What is Barium oxide?
BaO is a hygroscopic compound with chemical name Barium oxide. It is also called Barium monoxide or Barium protoxide or Calcined baryta. It is widely used as a drying agent for solvents, in cathode ray tubes, catalysts, and crown glass. Excessive quantities of BaO may result in death.
Barium protoxide is a cubic structure that appears as a white to yellow coloured powder which is non-flammable. It may be toxic when swallowed. Causes irritation in eyes, mucous membranes, and skin.
Table of Contents
- Properties of Barium oxide – BaO
- Barium oxide structure – BaO
- BaO Uses (Barium oxide)
- Production of Barium oxide
- Health hazards
Properties of Barium oxide – BaO
| BaO | Barium oxide |
| Molecular weight of BaO | 153.326 g/mol |
| Density of Barium oxide | 5.72 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point of Barium oxide | ~ 2,000 °C |
| Melting point of Barium oxide | 1,923 °C |
Barium oxide structure – BaO
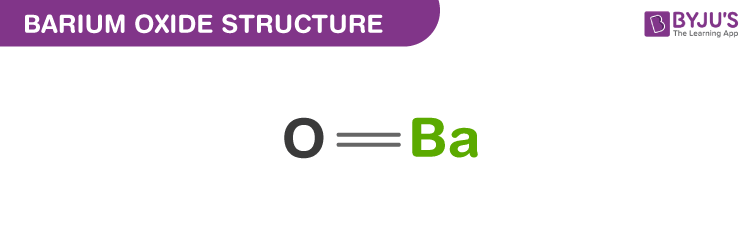
The exact mass and the monoisotopic mass of Barium monoxide is 153.9 g/mol. The number of hydrogen bond acceptor equals to one and the number of hydrogen bond donor equals to zero. This compound is canonicalised and has one covalently bonded unit.
BaO Uses (Barium oxide)
- Barium oxide is used to coat hot cathodes.
- Used in the production of optical crown glass.
- Used as an ethoxylation catalyst.
- Used as a source of pure oxygen via heat fluctuation.
- Used to oxidise to BaO2.
- Used in the process of isomer separation.
- Used in fuels.
- Used as an excellent oxidising.
- Used as an adsorbent.
- Used as a strong reducing agent.
Production of Barium oxide
Calcined baryta is obtained by heating barium carbonate (BaCO3). It may also be made by thermally decomposing barium nitrate (Ba(NO3)2).The reactions are as follows:
2Ba + O2 → 2BaO
Health hazards
It is a toxic and corrosive compound which is non-combustible and water sensitive. Inhalation, swallowing, or contact (with skin or eyes) with vapours, substance or dust causes severe burns or death. On reacting with water it generates heat that increases the fumes concentration in the air. When this compound catches fire it liberates irritating, toxic, and corrosive gases.
Learn more about the Structure, physical and chemical properties of BaO from the experts at BYJU’S.


Comments