TABLE OF CONTENT
A. GS1 Related B. GS2 Related POLITY 1. 50% quota for women now in Punjab’s civic bodies 2. India has second highest number of obese children in world: Study INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS 1. At Geneva, India agrees to total ban on child labour C. GS3 Related ECONOMICS 1. New labour survey to generate quarterly and annual data 2. The best of times, the worst of times INTERNAL SECURITY 1. DRDO successfully test fires third generation anti-tank ‘Nag’ missile in Rajasthan SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 1. What ails the Navigation Indian Constellation D. GS4 Related E. Concepts-in-News: Related Concepts to Revise/Learn F. Bills/Acts/Schemes/Orgs in News G. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
UPSC Current Affairs 2017: News Analysis
A. GS1 Related
Nothing here for Today!!!
1. 50% quota for women now in Punjab’s civic bodies
Context: Bid to empower women and give them a greater role in governance.
In news:
- The Punjab Cabinet decided to increase women reservation in urban local bodies and panchayati raj institutions from the existing 33 per cent to 50 per cent.
- A Bill to amend the Panchayati Raj Act, 1994, the Punjab Municipal Act, 1911, and the Punjab Municipal Corporation Act, 1976, will be tabled in the Budget Session.
- The move will enhance reservation for women in direct elections for members of municipal corporations, municipal councils, nagar panchayats, gram panchayats, panchayat samitis and zila parishads.
2. India has second highest number of obese children in world: Study
In news:
- “A disturbing global public health crisis,” according to a study published in The New England Journal of Medicine:
- India has the second highest (4 million kids) number of obese children in the world after China.
- Diseases associated with obese: cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer, and other life-threatening conditions
Trend around the world:
- Over two billion children and adults suffer from health problems related to being obese, and an increasing number die from these conditions.
- In 2015, excess weight affected 2.2 billion children and adults worldwide, or 30% of all people.
- Among the 20 most populous countries, the highest level of obesity among kids and young adults was in the US at nearly 13%; Egypt topped the list for adult obesity at about 35%. Lowest rates were in Bangladesh and Vietnam, respectively, at 1%. China with 15.3 million and India with 14.4 million had the highest numbers of obese children; the US with 79.4 million and China with 57.3 million had the highest numbers of obese adults in 2015.
Category: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
2. At Geneva, India agrees to total ban on child labour
In news:
- India ratified two fundamental conventions against child labour — the Minimum Age Convention, 1973 and the Worst Forms of Child Labour Convention, 1999— at the International Labour Organisation (ILO) conference currently under way in Geneva.
- The conventions provide a framework for the abolition of child labour so that each and every child has the opportunity to develop physically and mentally to their full potential and not getting engaged in work that jeopardises their education and development.
- The conventions allow a distinction to be made as to what constitutes acceptable and unacceptable forms of work for children at different ages as well as stages of development.
What needs to be done after ratification?
- India will now be responsible to develop and implement programmes to progressively eradicate child labour.
National rules and legislation:
- The amended Child Labour (Prohibition and Regulation) Central Rules completely prohibited employment of children aged below 14 years in any occupation or process, and of adolescents (aged 14 to 18 years) in hazardous occupations and processes.
- The amended ruled provided a broad and specific framework for the prevention, prohibition, rescue and rehabilitation of child and adolescent workers.
International Labour Organization (ILO):
- International Labour Organization (ILO), specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) dedicated to improving labour conditions and living standards throughout the world.
- Established in 1919 by the Treaty of Versailles as an affiliated agency of the League of Nations, the ILO became the first affiliated specialized agency of the United Nations in 1946. In recognition of its activities, the ILO was awarded the Nobel Prize for Peace in 1969.
- The functions of the ILO include the development and promotion of standards for national legislation to protect and improve working conditions and standards of living. The ILO also provides technical assistance in social policy and administration and in workforce training; fosters cooperative organizations and rural industries; compiles labour statistics and conducts research on the social problems of international competition, unemployment and underemployment, labour and industrial relations, and technological change (including automation); and helps to protect the rights of international migrants and organized labour.
- Among intergovernmental organizations the ILO is unique in that its approximately 187 member states are represented not only by delegates of their governments but also by delegates of those states’ employers and workers, especially trade unions. National representatives meet annually at the International Labour Conference. The ILO’s executive authority is vested in a 56-member Governing Body, which is elected by the Conference. The International Labour Office in Geneva, Switzerland, composed of the permanent Secretariat and professional staff, handles day-to-day operations under the supervision of an appointed director general.
- Among the ILO’s many publications are the International Labour Review and the Year Book of Labour Statistics.
C. GS3 Related
1. New labour survey to generate quarterly and annual data
In News:
- The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation has started a Periodic Labour Force Survey
- It will provide quarterly labour and employment data for urban India and annual data for rural India
- It would supply data not only about the formal sector, but also about the informal sector
- This survey will supersede the earlier system where such data was available only every five years
- The first release of data will be in December 2018
Revision of base year:
- The Statistics Ministry is also preparing to revise the base year of national accounts to 2017-18 from 2011-12
- This will be done after the completion of the household consumer expenditure survey and the labour force survey at the end of 2018
CAPI method:
- The Periodic Labour Force Survey will also incorporate a Computer Assisted Personal Interviewing (CAPI) method
- In this method, field operators will be using tablets to enter the data in order to generate more accurate and timely information
Other measures in pipeline:
- The Ministry of Statistics is also developing a fact sheet on the Indian economy, incorporating inputs from all important ministries on 100 indicators
- It is also considering an Annual Survey of Services, along the lines of the Annual Survey of Industries already being carried out
2. The best of times, the worst of times
Context:
- The ongoing farmers’ agitation has taken on a shockingly violent form
- Discussion has revolved around an apparent paradox: why are farmers rioting after a bumper crop?
Immediate and other factors leading to this crisis:
- Demonetisation: Demonetisation squeezed so much liquidity out of the system that traders did not have requisite cash to buy the farmers’ produce
- Farmers also feel that persisting with imports, even after clear signs of a bumper harvest, further depressed prices
- FCI procurement focusses only on rice and wheat
Problems with Indian agriculture:
- We are still stuck with the so-called Green Revolution of the 1970s
- This was primarily a rice and wheat revolution
- It completely neglected two-thirds of Indian agriculture and crops grown and eaten by the poorest people of our country — pulses and millets
- Also, over the years, it has caused a deep crisis of sustainability, economic and ecological
- Large-scale use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides has had an extremely adverse impact on our soil and water
- Deep drilling by tubewells to grow these water-intensive crops has happened without keeping in mind India’s unique hydrogeology, where nearly two-thirds of our land is underlain by hard rock formations which have very low rates of natural recharge
Subsequent problems:
- There is now a serious water crisis, with both water tables and water quality falling rapidly
- Arsenic, fluoride, mercury, even uranium have entered in drinking water, creating serious health issues
- To get the same increase in production, farmers have to apply more and more fertilisers and pesticides over time which raises costs of cultivation, without a proportionate increase in production
Way forwards:
- First- We need transition to a more ecologically resilient agriculture (becomes more urgent in the context of climate change)
- Second- We must radically reform the management of both surface and groundwater
- Third- We require continued diversification to other forms of livelihood, such as livestock and fisheries, which are among the fastest-growing segments of the rural economy
- We must also shift focus away from water-intensive rice and wheat
- This means radical changes in the way we grow these crops (seed, water and input regimes) but also much greater encouragement to millets and pulses, which are nutritionally far superior alternatives in a country beset with the diabetes epidemic
- The best way would be to include millets and pulses in the massive anganwadi and mid-day meal programmes
- Fourth- Investments in agro-processing infrastructure are urgently required that would enable farmers to move up the value chain
- Fifth- we need to ensure access to credit and crop insurance, especially to our 85% small and marginal farmers
- Sixth- We need strong Farmer Producer Organisations, to overcome massive handicaps faced by isolated farmers and enable them to really benefit from market participation
Results:
- More production at less costs: As farmers reduce their dependence on synthetic fertilisers and pesticides, they slowly emerge from the ecological vicious cycle and are also able to dramatically reduce their costs of cultivation, without compromising on production
- Water availability: This will ensure that the water in our irrigation commands reaches the farmers for whom it is meant and groundwater is managed sustainably in a way that ensures that no one is deprived of their right to water for life
1. DRDO successfully test fires third generation anti-tank ‘Nag’ missile in Rajasthan
In news:
- The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully test fired the anti-tank missile “Nag”
- The Nag missile is a third generation “fire and forget” anti-tank missile
- It is equipped with highly advanced Imaging Infrared Radar (IRR) seeker and has integrated avionics technology in its arsenal
- This integrated avionics technology is possessed by very few countries
Basic Information:
- Nag is a third generation “fire-and-forget” anti-tank missile developed in India
- It is one of five missile systems developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) under the Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP)
1. What ails the Navigation Indian Constellation
In news:
- The clocks on the first satellite, IRNSS-1A had failed in June 2016, affecting the accuracy of the “GPS”
- ISRO is trying to rectify this problem
What is NavIC?
- Navigation Indian Constellation (NavIC) is an independent Indian satellite-based positioning system for critical national applications
- NavIC consists of a constellation of seven satellites, three of which are in a geostationary orbit and four in a geosynchronous
- Its purpose is to provide ‘reliable position, navigation and timing services over India and neighbourhood’
- According to ISRO, the applications of IRNSS are: terrestrial, aerial and marine navigation, vehicle tracking and fleet management, terrestrial navigation for hikers and travellers, disaster management, integration with mobile phones, mapping and geodetic data capture and visual and voice navigation for drivers
What’s the problem?
- NavIC relies on rubidium clocks as navigation requires the most accurate clocks
- This January, the ISRO confirmed that the clocks on the first satellite, IRNSS-1A had failed in June 2016
- Though six of the satellites are working fine, the one faulty one means the “GPS” isn’t working as accurately as it ought to be
Future prospects:
- Rubidium clocks were the previous standard in accurate clocks and most organisations, that need precise time estimates, need cesium clocks
- Future clocks on such satellites, each with a lifespan of 10 years, will host such clocks
Nothing here for Today!!!
Intensified Diarrohoea Control Fortnight
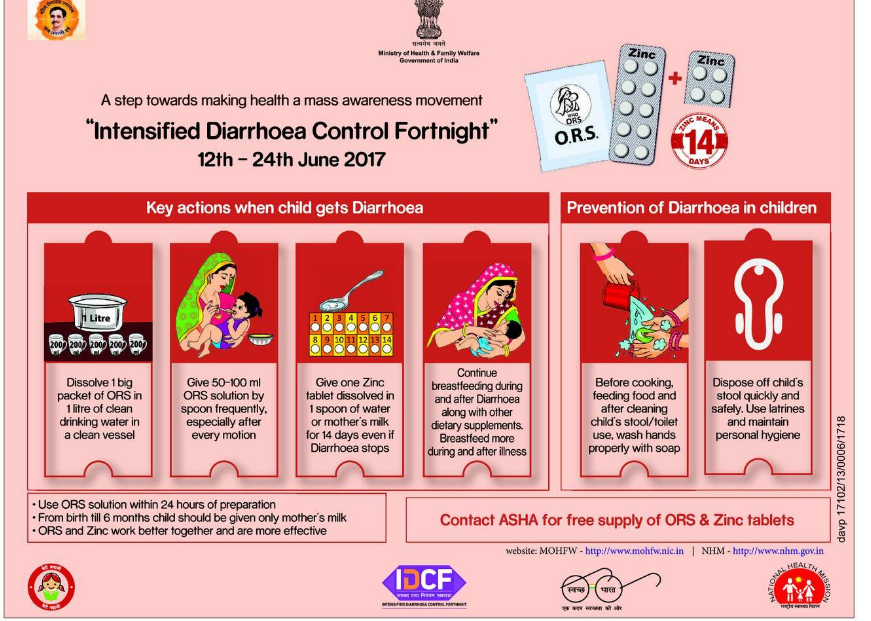
|
Bill/Acts/Schemes in News |
About the Schemes |
Question 1: Consider the following statements:
- In Multidrug Resistan Tuberculosis, patients do not respond to second-line of drugs.
- Drugs like Bedaquiline and Delamanid are not adequately available in India’s national healthcare system.
- India shoulders the highest TB burden in the world
Choose the correct answer.
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- All are correct
- 1 and 3 only
Question 2: Identify the correct Statement.
- The Representation of the People Act bar political parties from receiving foreign funds.
- The Foreign Contribution Regulation Act bar political parties from receiving foreign funds.
- Both A and B
- Neither A nor B
Question 3: The main aim of ‘Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana’ is ______.
- Providing irrigation facilities for organic farming
- Promoting sprinkler-irrigation among agriculturists in water-scarce and hill regions
- Promoting the utilisation of renewable energy in irrigation-intensive regions
- Providing some means of protective irrigation to all agricultural farms in the country
Question 4: Identify the correct statement with reference to “Fortification of foods”.
- Fortification of food is a technique of adding key vitamins ,minerals and other nutrients to staple foods
- Fortification of food techniques main idea is to fight against malnourishment
- Both A and B
- None of the above
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Online Current Affairs Crash Course’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
Practice More: Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series


Comments