TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS1 Related B. GS2 Related Polity 1. Collegium moves to devise norms to pick, shift judges 2. After foodgrain and LPG, direct transfer of benefits for fertilizers kicks in from Sunday 3. Reforms money can’t buy 4. Major Swachh hiccups: Funds crunch, failure to transport and segregate waste Environmental Science and Ecology 1. Govt’s wildlife action plan to focus on e-surveillance C. GS3 Related D. GS4 Related E. Prelims Fact F. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions G. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
A. GS1 Related
Nothing here for Today!!!
B. GS2 Related
1. Collegium moves to devise norms to pick, shift judges
Context:
- Appointment of judges and transfer of high court judges.
- Transparency in the selection process
In news:
- The five-member Supreme Court collegium headed by Chief Justice Dipak Misra has resolved to devise a procedure to streamline the process to select judges of constitutional courts.
December 16, 2015 judgment
- The SC had asked the government to frame a new memorandum of procedure for selection of judges
- Disagreement: The draft is stuck over a disagreement on the Centre’s insistence on including a “national security” clause to enable the government to reject a name recommended for appointment as judge of the SC or HCs on these grounds.
- Tussle between Judiciary and Government:
- The collegium has been firm that the Centre must put in writing its objections, including on national security grounds, for rejecting a recommendation and insists that if the collegium reiterates its recommendation the appointment must go through.
- But the Centre remains firm it will only show intelligence inputs on a person to the collegium and not put it in writing as this could jeopardise the future of a person whose appointment was stalled because of national security apprehensions
- The collegium headed by CJI Misra will soon give effect to the December 16, 2015 judgment of a five-judge bench mandating establishment of secretariats in the SC and each HC.
- The secretariat will collate data on the track record of persons being considered for appointment as judges and place it before the collegium.
2. After foodgrain and LPG, direct transfer of benefits for fertilizers kicks in from Sunday
In news:
- The government will launch the much-awaited direct benefit transfer (DBT) of fertiliser subsidy in Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland, Daman and Diu, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Puducherry and Goa.
- Unlike other DBTs such as cash transfer for foodgrains or subsidised gas connection where the subsidy amount is directly transferred to beneficiary accounts, in this case the subsidy will go to the manufacturer or marketing firm.
- No- denial policy: The government will follow the no-denial policy, which means anyone can buy any quantity of fertiliser after giving details of his Aadhaar card at the retail outlet.
- Under this scheme, the retail fertiliser outlets equipped with PoS machines will be able to read buyers’ Aadhaar cards. As the farmer buys, the difference between market rate and the subsidised amount will be credited to the bank account of the manufacturer or the marketing company concerned.
- First phase of implementation: After assessing the success of its implementation and capturing the details of consumption, government will consider to launch phase-II, which will be transferring the subsidy to the accounts of farmers.
- Advantages:
- Records of sales and purchase will bring transparency about the quantity of fertilisers that companies are selling to farmers.
- Experts opinion: this move will reduce the total sale by 10-15% and thereby reduce the burden on the exchequer by about Rs 6,000 crore annually.
Context:
- The Centre recently approved Rs 25000 Cr modernisation of police force scheme which will be implemented between 2017 and 2020.
Police force modernization:
- It will strengthen the law and order apparatus, modernise state police forces and enhance their capacity to combat terrorism.
- It also has special provisions for women’s security, mobility of police forces, logistical support, hiring of helicopters, upgradation of police wireless, satellite communications, crime and criminal tracking network and systems (CCTNS) and e-prisons.
- The idea is to assist the states to upgrade their police infrastructure, especially in respect of transport, communications and forensic support, to enable them to effectively tackle the emerging challenges.
Funding Pattern:
- Centre share 75 per cent while the states’ share will be the rest.
- Under the scheme, J&K, north-eastern states and states affected by Left-Wing Extremism will get a boost of Rs 10,132 crore.
- 14th Finance Commission’s recommendations increased the state’s share of central taxes from 32 per cent to 42 per cent, following which Centre de-linked eight centrally sponsored schemes (CSS) from its support in 2015.
- While central funding of modernisation of police was stopped, non-plan funding for the same would continued.
- Thereafter, majority of state governments were disinclined to make any investments in police.
- But, the Centre again started its funding in internal security with modernization of police forces scheme on the recommendation of Cabinet Committee on Security.
Smart Police
- The PM in 2014 enunciated the concept of SMART police. The smartness has two dimensions external and internal.
- External Dimension refers to the uniform a policeman wears, the way he carries himself, his weapons, the communication equipment on his person, his mobility, response time, et al. The scheme would enhance his capabilities to respond to and deal with the kind of challenges he is confronted with in his day to day work.
- Internal Dimension refers to the expanded acronym of SMART that is, the police should be strict and sensitive, modern and mobile, alert and accountable, reliable and responsible, tech-savvy and trained. This is far more important than the external dimension but the scheme hardly improves this aspect.
Problems:
- Today we have Ruler’s police but what we need is People’s police.
- Accountability has to be to the Constitution, the laws of the land and the people of the country.
- The police is being accused of being insensitive to poor and tribals.
Way Forward
- Reliability would increase only when the police are objective, fair and impartial. Gadgetry won’t help here.
- It is the state of mind which matters. And to achieve that state of mind, police must be freed from the stranglehold of politicians.
- The scheme must be followed by structural reforms, institutions like the state security commission, police establishment board and complaints authority must be set up in every state in keeping with the directions of the Court.
- The GOI should bring police and public order in the Concurrent List of Schedule VII of the Constitution. Constitutional experts like Fali S. Nariman have strongly spoken in favour of such an amendment.
- Sustained economic progress needs the solid foundation of good law and order, and we cannot have good law and order in the country unless the police are reorganised, restructured and rejuvenated.
Cabinet Committee on Security Central Sector Scheme Centrally Sponsored Schemes 4. Major Swachh hiccups: Funds crunch, failure to transport and segregate waste Context: In news: Reasons:
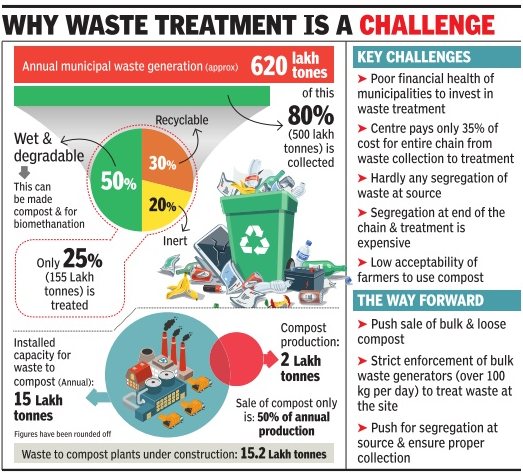
Category: ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE AND ECOLOGY
1. Govt’s wildlife action plan to focus on e-surveillance
Context:
- New National Wildlife Action Plan (2017-31).
- The action plan will be launched by environment minister Harsh Vardhan on the inaugural day of the Global Wildlife Programme (GWP)
In news:
- The Centre will announce its new National Wildlife Action Plan (2017-31) on October 2 to strengthen conservation measures.
- Use of technology, including e-surveillance through drones, and modalities to involve people living around national parks and sanctuaries in conservation efforts will be key to this 14-year roadmap.
- The action plan spells out how India will go about handling these issues in a time-bound manner in the next 14 years.
- It covers all the issues concerning conservation, ranging from rehabilitation of threatened species to integrating climate change in wildlife planning.
- The plan has a road map to deal with poaching and illegal trade of animals and animal parts, and management of tourism in wildlife areas.
- Setting up special courts for effective implementation of the Wildlife Protection Act to ensure the speedy trial of wildlife crimes, identification and validation of Indigenous Traditional Knowledge (ITK) available in various parts of the country for dealing with human-wildlife conflicts, and use of mobile technology to develop ‘Digital Field Guides’ for easy identification of various wildlife goods and their derivatives are other key features of the plan.
- The plan cites as a model the Gujarat forest department’s initiative to appoint local youth as ‘Vanya Praani Mitra’ (friends of wild animals) in in high conflict zones.
- The four-day conference will give India an opportunity to get acquainted with best practices on the management of wildlife habitats and minimising human-wildlife conflict situations.
Global Wildlife Programme (GWP):
- The GWP, initiated in 2015, is a World-Bank led partnership of 19 countries to promote the conservation and sustainable development by combating trafficking in wildlife.
C. GS3 Related
Nothing here for Today!!!
D. GS4 Related
Nothing here for Today!!!
E. PRELIMS FACT
Nothing here for Today!!!
F. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
Question 1. Consider the following statements with reference to Global
Wildlife Programme.
- It is a World-Bank led partnership of 19 countries.
- It seeks to promote the conservation and sustainable development by combating trafficking in wildlife.
Choose the correct answer
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Question 2. Among the following who are the Agaria Community?
- A traditional toddy tappers community of Andhra Pradesh
- A traditional fishing community of Maharashtra.
- A traditional silk-weaving community of Karnataka
- A traditional salt-pan workers community of Gujarat.
Question 3. In which State is the Buddhist site Tabo Monastery located?
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Himachal Pradesh
- Sikkim
- Uttarakhand
Question 4. In which one of the following States has India’s largest private
sector sea port has been commissioned recently?
- Andhra Pradesh
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Tamil Nadu
Question 5. An increase in the Bank Rate generally indicates that the
- Market rate of interest is likely to fall
- Central Bank is no longer making loans to commercial banks
- Central Bank is following an easy money policy
- Central Bank is following a tight money policy
Question 6. If Panchayats is dissolved, elections are to be held within
- 1 month
- 3 months
- 6 months
- 1 year
G. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
GS Paper II
-
Electronic cash transfer system for the welfare schemes is an ambitious project to minimize corruption, eliminate wastage and facilitate reforms. Comment.
GS Paper III
- What were the reasons for the introduction of Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act, 2013? Discuss critically its salient features and their effectiveness.
- What is the meaning of the term ‘tax expenditure’? Taking housing sector as an example, discuss how it influences the budgetary policies of the government.
Also, check previous Daily News Analysis
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Current Affairs Webinar’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series
Comments