between this syndrome and MSG. This compound is a permitted food additive in most countries.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is monosodium glutamate made?
MSG occurs naturally in a number of foods, including tomatoes and cheeses. Today MSG is created by the fermentation of starch, sugar beets, sugar cane or molasses instead of extracting and crystallising MSG from seaweed broth. The process of fermentation resembles that used to produce yoghurt, vinegar and wine.
What is monosodium glutamate made of?
Monosodium glutamate was discovered by a Japanese chemist named Kikunae Ikeda more than 100 years ago, who obtained it from seaweed and found it had unusual flavour-enhancing properties. According to the FDA, MSG is made nowadays by fermenting starch, sugar beets, sugar cane, or molasses.
What is monosodium glutamate used for?
Glutamic acid is naturally present in onions, raisins, cheeses, mushrooms and other foods. MSG is used as a flavour enhancer in the food industry with an umami taste that intensifies the meaty, savoury flavour of food, as naturally occurring glutamate does in products like stews and meat soups.
How does monosodium glutamate work?
Monosodium glutamate (MSG) is the glutamic acid sodium salt and is a non-essential amino acid. Interestingly, glutamic acid has no umami flavouring itself, but MSG in food stimulates glutamate receptors in the buds of the palate. They relay signals, triggering the characteristic taste, to distinct regions of the brain.
Why is MSG bad for your health?
There is a lot of debate within the natural health culture surrounding MSG. Asthma, headaches and even brain damage are reported. In comparison, most official sources such as the FDA say MSG is safe.
To learn more about monosodium glutamate and other sodium compounds (such as sodium thiosulfate), register with BYJU’S and download the mobile application on your smartphone.

Comments