What is Stearic acid?
Stearic acid is a long-chain saturated fatty acid. It is also called Octadecanoic acid or Stearophanic acid.
- It is usually found in various plants and animal fats.
- It is majorly found as a component of shea butter and cocoa butter.
- The chemical formula of Stearic acid is C18H36O2.
- In its solid form, it appears as a white solid and has a mild pungent, oily odour.
- It floats on water. It functions as a plant metabolite, an algal metabolite, a Daphnia magna metabolite, and a human metabolite. It is derived from an octadecane.
Table of Contents
Properties of Stearic acid – C18H36O2
| Stearic acid | C18H36O2 |
| Molecular weight of Stearic acid | 284.484 g/mol |
| Density of Stearic acid | 0.9408 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point of Stearic acid | 69.3 °C |
| Boiling point of Stearic acid | 361 °C |
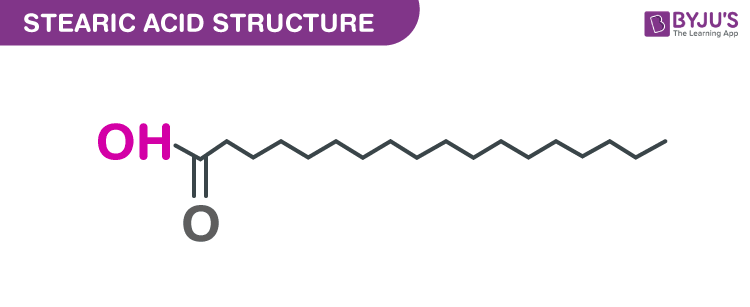
Structure of Stearic acid (C18H36O2)
Uses of Stearic acid (C18H36O2)
-
-
-
- Stearic acid is used as a lubricating agent.
- It is used as a food additive.
- Used in the production of detergents.
- It is widely used in cosmetics, soaps, and shampoos.
- It is used in the manufacturing of pharmaceuticals.
- It is used in making insulators.
- Used in the food packaging industry.
-
-
Production of Stearophanic acid (Stearic acid)
It is produced from oils and fats by the process of saponification of triglycerides by using hot water at about a temperature range of 100 degree celsius. The mixture produced is distilled. Commercially obtained octadecanoic acid is usually a mixture of palmitic acid and stearic acid.
The oil and fats content of Stearophanic acid is rich in animal fat when compared to vegetable fat. Few exceptions are in the foods such as shea butter and cocoa butter, with the stearic acid content of about 28–45%.
It is also produced biosynthetically from carbohydrates through the synthesis of fatty acid machinery.
Effects on Health
This chemical compound is combustible and heats spontaneously. It is generally nontoxic but can cause irritation in the throat, nose, and eyes when inhaled.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the uses of stearic acid?
Stearic acid is used mainly in the manufacture of soaps, detergents, and several other cosmetics such as shaving creams and shampoos. Soaps are not produced directly from this compound, but indirectly via the saponification of stearic acid esters consisting of triglycerides. Stearic acid esters of ethylene glycol, glycol stearate, and glycol distearate are used in shampoos, soaps, and other daily use cosmetic items to achieve a pearly effect.
How is stearic acid produced?
Stearic acid is usually derived from fats and oils with the help of hot water (generally kept at its boiling point, about 100 ° C) to saponify the triglycerides. The resulting mixture is then subjected to distillation. Commercially sold stearic acid is mostly a mixture of stearic and palmitic acids, though there does exist commercially available pure stearic acid. When it comes to biosynthesis, this compound is usually produced in the body from the consumed carbohydrates via a process known as fatty acid synthesis.
Is stearic acid soluble in water?
Stearic acid is not very soluble in water. Only a fraction of a milligram of stearic acid can be dissolved in a hundred grams of water. This compound is, however, soluble in many organic solvents. For example, stearic acid is moderately soluble in alcohols, phenyls, and alkyl acetates. This compound is also soluble in carbon tetrachloride, carbon disulfide, and methyl formate (also known as methyl methanoate). The solubility of stearic acid in dichloromethane under ambient temperatures corresponds to 3.58 grams per 100 grams of dichloromethane.
Learn more about the physical and chemical properties of Stearic acid (C18H36O2) from the experts at BYJU’S.

Comments