CNA 11 Dec 2021:- Download PDF Here
TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS 1 Related B. GS 2 Related POLITY AND GOVERNANCE 1. ‘80% of funds for Beti Bachao was spent on media campaigns’ C. GS 3 Related ENVIRONMENT 1. President calls for a debate on right to climate justice 2. Center looking to use stubble as biofuel D. GS 4 Related E. Editorials ECONOMY 1. Goods and Services Tax as an unfinished agenda HEALTH 1. Make the mental well-being of teachers a priority F. Prelims Facts 1. Summit for Democracy 2. Singareni Mines 3. International Solar Alliance G. Tidbits 1. Algo trading H. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions I. UPSC Mains Practice Questions

A. GS 1 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
B. GS 2 Related
Category: POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1. ‘80% of funds for Beti Bachao was spent on media campaigns’
Topic: Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States, issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure, devolution of powers and finances up to local levels and challenges therein.
Mains: Critical Evaluation of Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao Scheme
Context
The Parliamentary Committee on Empowerment of Women has urged the government to revisit the strategy for ‘Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao’ (BBBP) as 80% of its funds are spent on media campaigns.
Read more on Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao in the linked article.
Criticism of Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao
- Excessive expenditure on communication-related activities: The committee noted that the massive spending on advertisements was despite the clearly laid-down formula for utilization of funds.
- Inefficient allocation and release of funds: The C&AG issued a study criticizing the scheme’s execution, saying that fewer than 20% of the total funds provided by the Centre were actually spent at the state level in 2016-17.
- Implementation challenges: The scheme faces several challenges ranging from underutilisation of available funds, to lackadaisical implementation and failure of monitoring mechanisms, particularly at the state and district levels.
- Unbalanced expenditure patterns: The expenditure planned for the BBBP is highly skewed towards just one pillar of the BBBP scheme. This provides no provision for improving the scheme’s long-term, quantifiable effects on education and health.
Recommendations to strengthen BBBP implementation

Conclusion:
To guarantee that the BBBP’s implementation is reoriented in the proper direction, task forces at the national, state and district levels must accept overall responsibility for scheme implementation at each level and be held accountable for achievements and failures.
C. GS 3 Related
1. President calls for a debate on right to climate justice
Topic: Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
Mains: Right of Climate Justice; Concerns of Climate Justice in India and Recommendations
Context
- The Indian President had called for a debate on the right to climate justice.
What is Climate Justice?
- “Climate justice” refers to the recognition that climate change can have varying social, economic, public health, and other negative effects on vulnerable groups.
- Key factors of Climate Justice are:

Human Rights and Climate Change
- Climate change, as emphasized by the United Nations Human Rights Council in Resolution 26/27, “is an urgent global problem requiring a global solution.”
- There are challenges posed by climate change to the realization of all human rights for everyone, particularly those in vulnerable situations.
Aspects of Climate Justice:
- Procedural justice and distributional justice are two fundamental facets of climate justice.
- Procedural Justice ensures democratic decision-making that includes all people affected by climate change.
- Distributional Justice guarantees that the costs and rewards of dealing with the climate change problem are divided equitably and fairly based on responsibility and ability.
Concerns of Climate Justice in India:
- Extent of Sea-level Rise (SLR) Vulnerability: The level of SLR susceptibility in any specific coastal region is determined by a number of factors, including topography and climate conditions, population density, the area and proportion of the flooded zone, economic conditions, and the current political context.
- Floods: Recent research has shown social dangers connected with floods, to which certain groups are particularly vulnerable. Flooding, in particular, has not been recognised as an environmental justice issue with disproportionate risk exposure in south India.
- Pollution: Pollution is a source of stress, and when combined with SLR, the danger doubles for those living near coasts. They are vulnerable not just to high water levels and extended flooding caused by catastrophic weather occurrences, but also to pollution from the city and businesses.
- Climate risk vulnerability and justice: Climate change exposes the population and its weaker demographics to economic and health dangers. Socioeconomic, demographic, geographic and personal (disability) coordinates or ‘locations’ converge to render individuals vulnerable to climate change-induced repercussions.
Recommendations to Ensure Climate Justice:
- Appointment of a Special Rapporteur on human rights and climate change to identify best practices.
- Integration of human rights requirements, norms, and principles into international and national climate policy and action, including COP 21.
- Ensure mitigation and adaptation activities that put people first, are gender-sensitive, and protect people’s rights.
- Improved regulation of the private sector to reduce its impact on climate change and ensure human rights compliance in all of its operations.
- Increased collaboration based on justice and fairness principles to provide enough financing and research into adoption methods.
Conclusion:
- Incorporating justice into the climate problem can assist to build a brighter future for future generations while also better equipping society to deal with environmental dangers such as pandemics and climate change.
2. Center looking to use stubble as biofuel
Topic: Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
Mains: Potential of Stubble as biofuel
Context
- The centre is working on a plan to use stubble as a biofuel and manure to deal with stubble burning.
Stubble burning:
- Stubble burning is the purposeful burning of straw that remains after crop harvest.
- Farmers in Punjab, Haryana, and portions of Uttar Pradesh burn paddy and wheat straws, which has been identified as a major source of air pollution in Delhi NCR.
Potential of Stubble as Biofuel:
- Cultivation of silage crops (hybrid sorghum, hybrid napier grass, maize): They have a high yield, enabling farmers to meet the feedstock needs of cattle. They can also be used to produce biofuel plants.
- Biomass Depots: It is essential to undertake on-field baling of stubble, aggregate bales in a depot and enter into “bankable” agreements for supplies to Bio-Energy Plants. There should be fiscal incentives enabling green entrepreneurship.
- Solid Biofuels: These comprise briquettes and pellets. Briquettes are fired in industrial boilers or combustors but the demand in Punjab and Haryana is not high. Pellets can be co-fired in utility range boilers.
- Liquid Biofuels: They encompass bioethanol, drop-in fuels, bio-oil, bio-methanol. The current focus is on 2G Ethanol.
- Gaseous Biofuels: They include producer gas, biogas and green hydrogen. The current focus is on biogas upgraded to Bio-CNG, with co-product being compost.
Conclusion:
- Processing agricultural leftovers into bio-CNG and compost will assist many more farmer households, with other collateral advantages accruing from the assured provision of sustainable transportation. It is critical that India have a strategy that is technology-neutral in order to promote advanced biofuels.
Know more about Stubble Burning.
D. GS 4 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
E. Editorials
1. Goods and Services Tax as an unfinished agenda
Topic: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
Mains: Critical evaluation of Goods and Services Tax in the Indian Context.
Context
- This article criticizes the implementation of GST in the Indian context.
What is GST?
- GST, or Goods and Services Tax, is a tax innovation packaged in a “one nation, one tax” system.
- It was adopted by India in 2017, with modifications to fit the Indian context.
- GST is based on the destination-based consumption taxes theory.
- It provides for the seamless input tax credit with CGST imposed by the Centre, SGST levied by the States, UTGST levied by the Union Territories, and IGST levied on inter-state supplies, including imports.
- Except for human use alcohol and five designated petroleum products, GST applies to all goods and services.
- The GST paradigm in India is built on two pillars: revenue neutrality and GST compensation for states.
Know more about Goods and Services Tax (GST).
India’s GST architecture
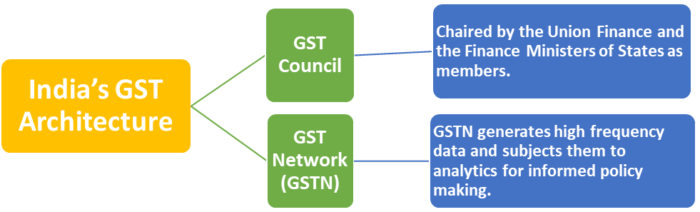
Issues with GST:
- States’ Concerns with GST:
- GST was only conceivable in India because the states agreed to give up a large portion of their constitutionally inherited indirect levies.
- Given the lack of revenue neutrality and a slew of other challenges, many states are left with little choice but to rely on GST compensation.
- While compensation must lawfully coexist with GST, even the constitutionally stipulated five-year compensation has not been provided in letter and spirit, requiring states to ask for their due.
- GST discriminates against manufacturing states, highlighting the necessity for a revenue-sharing model that properly incentivizes exporting states by dividing IGST money among three parties rather than two.
- Issues with IGST:
- Although IGST is a significant source of income for many states, the clearing house method and procedure remain unknown.
- There is a virtual information vacuum, particularly with regard to IGST, and there are various flaws in the digital architecture.
- GSTN is now in a slump. It does not make efficient use of the vast amounts of useful data being created, nor does it share it so that others might use it.
- Such “data monopoly” behaviour was a matter of history in India’s statistics system and must be eliminated sooner rather than later.
- Other Issues:
- The promised revenue neutrality remains a fantasy, and several states have seen their tax-to-GDP ratios fall.
- According to studies, the ratio of own tax income to GDP has decreased in the major 18 states.
- There are significant disparities in Revenue Neutral Rates (RNR) between producing and consumer states.
- The difficulties were exacerbated by widespread evasion following the removal of checkpoints, and then by the proliferation of bogus invoices, which rose by leaps and bounds.
- Exemptions and subventions exacerbated and aggravated the problem.
- Despite the fact that two expert panels recommended a bigger allocation for the states, GST is split evenly between the Centre and the States.
Global Experiences:
- South Africa: The South African experience illustrates how zero-rating and large exemptions have defeated revenue goals.
- Canada: Reviewing 30 years of the Canadian experience with GST, it is shown that GST could be improved by limiting zero-rating, tax exemptions and harmonizing tax rates.
- Brazil: The Brazilian experience indicates that transfers through social security or subsidies tend to be more progressive than subventions or exemptions.
Conclusion:
GST should be viewed as a revenue generator and a fiscal policy instrument for efficiency, competitiveness, and growth. It is debatable whether such undertakings as broadening exemptions and replacing the income tax with GST in the case of small and medium firms are appropriate approaches in the Indian environment.
1. Make the mental well-being of teachers a priority
Topic: Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
Mains: Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic on the mental health of teachers in India.
Context:
- This article discusses the impact of Covid-19 on the mental health of teachers.
Background:
- During the new coronavirus outbreak, India’s school education sector faltered.
- Learning loss, exhaustion from online learning, and mental stress have all been reported as issues with online learning for youngsters.
- Teachers were also challenged by relevant pedagogies integrated with digital media.
Pandemic-induced Challenges for Teachers:
- Significant challenges are:
- Working in schools under the Union government with better qualifications, working conditions
- Salaries and systemic protection to those in low-fee private schools with abysmally low salaries
- Poor working conditions and no systemic protection
- Those in medium-sized, metropolitan private schools experienced a new sort of “bullying” by being constantly “watched” by parents who pointed out even the smallest flaws.
- The challenges of COVID-19 duty were deployment and door-to-door operations. COVID-19 surveys, distribution of immunity booster pills, and police inter- and intra-district checkpoints are all part of the job.
- They had to keep records at COVID-19 care facilities, and managing lineups outside booze stores caused them to feel a ‘loss of identity’ at times.
- This unusual circumstance, along with media stories claiming that “teachers earned compensation without doing any job,” caused a great deal of emotional anguish.
- Teachers were also under continual pressure to present documentation of their attempts to keep learning ‘alive.’
- These attempts could not be adequately validated, nor could their efficacy be assessed.
- One of the most difficult issues for teachers throughout the pandemic was being completely cut off from touch with children during the Pandemic.
Consequences of the Pandemic on the Mental Health of Teachers:
- Teaching is not only a career for many instructors, but it is also the most fulfilling occupation since connecting with young children and teenagers provides them enormous pleasure and delight.
- Teachers’ imaginative answers to mitigating their own stress and strain resulted from mental tension caused by being cut off from children, which was fueled by the public opinion of teachers’ salaries as a big burden.
- It is becoming increasingly evident that our children are facing a mental health and well-being crisis.
- The pandemic brings to light the quiet epidemic of mental illness in teenagers and young people throughout the world.
- Teachers, as one of the main caregivers for children, have an impact on both the emotional environment of the classroom and the emotional and behavioural well-being of individuals in their care.
- The ability of the teacher to negotiate this obligation is heavily influenced by their own mental health and well-being.
Recommendations:
- Creating a friendly atmosphere in which teachers may talk about their everyday pressures and well-being with their colleagues.
- Teachers’ communities of practice and teacher unions can prioritize this issue.
- Incorporating mental health, well-being, and burnout management into teacher training and refresher training can help to prioritize mental health.
- Systemic investments in school mental health enable the creation of a well-being-focused environment, which is addressed through clearly defined policies on anti-bullying, redress of harassment and grievances, and the establishment of a support system of psychosocial services that teachers can access.
- Focusing on teachers’ little successes also contributes significantly to the development of a strengths-based culture.
- Recognizing and tackling this stigma at a systemic level will assist schools in creating an atmosphere where mental health may be discussed openly.
Conclusions:
There is no other option than to prioritize our instructors’ mental health. It is a critical first step in addressing our children’s mental health and well-being. Recognizing the structural obstacles that have been created for teachers, as well as focusing on teachers’ well-being and mental health, may help to ensure a safe and secure ‘future of our future.’
F. Prelims Facts
Context
- Indian PM at the Summit for Democracy highlighted the significance of India as the largest democracy.
Summit for Democracy
- The summit was convened by the US President.
- Aim: To strengthen democracies around the world.
- Presidential Initiative for Democratic Renewal:
- It was established by the US President.
- It plans to provide funds for supporting free and independent media, fighting corruption, strengthening democratic reforms, advancing technology for democracy, and defending free and fair elections.
Context
- Coal production at Singareni coal mines has been affected due to workers’ strikes.
Singareni Mines:
- Singareni is a village in the district of Khammam, Telangana, India.
- Singareni was the first place in Telangana where coal deposits were discovered.
Reference:
3. International Solar Alliance
Context
- The International Solar Alliance (ISA) has been granted Observer Status by the UN.
Reference:
International Solar Alliance (ISA)
G. Tidbits
Nothing here for today!!!
H. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions
Q1. Which of the following statements is/are correct with respect to the Soil Health Card Scheme?
- The card will contain an advisory based on the soil nutrient status of a farmer’s holdings.
- It will provide insurance coverage and financial support to the non-loanee small and marginal farmers in case of Soil erosion.
- It aims to expand cultivable area under assured irrigation to maintain soil fertility.
Options:
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 1, 2 and 3
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: a
Explanation
- A Soil Health Card is used to assess the current state of soil health and, over time, to detect changes in soil health caused by land management. The card will provide an advisory based on a farmer’s holding’s soil nutrient level. Hence Statement 1 is correct.
- The scheme will monitor the soil of the farmers well and will give them a formatted report.
- The soil card will give the farmers a proper idea of which nutrients their soil is lacking.
- The main aim behind the scheme was to find out the type of particular soil. And then provide ways in which we can improve it.
- The Soil Health Card does not provide insurance coverage and it does not aim to expand the cultivable area under irrigation. Hence Statements 2 and 3 are incorrect.
Q2. With reference to Atmanirbhar Hastshilpkar Scheme, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- It is an initiative of the Ministry of Culture to promote development of new talents in the field of music and dance, folk and tribal art forms.
- Under this scheme artisans are provided with a credit facility that is collateral-free and carries a subsidized interest rate of 6% p.a., which is repayable in 24 months.
Options:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both
- None
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: b
Explanation
- The North Eastern Development Finance Corporation Ltd (NEDFi) has launched the ‘Atmanirbhar Hastshilpkar’ initiative to help artisans in the Northeast. Hence Statement 1 is incorrect.
- The scheme’s goal is to give financial support in the form of a term loan for revenue-generating activities.
- The scheme provides a credit facility that is collateral-free and has a subsidized interest rate of 6% p.a., with a repayment term of 24 months. Hence Statement 2 is correct.
Q3. Which amongst the following ministries is/are associated with the Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao scheme?
- Ministry of Women and Child Development
- Ministry of Law and Justice
- Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
- Ministry of Education
- Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment
Options:
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 5
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: c
Explanation
- The Beti Bachao Beti Padhao Yojana is a national initiative jointly run by the Ministry of Women and Child Development, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and the Ministry of Education.
- Each body is accountable for different aspects of the scheme.
- Budgetary control and administration of the BBBP falls under the MoWCD’s purview. However, capacity building and quality control are responsibilities of the MoH&FW.
- Hence Option C is correct.
Q4. Royal Gold Medal is an award given to individuals who have made significant contributions to the field of
- Architecture
- Medicine
- Mathematics
- Journalism
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: a
Explanation
- The Royal Gold Medal for Architecture is presented yearly on behalf of the British monarch by the Royal Institute of British Architects in appreciation of an individual’s or group’s significant contribution to world architecture.
Q5. What is/are the most likely advantages of implementing ‘Goods and Services Tax (GST)’?
- It will replace multiple taxes collected by multiple authorities and will thus create a single market in India.
- It will drastically reduce the ‘Current Account Deficit’ of India and will enable it to increase its foreign exchange reserves.
- It will enormously increase the growth and size of economy of India and will enable it to overtake China in the near future.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: a
Explanation
- The Goods & Services Tax (GST) is a value-added tax applied on the majority of goods and services. GST is a destination-based tax which aims to create a single market in India. Hence Statement 1 is correct.
- The GST Bill was initially proposed in India as the 122nd Constitutional Amendment Bill in 2014. Because of crude oil imports and the OPEC cartel that manipulates its pricing, GST is unlikely to ‘dramatically’ lower the current account deficit. As a result, statement 2 is erroneous. India will not be able to overcome China in the foreseeable future since it will need currency depreciation and labour exploitation. Hence Statements 2 and 3 are incorrect.
I. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
- What steps are being taken by the Government of India to realize the complete potential of biofuels in the country? Also discuss the potential of such policy measures. (250 words; 15 marks) [GS3, Environment]
- We must give as much importance to the mental health of an individual as we do to physical health. In light of this statement, bring out the initiatives taken by the government to support the mental well-being of Indian citizens. (250 words; 15 marks) [GS2, Health]
Read the previous CNA here.
CNA 11 Dec 2021:- Download PDF Here

Comments