Table of Contents
What is Butane?
Butane is an organic compound with the formula C4H10. Butane is a saturated hydrocarbon containing 4 carbons, with an unbranched structure.
Butane is primarily used as a gasoline mixture, either alone or in a propane mixture. It is also used as a feedstock for ethylene and butadiene production. Butane, like propane comes from natural gas or petroleum refineries and the two gases are usually found together. The butane is stored under pressure as a liquid. When the curler is switched on, butane is released and changes to a gas.
Other names – Methylethylmethane, n-Butane
| C4H10 | Butane |
| Density | 2.48 kg/m³ |
| Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass | 58.12 g/mol |
| Boiling Point | -1 °C |
| Melting Point | -138 °C |
| Chemical Formula | C4H10 |
Butane Structure – C4H10
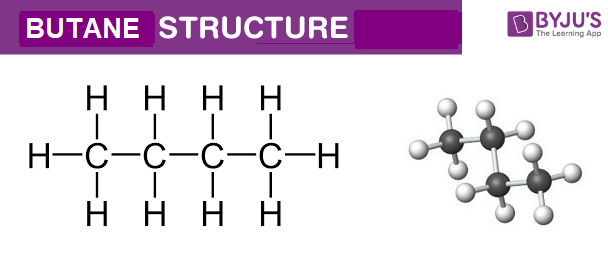
Butane Structure – C4H10
Physical Properties of Butane – C4H10
| Odour | Odourless |
| Appearance | Colourless gas |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit | 1 |
| Specific Gravity | 0.601 |
| Complexity | 2 |
| Solubility | Insoluble in water |
Chemical Properties of Butane – C4H10
-
-
-
-
- Butane undergoes oxidation which results in the formation of carbon dioxide and water. The chemical equation is given below.
-
-
-
2C4H10 + 13O2 → 8CO2 + 10H2O
-
-
-
-
- Butane reacts with chlorine resulting in the formation of butyl chloride and hydrogen chloride. The chemical equation is given below.
-
-
-
Uses of Butane – C4H10
-
-
-
- Generally used for domestic purposes in cylinders painted red and is sold under various trade names.
- Used for gasoline blending, as fuel gas and as a feedstock in the production of ethylene and Butadiene.
- Used to produce methyl tertiary-butyl ether (MTBE)
- Used in catalytic dehydrogenation of butane or cracking of feedstocks to n-butenes and higher and lower boiling fractions.
-
-
Frequently Asked Questions
What is butane used for?
Butane is a petroleum-derived gaseous liquid. This is primarily used for camping, cooking at the backyard and in cigarette lighters. Butane is blended with propane and marketed as LPG, or liquefied petroleum gas, in trade. LPG fuel is used in heating appliances and cars.
What is the common name of butane?
Butane is also called n-butane, or regular butane. Popular butane gas uses include lighter fuel, cigarette lighters, and production of gasoline. The molecular formula of butane is C4H10.
Is butane a hydrocarbon?
Butane is a colourless, odourless, gaseous hydrocarbons (carbon and hydrogen compounds), that are part of the paraffinic hydrocarbon group. All compounds occur in both natural gas and crude oil and are produced to produce gasoline in large quantities in petroleum refining.
Are there different types of butane?
Butane, or C4H10, is a saturated hydrocarbon. It can have two structural isomers namely n-butane and iso butane or a combination of the two. These isomers differ in the number of carbon atoms in their main chain.
What is Butane made of?
Butane is a simple alkane chain consisting of four carbon atoms. This has a job as a food-propeller and a coolant. It is a molecular form of water and an alkane.

Comments