August 3rd, 2020 PIB:- Download PDF Here
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. Foreign Direct Investment in Commercial Coal Mining in India 2. Electronic Vaccine Intelligence Network (eVIN)
1. Foreign Direct Investment in Commercial Coal Mining in India
Context:
100% FDI under automatic route in coal mining activities allowed.
Details:
- In June 2020, the Ministry of Coal under GOI started the auction process of coal mines for commercial coal mining in India. For more on commercial coal mining, check PIB dated June 11, 2020.
- The government also amended the FDI Policy 2017 to permit 100% FDI under automatic route in coal mining activities including associated processing infrastructure, for sale of coal, subject to the provisions of Coal Mines (Special Provisions) Act, 2015 and the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957.
- Associated processing infrastructure – this includes coal washery, crushing, coal handling, and separation (magnetic and non-magnetic).
- As per this FDI policy, 100 per cent FDI under automatic route is allowed for coal and lignite mining for captive consumption by power projects, iron and steel and cement units and other eligible activities permitted under and subject to applicable laws and regulations.
- In addition, 100% FDI under automatic route is also allowed for setting up coal processing plants such as washeries subject to the condition that the company shall not do coal mining and shall not sell washed coal or sized coal from its coal processing plants in the open market and shall supply the washed or sized coal to those parties who are supplying raw coal to processing plants.
- It is also clarified by the government that for FDI on coal mining, an entity of a country, which shares a land border with India or where the beneficial owner of investment into India is situated in or is a citizen of any such country, can invest only under the Government route.
- Further, a citizen of Pakistan or an entity incorporated in Pakistan can invest, only under the Government route, in sectors/activities other than defence, space, atomic energy and sectors/activities prohibited for foreign investment.
Benefits of this move:
- Allowing 100% FDI and opening up the sector for private players are likely to attract global miners to invest in India.
- Private sector participation would result in faster ramp-up of coal production, helping gradually reduce India’s import dependence, especially for thermal coal.
- The ushering in of global players on the scene can also lead to increased technology adoption and mechanisation in mining operations, resulting in better operational efficiency for the industry.
Coal industry in India:
- Coal reserves in India constitute about 9.4% of the world’s reserves (which is the fifth-largest).
- In terms of production, India is the second-largest producer of coal next only to China.
- Coal in India is chiefly consumed for electricity generation, by the steel and washery industries, sponge iron industry and cement industry.
- Despite India’s large domestic resources, our import dependency has continued to rise from 12% in 2007 to 31% in 2017. This is largely due to high growth in demand and poor quality of our domestic coal which, often does not meet international quality standards.
- Besides playing a crucial role in the energy sector, the coal mining sector has major economic significance for the country.
- It provides employment to over 355,000 people and is a major source of revenue and generates employment in resource-rich states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh and Odisha.
- The coal sector’s contribution to the GDP of the country is just about 2%.
- Tidbits:
- Major coal mines are located in eastern and south-central India.
- Jharkhand has the largest coal deposits followed by Odisha.
- Dhanbad in Jharkhand is the largest coal-producing city in India.
- Coal was first mined in 1774 when two employees of the East India Company started commercially exploiting the Raniganj Coalfield.
- Coal mines were nationalised in the seventies.
2. Electronic Vaccine Intelligence Network (eVIN)
Context:
Electronic Vaccine Intelligence Network (eVIN) has ensured essential immunization services during the COVID pandemic.
About eVIN:
- eVIN is an indigenously developed technology system in India that digitizes vaccine stocks and monitors the temperature of the cold chain through a smartphone application.
- eVIN aims to support GOI’s Universal Immunization Programme by providing real-time information on vaccine stocks and flows, and storage temperatures across all cold chain points in these states.
- The initiative aims to strengthen the evidence base for improved policy-making in vaccine delivery, procurement and planning for new antigens in India.
- eVIN provides an integrated solution to address widespread inequities in vaccine coverage by supporting state governments in overcoming constraints of infrastructure, monitoring and management information systems and human resources, often resulting in overstocking and stock-outs of vaccines in storage centres.
- The technological innovation is implemented by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in partnership with the Government of India.
- All cold chain handlers are provided smartphones with the eVIN application which allows for the digitization of vaccine inventories.
- eVIN is a combination of software and SIM-enabled temperature loggers specially designed to improve vaccine stock keeping practices and temperature monitoring across states where this is implemented.
- With eVIN, district officials can:
- View real-time stock and temperature
- Understand vaccine requirement
- Enable emergency management
- Keep track of consumption patterns
- Have efficient stock reallocation
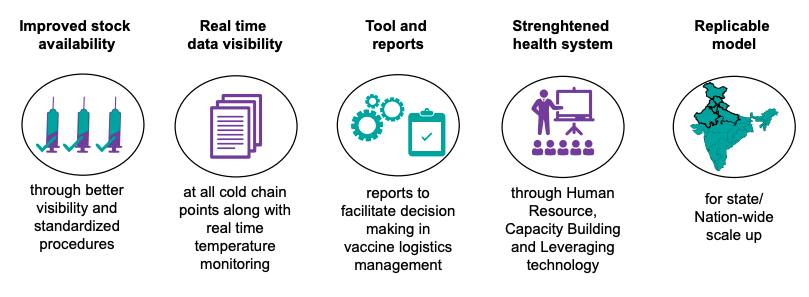
The following image gives the benefits of eVIN:
Read previous PIB here.
August 3rd, 2020 PIB:- Download PDF Here
| Related Links | |||
| UPSC 2020 | Government Exams | ||
| UPSC Current Affairs Quiz | UPSC Prelims Exam | ||
| UPSC Monthly Magazine for Current Affairs | IAS Eligibility | ||

Comments