What is Phosphoric Acid?
Orthophosphoric acid refers to phosphoric acid. Phosphoric Acid is a weak acid with the chemical formula H3PO4.
Phosphoric Acid is an acid-containing four atoms of oxygen, one atom of phosphorus, and three atoms of hydrogen. It is also known as phosphoric(V) acid or orthophosphoric acid. It is present in teeth and bones and helps in metabolic processes. In its liquid form, it appears as a clear, colourless solution and in its solid form, it appears as a transparent, crystalline solid.
Table of Content
- Structure of orthophosphoric Acid H3PO4
- Physical Properties of Phosphoric Acid H3PO4
- Preparation of orthophosphoric Acid H3PO4
- Synthesis of Phosphoric Acid – H3PO4
- Chemical Properties of Phosphoric Acid H3PO4
- Basicity of Orthophosphoric Acid H3PO4
- Uses of Phosphoric Acid H3PO4
- Health Hazard of Phosphoric acid
- FAQs
As a sequestering agent, it helps in the binding of divalent cations. It is widely used in orthodontics and dentistry. Phosphoric acid is important in biogeochemistry and biochemistry. It is a tribasic acid. All three hydrogens are acidic, the pKa value of first, second and third hydrogen are respectively pKa1 = 2.14, pKa2 = 7.20, and pKa3 = 12.37
Read more: Uses of Phosphoric Acid
Structure of Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4)
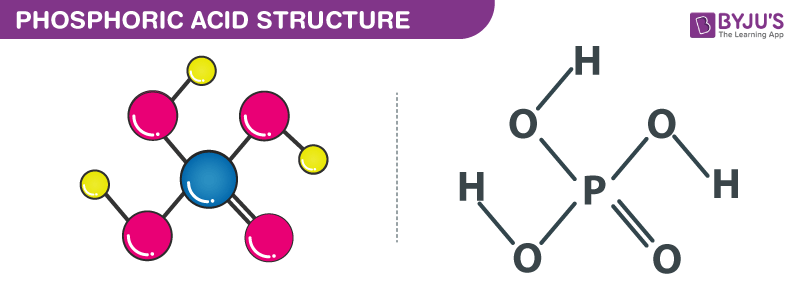
Structure of phosphoric acid
Physical Properties of Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4)
| H3PO4 | Phosphoric Acid |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 97.994 g/mol |
| Density | 1.88 g/cm³ |
| Boiling Point | 158 °C |
| Melting Point | 42.35 °C |
- Phosphoric acid is an odourless, colourless, viscous liquid, possessing in a high degree the property of reddening litmus. It cannot be obtained free from water.
- When exposed to a red heat and afterward cooled it forms a transparent brittle glass.
- This fusion should be effected in a platinum crucible since phosphoric acid when heated to redness attacks either glass or porcelain.
- The acid if examined after this exposure to heat is found although its composition remains the same to have acquired new properties.
- On this account the name of para phosphoric has been given to it; while the term phosphoric is applied to designate the acid in the state first described.
- Nitrate of silver yields with phosphoric acid a yellow precipitate with para phosphoric acid a white one. Albumen is coagulated by the latter but not by the former.
Preparation of Phosphoric acid
It can be conveniently prepared by dissolving P2O5 in water followed by boiling the solution to form a thick syrup.
P2O5 + 3H2O ⇌ 2H3PO4
Red phosphorus when heated with conc. HNO3 yields orthophosphoric acid.
P + 5HNO3 → H3PO4 + H2O + 5NO2
On a large scale, it is prepared by treating phosphorite rock with dil.H2SO4.
Ca3(PO4)2 + 3H2SO4 → 3CaSO4 + 2H3PO4
Synthesis of Phosphoric Acid – H3PO4
- Phosphoric acid may be obtained by adding sulphuric acid to the phosphate of baryta suspended in water.
- The sulphuric acid unites with the baryta forming an insoluble salt which precipitates while the phosphoric acid remains in solution.
- When phosphorus is gradually added to nitric acid, phosphoric acid is generated and remains mingled with the residual nitric acid.
Chemical Properties of Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4)
- Phosphoric acid is a deliquescent solid, generally encountered as a viscous aqueous solution.
- It is weakly acidic, with three possible sequential deprotonation steps, forming phosphates.
- Like carboxylic acids, phosphoric acid can dimerize via a dehydration reaction to form phospho anhydrides.
- Phosphoric acid undergoes dehydration in three steps and is referred to as tribasic.
- As a result mono and di sodium and potassium salts of phosphoric acid are routinely used as pH buffers.
- One of the most important reactions of phosphoric acid and its derivatives is multimerization.
- As with carboxylic acids, two phosphoric acid molecules may combine with the loss of water to form a di phosphate ester also referred to as pyrophosphate.
- However, as phosphoric acid has further -OH functionalities triphosphates may also be formed.
- Salts of phosphoric acid are solid and many are relatively water-insoluble unless a strong mineral acid is present.
Basicity of Orthophosphoric Acid (H3PO4)
The basicity of acids is represented by the number of hydrogen atoms which can be replaced by electropositive atoms. Basicity of an acid is the number of hydrogen ions that can be produced by the ionization of one molecule of the acid in its aqueous solution.
An acid which produces three hydrogen or hydronium ions by the ionization of one molecule of the acid, is called a tribasic acid or tri protic acid. For example, H3PO4 and H3PO3 are tribasic acids.
| Acid | Basicity |
| Hypophosphorous acid (H3PO2) | Oxidation number of Phosphorus = +1
Basicity = 1 |
| Phosphorus acid (H3PO3) | Oxidation number of Phosphorus = +3
Basicity = 2 |
| Orthophosphoric acid (H3PO4) | Oxidation number of Phosphorus = +5
Basicity = 3 |
| Pyrophosphoric acid (H4P2O7) | Oxidation number of Phosphorus = +5
Basicity = 4 |
| Metaphosphoric acid (HPO3) | Oxidation number of Phosphorus = +5
Basicity = 1 |
Uses of Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4)
Phosphoric acid (H3PO4) has many essential applications, in particular in the manufacture of fertilizers. Many acids are derived from phosphate rocks by a wet process based on the reaction between phosphate rocks and acid solutions. This acid (H3PO4) is a medium-strong acid, but is also highly corrosive to ferrous or ferrous alloys.
- Around 90% of phosphoric acid produced is used as fertilizers
- It is used as a supplement feed for pigs, cattle, poultry
- It is used in skincare products, cosmetics as a pH adjuster
- It is used in brewing, food and dairy industries as a sanitizing agent
- It is used in beverages and food like jam and cola to acidify them
- It is used to remove rust from the surface to metals
Health Hazard
Phosphoric acid is less corrosive and hazardous than is concentrated sulphuric or nitric acid. Its concentrated solutions are irritants to the skin and mucous membranes. The vapours contain P2O5 fumes can cause irritation to the throat and coughing but could be tolerated at <10mg/m3.
Phosphoric acid is a noncombustible substance in both solid and liquid forms. It may be fatal if inhaled. Fumes from fires are irritating to respiratory passages, eyes, skin, and may contain phosphine, phosphoric acid, and hydrogen chloride.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is orthophosphoric acid used for?
Phosphoric acid, also called orthophosphoric acid, (H3PO4), the most important -oxy acid of phosphorus, is used to make phosphate salts for fertilizers. This is also used in dental cement, albumin derivatives preparation and in the sugar and textile industries.
What happens when orthophosphoric acid is heated?
The orthophosphoric anhydrous acid is a white, crystalline solid which melts at 42.35°C. If phosphoric acid is heated to temperatures of around 200°C, there will be a loss of constituent oxygen. Dehydration produces a sequence of acids, ranging from pyrophosphoric acid, H4P2O7, to metaphosphoric acid
Why is phosphoric acid in Coke?
Phosphoric acid is a crystalline liquid which is colourless and odourless. It gives a tangy taste to soft drinks and prevents mould and bacteria from developing, which can easily multiply in a sugar solution. Much of the acidity of soda also comes from the phosphoric acid. Becoming phosphoric acid it is then processed again.
What happens when orthophosphoric acid is heated?
The orthophosphoric anhydrous acid is a white, crystalline solid which melts at 42.35°C. As phosphoric acid is heated to temperatures above about 200°C, there will be a loss of constituent vapour. Dehydration produces a sequence of acids, ranging from pyrophosphoric acid, H4P2O7, to metaphosphoric acid, (H3PO4) n.
What are the side effects of orthophosphoric acid?
Can cause burning of lips, tongue, throat and stomach on ingestion. It may also cause nausea, vomiting, cramps in the stomach and diarrhoea. Long-term effects of exposure to orthophosphoric acid may include dermatitis.
Is phosphoric acid strong?
Phosphoric acid is a weak acid because of partial dissociation in water. It is weaker than nitric acid and sulphuric acid.
Does phosphoric acid dissolve rust?
Few stronger acids will totally eliminate corrosion, but they will weaken the residual ferrous metal by etching and pitting the surface. Phosphoric acid is one of the few acids that can kill rust without oxidizing or destroying the iron beneath.
Is phosphoric acid a disinfectant?
Bowl Cleanse is a phosphoric acid solution that supplies disinfectant treatment for the removal of certain harmful bacteria present in toilet bowls and urinals. The 25% phosphoric acid solution quickly extracts mineral particles in toilets without destroying plumbing.
Also Read:
| Uses of Phosphoric Acid | Oxoacids Of Phosphorus |
| Preparation, Properties And Uses – Phosphine | Oxyacids and Ammonia |
Learn more about the chemical behaviour and importance of H3PO4 with the expert faculties at BYJU’S – India’s largest education company.

Comments