What is Barium Hydroxide?
Barium hydroxide is also called as baryta with the formula Ba(OH)2. It is a clear white powder with no odour. It is poisonous in nature. It is ionic in nature for example, Ba(OH)2 (barium hydroxide) in aqueous solution can provide two hydroxide ions per molecule. Barium hydroxide is the only reagent described for metalizing carboxamidesBarium hydroxide was less degradative as compared to barium oxide.
Other name – Caustic baryta, Barium dihydroxide, barium(2+) dihydroxide
| Ba(OH)2 | Barium Hydroxide |
| Density | 3.74 g/cm³ |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 171.34 g/mol |
| Boiling Point | 780 °C |
| Melting Point | 78 °C |
| Chemical Formula | BaH2O2 |
Table of Contents
Barium hydroxide Structure – Ba(OH)2
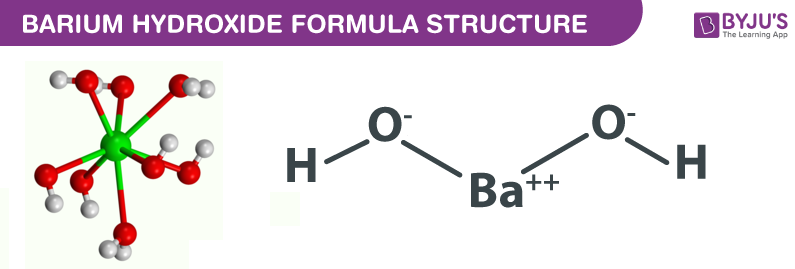
Physical Properties of Barium hydroxide – Ba(OH)2
| Odour | Odourless |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit | 3 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.48 kPa at 17.6 deg C |
| pH | 11.27 |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble in cold water |
Uses of Barium hydroxide – Ba(OH)2
-
-
-
- Barium hydroxide forms a strong caustic base in aqueous solution. It has many uses, e.g., as a test for sulphides; in pesticides; in the manufacture of alkali and glass.
- Use of barium hydroxide lime rather than soda lime, high sevoflurane concentration, high absorbent temperature, and fresh absorbent use.
- Used in the manufacture of alkalis, glass, oil and grease additives, barium soaps, and other barium compounds.
-
-
Health Hazard
-
-
-
- Inhalation of barium dusts can cause irritation of the nose and upper respiratory tract and may produce benign pneumoconiosis known as baritosis.
- Barium ions are toxic to muscles especially heart, producing stimulation and then paralysis.
- It is extremely dangerous neurotoxin. Adverse effect may result like effects on the heart and the function of the central nervous system (CNS).
-
-
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the uses of barium hydroxide?
Industrially, barium hydroxide is used as a precursor to several other barium compounds. The monohydrate of this compound is widely used to dehydrate and extract sulfate from different products. The very low solubility of barium sulfate is utilized in this application.
How is barium hydroxide prepared?
Barium hydroxide is usually prepared by dissolving barium oxide (chemical formula: BaO) in water. The chemical equation for this reaction is provided below.
BaO + 9 H2O → Ba(OH)2·8H2O
It can be noted that this compound crystallizes into the octahydrate form, which is then converted into a monohydrate by heating it in air.
What happens when barium hydroxide is heated?
When heated to 800° C, barium hydroxide decomposes to yield barium oxide. Barium carbonate is provided by reaction with carbon dioxide. The strongly alkaline, aqueous solution undergoes neutralization reactions with acids.

Comments