Students who aim to score well in the board exams will find this MP Board Class 10 Maths Syllabus very useful. Board exams can be a daunting experience for many of us. Also, if it is an upcoming Mathematics board examination, we really want to put our best forward on the answer scripts. MP Board Class 10 Mathematics as a subject, perhaps, is different from all the other subjects. If we master a couple of formulae in Mathematics we are good to go. To understand the marking scheme and exam pattern, students can also refer to the MP Board 10th blueprint 2021-22.
The following is the 2021-2022 syllabus for MP board 10th class:
Download MP Board Class 10th Maths Revised Syllabus 2021-22 PDF
We have also posted a screenshot of the chapters in Hindi from the current academic year.
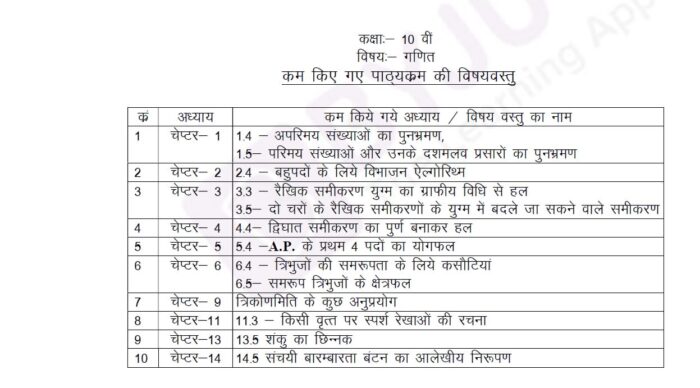
Meanwhile, for reference, find details of deleted portions from the previous academic year as well.
Download MP Board Class 10th Maths Syllabus Deleted Portion 2020-21 PDF
| Class 10 Maths Syllabus for MP Board | |
| Unit 1 | Number Systems
Real Numbers Periods-13 Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic — statements after reviewing work done earlier and after illustrating and motivating through examples. Proofs of results —irrationality of decimal expansions of rational numbers in terms of terminating/ non-terminating, recurring decimals. |
| Unit 2 | Algebra Periods- 6
1. Polynomials Zeros of a polynomial. Relationship between zeros and coefficients of a polynomial with particular reference to quadratic polynomials. 2. Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Periods-15 Pair of linear equations in two variables. Geometric representation of different possibilities of solutions/ inconsistency. Algebraic conditions for number of solutions. Solution of pair of linear equations in two variables algebraically — by substitution, by elimination. Simple situational problems must be included. Simple problems on equations reducible to linear equations may be included. 3. Quadratic Equations Periods-15 Standard form of a quadratic equation , Solution of quadratic equations (only real roots) by factorization and by completing the square, i.e, by using the quadratic formula. Relationship between discriminant and nature of roots. Problems related to day-co-day activities to be incorporated. 4. Arithmetic Progressions (AP) Periods-8 Motivation for studying AP Derivation of standard results of finding the nth term and sum of first n terms. |
| Unit 3 | Trigonometry
I. Introduction to Trigonometry Period- 18 Trigonometric ratios of an acute angle of a right-angled triangle. Proof of their existence (well defined); motivate the ratios, whichever are defined at Values (with proof) of the trigonometric ratios of Relationships between the ratios. Trigonometric Identities: Proof and applications of the identity Only simple identities to be given. Trigonometric ratios of complementary angles. 2. Heights and Distances Periods-8 Simple and believable problems on heights and distances. Problems should nor involve more than two right triangles. Angles of elevation/depression should be only |
| Unit 4 | Coordinate Geometry
Lines (In two-dimensions) Periods-15 Review the concepts of coordinate geometry done earlier including graphs of linear equations Awareness of geometrical representation of quadratic polynomials. Distance between two points and section formula (internal). Area of a triangle. |
| Unit 5 | Geometry
1. Triangles Periods-15 Definitions, examples counterexamples of similar triangles. 1. (Prove) if a line is drawn parallel to one side of 2 niangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio. 2. (Motivate) If a line divides two sides of a triangle in the same ratio, the line is parallel to the third side. 3. (Motivate) If in two triangles, the corresponding angles are equal, their corresponding sides are proportional and the triangles are similar. 4. (Motivate) If the corresponding sides of two triangles are proportional, their corresponding angles are equal and the two triangles are similar. 5.(Motivate) If one angle of a triangle is equal to one angle of another triangle and the sides including these angles are proportional, the two triangles are similar. 6. (Motivate) If a perpendicular is drawn from the vertex of the right angle to the hypotenuse, the triangles on each side of the perpendicular are similar to the whole triangle and to each other. 7. (Prove) The ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the ratio of the squares on their corresponding sides. 8. (Prove) In a right triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides. 9. (Prove) In a triangle, if the square on one side is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides, the angles opposite to the first side is a right triangle. 2. Circles Periods-6 Tangents to a circle motivated by chords drawn from points coining closer and closer to the point. I. (Prove) The tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact. 2. (Prove) The lengths of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal. 3. Constructions Periods- 8 1. Division of a line segment in a given ratio (internally). 2. Tangent to a circle from a point outside it. 3. Construction of a et-bogie similar to a given triangle. |
| Unit 6 | Mensuration
1. Areas Related to Circles Periods-12 Motivate the area of a circle; area of sectors and segments of a circle. Problems based on areas and perimeter/circumference of the above said plane figures. (In calculating area of segment of a circle, problems should be restricted to central angle of . Plane figures involving triangles. simple quadrilaterals and circle should be taken.) 2. Surface Areas and Volumes Periods-12
|
| Unit 7 | Statistics and Probability
1. Statistics Periods-15 Mean, Median and mode of grouped data (bimodal situation to be avoided). Cumulative frequency graph 2. Probability Periods-10 Classical definition of probability. Connection with probability as given in Class IX. Simple problems on single events, not using set notation. |
| Appendix | 1. Proofs in Mathematics
Further discussion on the concept of ‘statement’, ‘proof’ and ‘argument’. Further illustrations of deductive proof with complete arguments using simple results from arithmetic, algebra and geometry. Simple theorems of the “Given and assuming… prove ….. …”. Training of using only the given facts (irrespective of their truths) to arrive at the required conclusion. Explanation of ‘converse’, ‘negation’, constructing converses and negations of given results/statements. 2. Mathematical Modelling Reinforcing the concept of mathematical modelling, using simple examples of models where some constraints are ignored. Estimating probability of occurrence of certain events and estimating averages may be considered. Modelling fair instalments payments, using only simple interest and future value (use of AP). |
For more such resources for Class 11 or MP Board Textbooks, tune into BYJU’S.
Comments