CNA 24 Dec 2021:- Download PDF Here
TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS 1 Related B. GS 2 Related POLITY 1. Understanding the Election Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2021 INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS 1. India seeks early return of democracy in Myanmar C. GS 3 Related D. GS 4 Related E. Editorials ECONOMY 1. This clean cooking fuel plan needs more firing up 2. Do Indians need insurance for bank deposits? F. Prelims Facts 1. ‘Population not the sole factor in J&K delimitation’ G. Tidbits 1. Why the Indian Rupee is Weakening 2. CM Stalin launches green scheme 3. Not all Muslims oppose marriage Bill H. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions I. UPSC Mains Practice Questions

A. GS 1 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
B. GS 2 Related
1. Understanding the Election Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2021
Topic: Salient Features of the Representation of People’s Act.
Prelims: Representation of People’s Act – provisions
Mains: Arguments for and against the move to link voter ID with Aadhaar numbers
Context:
- The Election Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2021 seeks to amend the law relating to elections. It amends both the Representation of the People Acts of 1950 and 1951.
- A key amendment relates to the linking of the electoral rolls with the Aadhaar ecosystem.
For detailed information on the provisions refer to the following article:
UPSC Exam Comprehensive News Analysis of 21st Dec 2021
Arguments for and against Aadhaar-voter ID linking:
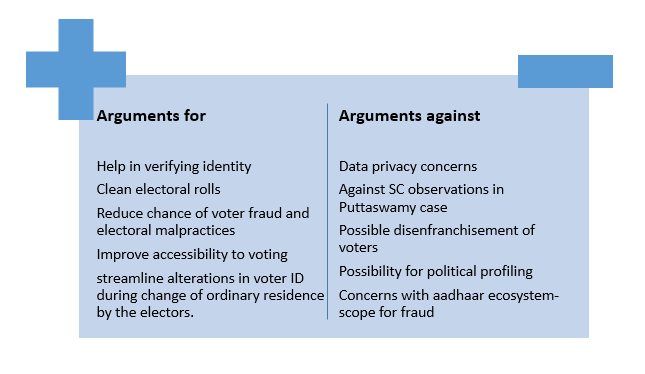
Arguments for:
- The linking of aadhaar and voter ID will help in verifying the identity of voters.
- The Aadhaar database contains the unique identification numbers of every resident in the country.
- Aadhaar information is authenticated using biometrics, which cannot be replicated, and in turn, the duplication of voter ID cards is prevented.
- The linking will help weed out bogus voters and those who figure in the electoral rolls in more than one constituency (help check multiple registrations of the same voter). Thus it will help in reducing voter fraud and cleaning the electoral rolls of the country. This will help in consequently reducing electoral malpractices.
- A Parliamentary Standing Committee report had also argued for linkage of unique Aadhaar ID Card numbers with voter I-card as it would help streamline alterations in voter ID during change of ordinary residence by the electors.
- As per the Election Commission of India, the integration can help improve accessibility to voting in India. The move can help allow migrant workers the right to vote regardless of their location, in order to let them participate in elections in their home states. One of the major reasons why India lags in voter participation compared to other large democracies is because of the large number of migrant workers in India— an estimated population of 300 million. Linking the two databases will allow the ECI to track migrant workers and improve election participation.
Arguments against:
- Given the reports of data insecurity of the data of the Aadhaar Card and the absence of robust data protection standards like a Personal Data Protection Law, there is always the danger of misuse and data leaks. This raises serious data privacy concerns.
- The linking of voter IDs and Aadhaar violates the fundamental right to privacy as defined by the Supreme Court in a judgment. The move goes against the Supreme Court judgment that limits the use of Aadhaar to the financial and welfare benefits given by the government, and bars the unnecessary expansion of the scope of Aadhaar to other areas of life.
- It may lead to large-scale deletion of names either inadvertently or by deliberate targeting. This possibility of disenfranchisement of voters is a major cause of concern associated with the move.
- The Aadhaar database is also strewn with errors and therefore linking it to the voters’ list could result in omission errors.
- A similar attempt to curate electoral rolls in Telangana and Andhra Pradesh through the UIDAI in 2018 by the election commission had resulted in the deletion of names of lakhs of voters in Telangana.
- Though the law states that the step is voluntary in nature, the provision that the inability or non-submission of aadhaar number must have “sufficient cause as may be prescribed”, means that it is not really voluntary, as only a set of reasons to be prescribed later can be given for those who cannot or do not wish to give their Aadhaar number.
- It may help political parties to profile voters as favourable or unfavourable. Hence it might be used for political profiling which does not augur well for a democracy. It could lay the foundation of targeted political propaganda which is against the model code of conduct as well.
- Such fear has precedent. There have been examples of targeted surveillance using Aadhaar information and demographic data.
- Justice B N Srikrishna, Chairman of the committee that drafted the Personal Data Protection Bill, had earlier called the ECI’s proposal to link the two databases “most dangerous,” arguing that “if [the government] can collate the data, [it] can profile human beings.
- Given the reported scope for fraud with Aadhaar, this process could undermine the sanctity of the voter roll.
- Some have pointed out the fact that Aadhaar is not proof of citizenship. They argue that the move to link aadhaar with voter ID could lead to giving voting rights to non-citizens.
Category: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. India seeks early return of democracy in Myanmar
Topic: India and its Neighborhood – Relations.
Mains: India-Myanmar bilateral relationship – Significance and challenges
Context:
- Indian Foreign Secretary’s visit to Myanmar.
Background:
- The military, led by General Min Aung Hlaing, had displaced a democratically elected government in Myanmar through a military coup.
- This was followed by protests by citizens demanding the restoration of democracy.
- The military had launched a campaign against the democratic elements in Myanmar, while the democratic protest has received support from the insurgent groups in Myanmar’s forested regions that border India. This had given rise to a cycle of violence in Myanmar.
Also read: India – Myanmar relations
Details:
- The visiting Foreign Secretary has called on the Myanmar administration for the early restoration of democracy and has also conveyed India’s offer to mediate between the various stakeholders to end the crisis in Myanmar through dialogue.
- The foreign secretary raised India’s past engagements with different stakeholders to stabilise the country.
- India had hosted various democratic groups of Myanmar for many years after the 1988 crackdown that forced them to seek shelter abroad.
- India emphasized its interest in seeing normalcy return in Myanmar.
- The large influx of displaced people from Myanmar into India and the escalating narcotic and insurgent movements in the northeastern States has added to India’s problems.
- Given that India shares a 1700-km long border with Myanmar that runs along the states of Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Nagaland and Mizoram, the developments in Myanmar would have a direct impact on India’s bordering regions. Hence peace and stability in Myanmar remain of utmost importance to India.
For more related information on this topic refer to the following article:
UPSC Exam Comprehensive News Analysis of 22nd Dec 2021
C. GS 3 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
D. GS 4 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
E. Editorials
1. This clean cooking fuel plan needs more firing up
Prelims: Ujjwala Scheme
Mains: Government Subsidies on LPG.
Context:
Sustaining LPG adoption in rural India.
Details:
- The Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) is ‘a flagship scheme of 2016, with an objective to make clean cooking fuel such as LPG available to the rural and deprived households which were otherwise using traditional cooking fuels such as firewood, coal, cow-dung cakes’.
- The scheme originally envisaged the distribution of 50 million LPG connections to women below the poverty line. Later, it aimed to provide LPG connections to eight crore women by March 2020. However, this target was achieved seven months prior, in September 2019.
- In Union Budget 2021, the government has extended the benefits under PM Ujjwala Yojana additional one crore beneficiaries.
Eligibility for Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana:
Any applicant who fulfils the below-mentioned criteria is eligible to apply for the Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana:
- The applicant must be a woman aged above 18 years. She must also be a citizen of India.
- She should belong to a family below the poverty line and no one else from the household should own an LPG connection.
- The overall monthly income of the family should not exceed a certain limit that is prescribed by the UT/State Governments.
- The applicant’s name should be in the list of SECC-2011 and should also match with the information provided in the BPL database of the oil marketing companies.
- The applicant should not be registered under any other similar scheme provided by the government.
Apart from the above, the applicant should also submit a set of documents indicating her BPL status, identity, etc.
Data on LPG use:
- Over the five years, the average per capita consumption among Ujjwala customers has risen from three cylinders per year (of 14.2 kg) to 4.2 (2020-21).
- Relatively poorer Ujjwala consumers are reaching the LPG consumption levels of relatively well-off non-Ujjwala rural consumers.
- A paper in Nature showed that only 45% of non-Ujjwala rural consumers use five or more cylinders per year, while data from oil marketing companies show that from October 2020 to September 2021, 32% of Ujjwala households were using five cylinders or more in a year.
Benefits of Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana:
- It has been seen that there are high returns in terms of health gains by targeting pregnant women to have LPG access.
- Cooking with gas helps tuberculosis patients.
- During extreme weather events, LPG cylinders come to the rescue. The scheme effectively addresses several difficulties faced by the people in the States of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, Assam, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, and Tripura in accessing LPG for cooking purposes.
- The scheme can be a tool for women empowerment in that LPG connections and clean cooking fuel can reduce cooking time and effort, and in most of India, cooking is a responsibility shouldered solely by women.
- Financial support of Rs. 1600 is provided by the scheme for each LPG connection for BPL households. The administrative cost of this support is borne by the Government. This subsidy is meant for the security fee for the cylinder, pressure regulator, booklet, safety hose, and other fitting charges.
- Under the scheme, oil marketing companies also provide interest-free loans for refilling and purchasing stoves.
- The Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana covers all the BPL families that come under all forms of distributorship and distributes various sizes of cylinders (14.2 kg, 5 kg, etc.) as per the field situation.
- The benefits of this scheme are also available for the people of all Hilly States including the NE States (who are treated as ‘Priority States’).
- The scheme also employs the rural youth in the supply chain of cooking gas.
Factors that helped:
- Government enhanced various capacities such as that of the ports for handling imports, of tanks for storage of LPG, of pipelines and trucks for transportation of gas, and of bottling plants for filling in more cylinders.
- Production of cylinders, pressure regulators, hose and affordable LPG stoves was also enhanced.
- Successful implementation of the Direct Benefit Transfer of LPG (DBTL) or PAHAL (Pratyaksh Hanstantrit Labh) scheme, also freed up the financial resources needed to dream of a large-scale programme for deposit-free LPG connections.
Way Forward:
- The push has to be such that every household moves toward adopting a more sustainable cooking energy basket.
- Improvements in regular and on-demand supplies of LPG.
- Financing option for refill.
- Alternative remunerative uses for cow dung and biomass — possibly on the pattern of procurement of cow dung as is being done in Chhattisgarh.
- A massive boost to women’s incomes through the National Rural Livelihoods Mission will also help in nudging to a more sustainable cooking mix.
2. Do Indians need insurance for bank deposits?
Topic: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization, of resources, growth, development and employment.
Prelims: Banking
Mains: Indian Economy
Context:
- Introduction of Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) Amendment Bill, 2021.
About the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) Amendment Bill, 2021:
- The deposit insurance scheme was upgraded through the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) Amendment Bill, 2021.
- It guarantees to compensate depositors up to a limit of ₹5 lakh within a period of 90 days from when a bank fails.
Causes of raising the deposit insurance limit:
- In India, the ₹1 lakh limit was set many decades ago. Now, if you do a simple calculation based on the inflation rate, the ₹1 lakh limit that was set in the 1990s is inadequate.
- India’s insurance limit is much lower than those of several comparable economies, e.g. South Korea, USA, etc.
- It is a step to try and infuse more confidence in the banking system. Raising the limit of deposit insurance will give confidence to depositors that if a bank does go down, they don’t need to run to the bank. They can keep their money in the bank, and the bank can continue operating without any financial trouble.
Disadvantages of India’s deposit insurance system:
- As India has implicit insurance of 100% of deposits, that is why it led to a lack of discipline in depositors and investors.
- On the other hand, premiums the banks pay to deposit insurance agencies are flat premiums. Hence there is no difference among risky or less risky banks, both pay the same premium. In finance, it is not a fair practice.
- Due to the lack of a risk-adjusted premium model, investors are not discerning enough to figure out the good banks.
- In the current risk management system, RBI is always a few steps behind the banks. It always plays a catch-up game in terms of figuring out the true level of risk that banks have taken.
Way Forward:
- India needs to move to a more risk-adjusted premium model. Hence, risk information will reach depositors sooner and they will be more wary of investing money.
- A better monitoring system of banks needs to be established.
- At the time of a banking crisis, the government should manage this issue. In India specifically, the RBI can do this decent job of regulating the system.
- The RBI and other regulatory agencies have to be really on top of the precise risk model, the disclosure of that information and quick action before a bank fails. To do this, the Indian banking system needs to have a good model to figure out which bank is under stress.
F. Prelims Facts
1. ‘Population not the sole factor in J&K delimitation’
- A provision in the delimitation acts from 1952 onwards states that other than population, factors like physical features, boundaries of administrative units, communication facilities and public convenience should be taken into account while drawing constituency boundaries.
- Section 9 (1) (a) of the Delimitation Act, 2002, states that all “constituencies shall, as far as practicable, be geographically compact areas, and regard shall be had to physical features, existing boundaries of administrative units, facilities of communication and public convenience”.
G. Tidbits
1. Why the Indian Rupee is Weakening
- The Indian rupee’s exchange rate has recorded a record slip in its value. The fall in its value is driven mainly by a widening trade deficit and foreign investors pulling out funds from equities.
- Notably, however, the rupee’s fall is modest when compared to the currencies of other emerging economies.
2. CM Stalin launches green scheme
- Tamil Nadu government has launched the ‘Meendum Manjappai’ scheme to promote the usage of cloth bags by the general public and discourage plastic bags.
- Indiscriminate usage of single use plastic bags is contributing to plastic pollution. Plastic pollution has harmful effects on not only the flora and fauna of the world but is also found to adversely impact human health.
3. Not all Muslims oppose marriage Bill
- While some political parties have opposed amendments to the child marriage law to raise the age of marriage for women to 21, terming them as an attack on personal laws, voices within the minority communities advocating equal rights, have welcomed the move.
- The Supreme Court in Independent Thought versus Union of India, 2017, had held that the Prohibition of Child Marriage act will over-rule personal laws.
- This has brought attention to the need to have a uniform civil code for all communities, as the lack of it is leading to deprivation of legislative protections when it comes to practices like polygamy, or child marriages or divorce in some cases.
- Experts are of the view that unlike a blanket reform through a move like the Uniform Civil Code, piecemeal reforms in personal laws are more desirable.
- In 2016, the Ministry of Law and Justice tasked the Law Commission to examine matters in relation to uniform civil code (UCC). In 2018, when the Commission submitted its Consultation Paper on Reform of Family Law it steered clear of making any recommendations on UCC and held that it was “neither necessary nor desirable” and favoured “piecemeal changes to laws”.
H. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions
Q1. Which of the following statements about Lala Lajpat Rai is/are correct?
- He was elected President of the Indian National Congress at the Calcutta session.
- He was also elected as the President of the All India Trade Union Congress.
- In England, he became a member of the British Labour party.
Options:
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- None
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: c
Explanation:
- One of the legendary triumvirates – Lal-Bal-Pal (Lala Lajpat Rai, Bal Gangadhar Tilak and Bipin Chandra Pal) of India’s freedom movement against the British colonial rule, Lala Lajpat Rai was a multi-faceted personality.
- He was part of the Arya Samaj, founded and led by Swami Dayanand Saraswati. Later on, he set up a Dayanand Anglo-Vedic school in Lahore.
- As early as 1897, he had founded the Hindu Relief Movement to provide help to the famine-stricken people.
- He visited USA and Japan where he kept in touch with the Indian revolutionaries. In England, he also became a member of the British Labour party.
- In recognition of his outstanding role in the freedom movement, he was elected President of the Indian National Congress at the Calcutta session (1920).
- As he took much interest in the condition of the working-class people, he was also elected as the President of the All India Trade Union Congress.
- Gifted with a perceptive mind, he was a prolific writer and authored several works like – “Unhappy India”, “Young India: An Interpretation”, “History of Arya Samaj”, “England’s Debt to India” and a series of popular biographies on Mazzini, Garibaldi and Swami Dayanand. As a visionary and man with a mission, he founded the Punjab National Bank, the Lakshmi Insurance Company and the Servants of the Peoples Society at Lahore.
Q2. Special Commissioner appointed to contain the rise of Manyam Rebellion is
- Augustus Abbott
- Thomas Adams
- T G Rutherford
- Robert Hope
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: c
Explanation:
- The Rampa Rebellion of 1922, also known as the Manyam Rebellion, was a tribal uprising, led by Alluri Sitarama Raju in Godavari Agency of Madras Presidency, British India. It began in August 1922 and lasted until the capture and killing of Raju in May 1924.
- Unable to contain the ‘Manyam’ uprising, the British Government deputed T G Rutherford in April 1924 to quell the movement.
Q3. Pralay recently seen in news is a/an
- Indigenously-developed second generation, Anti-Tank Guided Missile
- Air-to-Air Beyond Visual Range (BVR) missile
- Surface-to-surface tactical Short-range Ballistic Missile (SRBM)
- All-weather multi-target tracking radar
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: c
Explanation:
- Pralay is a canisterised surface-to-surface tactical short-range ballistic missile for battlefield use developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation of India
Q4. With respect to National Dope Testing Laboratory (NDTL), which of the following statements is/are correct?
- It is a premier analytical testing & research organization established as an autonomous body under the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports
- It is the only laboratory in the country responsible for human sports dope testing.
Options:
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both
- None
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: c
Explanation:
- The National Dope Testing Laboratory (NDTL) is a premier analytical testing & research organization established as an autonomous body under the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports, Government of India.
- It is the only laboratory in the country responsible for human sports dope testing. It is accredited by National Accreditation Board for Testing & Calibration Laboratories, NABL and World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) (2008) for testing of urine & blood samples from human sports.
- NDTL is one of the WADA accredited laboratories in the world.
Q5. With reference to ‘Quality Council of India (QCI)’, consider the following statements:
- QCI was set up jointly by the Government of India and the Indian Industry.
- Chairman of QCI is appointed by the Prime Minister on the recommendations of the industry to the Government.
Which of the above statements is/are correct? [UPSC 2017]
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: c
Explanation:
- Quality Council of India (QCI) was set up jointly by the Government of India and the Indian Industry represented by three premier industry associations i.e. ASSOCHAM, CII and FICCI to establish and operate a national accreditation structure and promote quality through a national quality campaign.
- The chairman of QCI is appointed by the Prime Minister on the recommendation of the industry to the government. The Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion, Ministry of Commerce and Industry is the nodal ministry for QCI.
I. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
- What kind of data is captured in the National Family Health Survey? How can such data be helpful in Government’s policymaking? (250 words; 15 marks)[GS-2, Governance]
- Evaluate the significance of the India-Myanmar relationship and its importance in ensuring peace in India’s Northeast region. (250 words; 15 marks)[GS-2, International Relations]
Read the previous CNA here.
CNA 24 Dec 2021:- Download PDF Here

Comments