TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS1 Related SOCIAL ISSUES 1. Law on Honor Killing ART AND CULTURE 1. Decks cleared for 'Padmaavat' release as SC stays States' ban B. GS2 Related POLITY 1. Electoral bonds will not solve transparency issues in political funding: CEC INTERNATIONAL AFFAIRS/BILATERAL RELATIONS 1. Israel pushes for free trade 2. Modi to visit Palestine in February C. GS3 Related ECONOMY 1. India to set up $350 mn fund for solar projects to meet renewable energy target ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE AND ECOLOGY 1. 2017 was the second or third warmest year: UN 2. Penetration of solar energy in agriculture INTERNAL SECURITY AND DEFENSE RELATED 1. Agni-V extends its reach DISASTER MANAGEMENT 1. Disaster warning system for Odisha by March D. GS4 Related E. Prelims Fact F. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions G. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
A. GS1 Related
1. Law on Honor Killing
What is the new proposed law on Honor Killing?
- The National Commission for Women (NCW) proposed a special law to punish honour killings incited by khap panchayats 8 years back.
- The Supreme Court has said that adults are free to marry persons of their own choice and hurting couples, or summoning them before clan members, groups, or a khap, is absolutely illegal.
- The Prevention of Crimes in the Name of ‘Honour’ and Tradition Bill, 2010 was an outcome of the spate of murders and dishonourable crimes in the name of honour.
- Though killings and crimes were reported mostly from north India — especially Haryana, Punjab, Delhi and western Uttar Pradesh — as well as west India, the problem was widespread and almost every part of the country has witnessed such incidents.
What is Honour Killing?
- A crime in the name of ‘honour’ is one of a range of violent or abusive acts. This includes emotional, physical and sexual abuse and other coercive acts. In each of these cases, the family of the girl who has chosen to exercise her choice to marry is implicated.
- Those instrumental in committing these killings are families of the couple. Either they kill the couple themselves or in association with other persons from the same caste or khap or community-based panchayats.
What is the role of Khap Panchayats?
- The purpose of these panchayats or associations is to terrorise people and prevent associations, including marriage, on the basis of choice.
- They justify their actions in various ways, but commonly on the basis of custom and tradition. These acts show a violation of fundamental rights, including the right to life and liberty.
- Khaps exercise their authority in various ways: they demand payment from couples, impose social or economic sanctions on them, order that they or their families be boycotted, divest the couple of any land or property that belongs to them, and harass, intimidate, or murder them.
What did the NCW recommend?
- The NCW recommended that the anyone who kills or hurts an adult couple who chose to marry of their own free will should be punished for murder or any offence under the Indian Penal Code.
- The government agreed to the Supreme Court’s suggestion to frame guidelines recognising honour killing as a separate offence.
1. Decks cleared for ‘Padmaavat’ release as SC stays States’ ban
Context:
Padmaavat:
- The movie portrays the 13th century historical battle between Maharaja Ratan Singh’s army of Mewar and Sultan Alauddin Khilji of Delhi.
- Gujarat and Rajasthan had issued notifications prohibiting the screening of the film.
- Haryana had, in principle, agreed to a ban on the movie’s exhibition and Madhya Pradesh had made statements that they intend to ban the screening of the movie.
- The movie has been certified by the Censor Board.
Supreme Court order:
- The Supreme Court stayed the notifications and orders passed by certain States to prohibit the exhibition of Padmaavat.
- The court ordered all States to ensure that public law and order situation is maintained during the screening of the film across the country.
- The court ordered the States to protect the artistes and the people involved in the movie from threats.
- It further forbade the States from passing any order, notification which amounts to prohibition of the exhibition of the movie.
- The court said the grant of certificate by the Central Board of Film Certification (CBFC) under the Cinematograph Act of 1952 denudes the States of any power to exercise prohibition on the exhibition of the film.
- The apex court held that “once Parliament has conferred the responsibility and power on a statutory Board and the Board has certified the film, non-exhibition of the film by the States is contrary to statutory provisions”.
B. GS2 Related
1. Electoral bonds will not solve transparency issues in political funding: CEC
Context:
- Electoral bonds and transparency.
In news:
- Chief Election Commissioner A K Joti opinion:
- Electoral bonds will not solve all problems pertaining to transparency in political funding.
Change of stance of EC
- EC had told a parliamentary committee that electoral bonds introduced by the government is a “retrograde” step
- The commission, in a written submission to the parliamentary standing committee on law and personnel in May, had said changes made in the election laws after the introduction of the bonds would compromise transparency in political fundings
Electoral bonds:
- Electoral bonds were introduced by the government to make funding to political parties transparent.
- It will allow a political donor to purchase bonds from authorised banks and can be redeemed by parties only through registered accounts in a prescribed time frame.
- An electoral bond can be purchased by any citizen of India or a body incorporated in India.
- The bonds will be issued in multiples of Rs 1,000, Rs 10,000, Rs 1 lakh, Rs 10 lakh and Rs 1 crore, and will be available at specified branches of the State Bank of India.
- Donors can donate the bonds to their party of choice which can then be cashed via the party’s verified account within 15 days.
- Every party that is registered under section 29A of the Representation of the People Act, 1951, and has secured at least one per cent of the votes polled in the most recent Lok Sabha or assembly election will be allotted a verified account by the Election Commission.
- Electoral bond transactions can be made only via that account.
Category: INTERNATIONAL AFFAIRS/BILATERAL RELATIONS
1. Israel pushes for free trade
In news:
- The Israeli government is pushing for a free trade agreement (FTA) with India to boost trade and investments.
- Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, pitched for lowering the tax rates and removal of excessive regulations which would help the private businesses to prosper.
- Israel has FTA with the U.S., E.U., Turkey, Brazil, Canada and Mexico and many with Asian countries.
- The bilateral trade with Israel increased to $5 billion FY17 from $4.9 billion FY16.
2. Modi to visit Palestine in February
In news:
- PM Modi is expected to travel to the Palestinian capital of Ramallah on February 10
- This will be the first time that an Indian Prime Minister will visit the Palestinian capital of Ramallah
India back at balancing between Israel-Palestine
- The trip indicates that India remains on track with its traditional stance on Palestine
- Palestine had praised India’s recent vote in the UN against the U.S. recognition of Jerusalem as the capital of Israel
- The issue of Indian support to the two-state solution was also discussed during the meeting between Prime Minister Modi and Mr. Netanyahu (Israel PM)
C. GS3 Related
1. India to set up $350 mn fund for solar projects to meet renewable energy target
In news:
- India will set up a $350 million fund to finance solar projects.
- The country steps up efforts to achieve its ambitious target of adding 175 gigawatts (GW) in renewable energy by 2022.
- Key fact:
- India will need at least $125 billion to fund a plan to increase the share of renewable power supply in the country’s grid by 2022, underlining the immense financing challenge ahead.
- India expects renewable energy to make up 40% of installed power capacity by 2030, compared with 18.2% at the end of 2017.
- Installed renewable power capacity is currently about 60 GW, and India plans to complete the bidding process by the end of 2019/20 to add a further 115 GW of installed renewable energy capacity by 2022.
- Foreign capital: India wants foreign capital to account for a bulk of its investments to meet its renewable energy target.
Category: ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE AND ECOLOGY
1. 2017 was the second or third warmest year: UN
In news:
United Nations World Meteorological Organization’s observation:
- The warmest year without an El Niño: 2017 was the second or third warmest on record behind 2016, and the hottest without an extra dose of heat caused by an El Niño event in the Pacific Ocean.
- Average surface temperatures in 2017 were 1.1°C (2.0 Fahrenheit) above pre-industrial times, creeping towards a 1.5°C (2.7 F) ceiling set as the most ambitious limit for global warming by almost 200 nations under the 2015 Paris climate agreement.
- Temperatures in both 2016 and 2015 were lifted by an El Niño , a natural event which can disrupt weather patterns worldwide every few years and releases heat from the Pacific Ocean into the atmosphere.
- Warmth in Arctic: Arctic warmth has been especially pronounced and this will have profound and long-lasting repercussions on sea levels, and on weather patterns in other parts of the world.
2. Penetration of solar energy in agriculture
Which states are using Solar power in Agriculture?
- Maharashtra is solarising its agricultural feeders by installing solar power plants at the substation level, through competitive bidding.
- Karnataka is promoting solar pumps for existing grid-connected farmers under a net-metering regime, allowing them to generate additional income by feeding back surplus energy into the grid.
- In eastern States, GIZ, a German development agency, has piloted community ownership models providing water-as-a-service using solar pumps.
What is the overall status of deployment in India?
- Despite the diversity of approaches and significant government subsidies, only about 1,42,000 pumps have been deployed till date against a target of one million pumps by 2021.
- Such limited demand, in a country with 132 million farmers and 28 million existing irrigation pumps, calls for a reflection on existing deployment approaches.
What is the scope of Solar power in Indian agriculture?
- In India, 53% of the net-sown area is still rain-fed. Solar pumps hold potential to enhance irrigation access, advance low-carbon agriculture, reduce the burden of rising electricity subsidies, and improve the resilience of farmers against a changing climate.
What can be done?
- Farmers’ perspectives have to be considered and the local context appreciated when deploying the technology to maximise economic returns.
The government needs to consider the following while promoting solar for irrigation.
- First, target marginal farmers with smaller solar pumps, particularly in areas with good groundwater development potential. Our research, based on a recent primary survey of 1,600 farmers in Uttar Pradesh, revealed that close to 60% of marginal farmers relied on buying water, the costliest option for irrigation, or on renting pumps to meet their needs.
- Second, couple solar pump deployment with micro-irrigation and water harvesting interventions at the farm and community levels. While lack of irrigation is a major bottleneck, 30% of farmers reported limited water availability for irrigation as a challenge.
- Third, focus on technology demonstration and deploy at least five solar pumps in each block of the country. CEEW research suggests that such efforts could have a profound effect on farmers’ willingness to adopt solar pumps and spur bottom-up demand.
- Fourth, in regions with already good penetration of electric pumps, prefer feeder solarisation through competitive bidding over solarisation of individual pumps. A comparative economic analysis finds that solarising individual grid-connected pumps is the costliest approach for the government to expand irrigation cover, while not being the most attractive option for farmers.
- Fifth, in regions with prevailing local water markets, promote community-owned solar pumps. CEEW research finds that while joint ownership drew interest from 20% of farmers, close to 80% of them were interested in buying water from a community-owned or enterprise-owned solar pump at competitive prices.
- Sixth, encourage sharing of solar pumps among farmers through farmer extension programmes. Given zero marginal cost of pumping with solar, water sharing, already a prevalent practice in many parts of the country, helps put a marginal price to the water.
- Seventh, provide interest-subsidy to farmers combined with reduced capital subsidy to enable large-scale deployment of solar pumps in a shorter span of time. Such an approach would cover a greater number of farmers, helping them reap the benefits of solar pumps sooner, and increase overall returns to the economy.
India must exploit the potential of this decentralised technology to achieve the dual national targets of 100 GW of solar and doubling farmers income by 2022 — setting a world-class example of greening the economy and overcoming its developmental challenges, simultaneously.
Category: INTERNAL SECURITY AND DEFENSE RELATED
1. Agni-V extends its reach
In news:
- India successfully tested Agni-V, validating the long range surface-to-surface ballistic missile’s reliability.
- Agni-V, with a range of over 5,000 km, is India’s longest range ballistic missile and can reach most parts of China, making it the mainstay of India’s triad to deliver nuclear weapons.
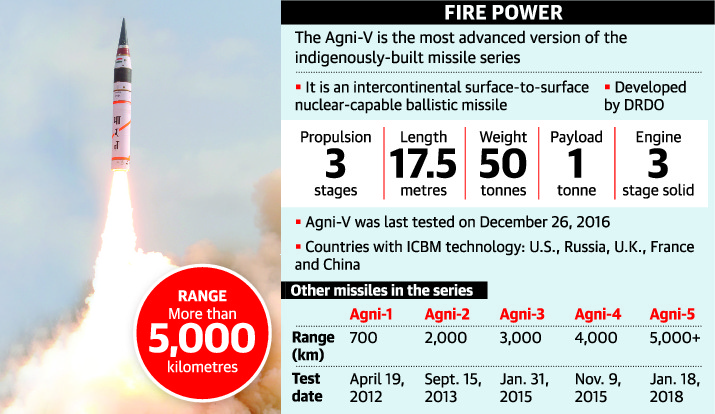
- The user associate test-flight of the missile has further boosted indigenous missile capabilities and deterrence strength of the country.
- Agni-V is the most advanced missile in the Agni series with new technologies incorporated in it in terms of navigation and guidance, warhead and engine.
- The missile is so programmed that after reaching the peak of its trajectory, it will turn towards the Earth to continue its journey towards the intended target with an increased speed due to the attraction of the Earth’s gravitational pull.
1. Disaster warning system for Odisha by March
Early Warning Dissemination System (EWDS):
- A project that aims at establishing a fool-proof communication system to disseminate disaster warning up to the community level.
- The EWDS is a first of its kind automatic public address system in the country.
- The EWDS for last mile connectivity is being implemented under a World Bank project.
- It will help the State to warn a vast population residing along its coast from the State headquarters through loud sirens from towers installed at 122 locations in the event of occurrence of natural disasters like a tsunami or cyclone.
- Some of the technical features of the project include satellite-based mobile data voice terminals (SBMDVT), digital mobile radio (DMR), mass messaging system to be operated from the State emergency operation centre and universal communication interface to allow interoperability among different communication technologies.
- SMS alerts: The mass messaging system facilitates sending warning messages through SMS to all mobile phone subscribers in a particular locality or area likely to be affected by a threatening disaster.
D. GS4 Related
Nothing here for Today!!!
E. Prelims Fact
Nothing here for Today!!!
F. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
Question 1. With reference to the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) and El Nino, consider the following
statements:
- While the El Nino causes the warming of the surface of Pacific Ocean, IOD causes warming of the Indian Ocean
- While the El Nino always brings deficient rainfall in India, IOD always brings more rains in India
Which among the above statements is / are correct?
- Only 1
- Only 2
- Both 1 & 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
See
Question 2. Consider the following statements with reference to Electoral Bonds.
- An electoral bond can be purchased by any citizen of India or a body incorporated in India.
- The bonds will be issued in multiples of Rs 1,000, Rs 10,000, Rs 1 lakh, Rs 10 lakh and Rs 1 crore, and will be available at specified branches of the State Bank of India.
- Donors can donate the bonds to their party of choice which can then be cashed via the party’s verified account within 15 days.
Identify the correct statement/s from the codes given below:
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1 only
- 1, 2 and 3
See
Question 3. Consider the following statements with reference to Agni-V missile.
- It is an intercontinental surface to surface ballistic missile
- It is the most advanced version of indigenously built missile series.
- Its range is more than 5000Kms.
Identify the correct statement/s from the codes given below:
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1 only
- 1, 2 and 3
See
Question 4. With reference to the Agreement at the UNFCCC Meeting in Paris in 2015, which
of the following statements is/are correct?
- The Agreement was signed by all the member countries of the UN and it will go into effect in 2017.
- The Agreement aims to limit the greenhouse gas emissions so that the rise in average global temperature by the end of this century does not exceed 2 °C or even 1.5 °C above pre-industrial levels.
- Developed countries acknowledged their historical responsibility in global warming and committed to donate $ 1000 billion a year from 2020 to help developing countries to cope with climate change.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
See
Question 5. Consider the following statements about Sukanya Samridhi Yojana.
- It is subpart of Beti Bachao campaign.
- Account will remain operative until she reaches 18 age.
- For initial account opening, minimum deposit Rs.1000 required.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- Only 1 and 2
- Only 2 and 3
- Only 1 and 3
- All of the above
See
G. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
GS Paper I
- Discuss the mechanism and origin of Monsoon winds and explain the role of El Nino on Monsoon circulation.
GS Paper IV
- You are the Executive Director of an upcoming InfoTech Company which is making a name for itself in the market.
Mr. A, who is a star performer, is heading the marketing team. In a short period of one year, he has helped in doubling the revenues as well as creating a high brand equity for the Company so much so that you are thinking of promoting him. However, you have been receiving information from many corners about his attitude towards the female colleagues; particularly his habit of making loose comments on women. In addition, he regularly sends indecent SMS’s to all the team members including his female colleagues.
One day, late in the evening, Mrs. X, who is one of Mr. A’s team members, comes to you visibly disturbed. She complains against the continued misconduct of Mr. A, who has been making undesirable advances towards her and has even tried to touch her inappropriately in his cabin. She tenders her resignation and leaves your office.
- What are the options available to you?
- Evaluate each of these options and choose the option you would adopt, giving reasons.
Also, check previous Daily News Analysis
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Current Affairs Webinar’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series
Comments