CNA 26 Nov 2021:- Download PDF Here
TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS 1 Related POPULATION 1. NFHS says women outnumber men B. GS 2 Related HEALTH 1. Centre mulls new testing modes after anaemia surge C. GS 3 Related D. GS 4 Related E. Editorials SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY 1. Is the crypto asset boom sustainable? HEALTH 1. Measuring progress: On the lessons of National Family Health Survey-5 ENVIRONMENT & ECOLOGY 1. Setting the tone at Glasgow, the job ahead in Delhi F. Prelims Facts 1. Scorpene class submarine INS Vela joins Navy 2. Russia puts into orbit classified military satellite G. Tidbits 1. ‘Bring in three-rate GST structure’ 2. India flays raising bilateral issues at SCO H. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions I. UPSC Mains Practice Questions

A. GS 1 Related
1. NFHS says women outnumber men
Context:
- Fifth edition of the National Family Health Survey.
Background:
National Family Health Survey-5:
- The National Family Health Survey (NFHS) is a large-scale, multi-round survey conducted in a representative sample of households throughout India. Compared to the decadal Census, the NFHS surveys are smaller in terms of surveyed households.
- The survey provides state and national information for India on fertility, infant and child mortality, the practice of family planning, maternal and child health, reproductive health, nutrition, anaemia, utilization and quality of health and family planning services.
- NFHS has had two specific goals: a) to provide essential data on health and family welfare needed by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and other agencies for policy and programme purposes, and b) to provide information on important emerging health and family welfare issues.
Details:
Improved sex ratio and child sex ratio:
- For the first time since the NFHS surveys, the proportion of women exceeded men: there were 1,020 women for 1,000 men (average value).
- The NFHS-4 noted there were 991 women for every 1,000 men.
- The sex ratio at birth for children born in the past five years has improved from 919 per 1,000 males in 2015-16 to 929 per 1,000.
- Thus the National Family Health Survey (NFHS)-5 confirms signs of a demographic shift in India.

Image source: The Hindu
Decreasing TFR:
- The NFHS data also show that India is on its way to stabilising its population, with most States and UTs having a Total Fertility Rate (TFR) of less than two.
- A TFR of less than 2.1 (Replacement TFR) suggests an eventual decline in population over time.
- While some states like Bihar, Meghalaya, Manipur, Jharkhand and Uttar Pradesh continue to have a TFR above two, the TFR in all these States has improved in the last five years.
Population levels:
- Despite the decreasing TFR, India is still poised to be the most populous country in the world, with the current projection by the United Nations population division forecasting that India’s population will peak at 1.6 billion to 1.8 billion from 2040 to 2050.
- The Union government’s report projects India overtaking China as the world’s most populous country around 2031.
B. GS 2 Related
1. Centre mulls new testing modes after anaemia surge
Context:
- The National Family Health Survey-5 (NFHS-5) reveals the rise in cases of anaemia across the spectrum of the population. Anaemia has increased in children, women, pregnant women and men.
For detailed information on this, refer to the following article:
UPSC Exam Comprehensive News Analysis of 25th Nov 2021
Anaemia:
- Anaemia is a condition in which the number of red blood cells or the haemoglobin concentration within them is lower than normal. Anaemia leads to reduced oxygen flow to the body’s organs.
- Anaemia is commonly characterised by low levels of iron in the body.
- Anaemia can also be due to a lack of adequate and quality nutrition and inadequate intake of fresh fruits and vegetables as well as a deficiency of vitamin B-12.
Governmental initiatives:
- The reduction of anaemia is one of the important objectives of the POSHAN Abhiyaan. Complying with the targets of POSHAN Abhiyaan and National Nutrition Strategy set by NITI Aayog, the Anaemia Mukt Bharat strategy has been designed to reduce the prevalence of anaemia by 3 percentage points per year among children, adolescents and women in the reproductive age group (15–49 years), between the year 2018 and 2022.
- Anaemia Mukt Bharat (Anaemia-free India) aims to reduce the proportion of anaemia among children to 40%, pregnant women to 32% and lactating women to 40% by 2022.
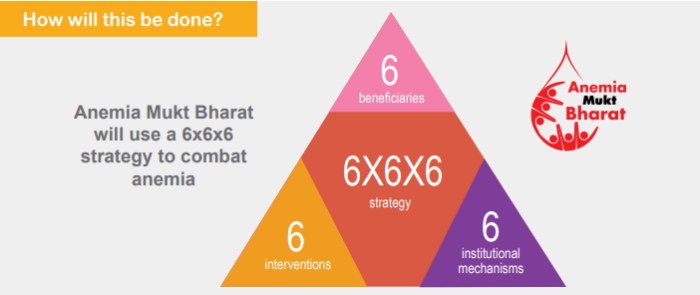

Image source: https://anemiamuktbharat.info/
C. GS 3 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
D. GS 4 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
E. Editorials
Category: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
1. Is the crypto asset boom sustainable?
Retail investors have shown significant interest in Cryptocurrencies which as of now are unregulated. The Centre has announced that it would introduce a new bill in the Winter Session of Parliament to bring these under regulation. This has brought back the debate on whether cryptocurrencies are a bubble or their rise is truly unstoppable.
Value of cryptocurrencies
- Traditionally, gold was an asset that was used to hedge inflation and against any risks in the financial system. It was used as a store of value. Cryptocurrency is another such asset outside the financial system which has offered higher returns than gold.
- The primary advantage of bitcoins is that their supply is limited based on the mathematically designed blockchain network. Hence, they are a better alternative to gold as a hedge against inflation.
- Cryptocurrencies are an asset class with many systems and processes built on the blockchain network such as decentralized finance systems. Transaction costs can be reduced in the long run.
- However, critics argue that the current valuations are not based on the true value of the assets and hence they call it a bubble.
Do cryptocurrencies have real-world value?
- According to one school of thought, Blockchain is being used around the world to better record-keeping and track asset transactions. Due to the high volatility in price, the use of cryptocurrencies for buying and selling goods and services has been limited. It is primarily being used for hedging investments. Governments do not accept taxes in the form of Bitcoin for example. As seen in the case of demonetization, investors have been sceptical of assets whose value can be wiped off by government orders. Bitcoin, being outside the financial system, is seen as a hedge against such system-wide actions and secure the investments better.
- On the other hand, there are businesses that accept Bitcoin for transactions, and many countries are adopting cryptocurrencies for monetary and financial transactions. With easy money policy followed by Central Banks around the world in the form of Quantitative Easing, the value of money has been decreasing significantly. The most important value of Bitcoin is that it is a great store of wealth and savings in it cannot be eroded by creating more and more money at the will of the government.
Risk of Government Sanctions
- Bitcoin is a revolutionary technology that has seen significant adoption. There are developments around the world in the areas of decentralized finance, NFTs and augmented reality. Banning them would lead to denial of access to significant advancements in technology.
- A ban on cryptocurrencies might be counterproductive as it will push the ecosystem underground and it would be wrong to ban crypto assets unless there are compelling reasons. A better policy would be to have a regulatory system in place and allow investments like any asset class. It will also ease the adoption of blockchain and take advantage of the technology in financial record keeping.
- The appeal of the private crypto networks arises from their decentralized nature and a government monopoly over the record-keeping system might not generate much interest.
Benefits of competition among different currencies
- Private currencies could have a beneficial effect in disciplining the central bank. The action in Zimbabwe is a case in point. Printing of excess money led to the loss of value of currency and people moved to the US dollar for transactions. This had a disciplinary effect by forcing the Zimbabwean government to ensure monetary reforms and curtail the supply.
- This was also raised by famous economist Milton Friedman who held that monopoly is considered counterproductive in most cases but monopoly power of the central bank is taken for granted without questioning it.
- Research suggests that private currencies that have a scarce supply would perform as s competing payment instrument and discipline the central bank. An analysis of which currency performs what functions can be undertaken to harness all these instruments within the financial system rather than cracking down on them.
- It would also help to curtain the political decisions on the part of the government to spend more than the supply of funds by printing more money.
1. Measuring progress: On the lessons of National Family Health Survey-5
Context: Latest National Family Health Survey launched by the Union Health Ministry.
Details:
Gains
- There has been an improvement in measures of population health like maternal and child health, sex ratio, and population control.
- India has successfully contained its population explosion as indicated by the drop in total fertility rate from 2.2 during NFHS-4 to 2 in NFHS-5.
- Wasting (weight-for-height) is 19.3 percent among children under five years as compared to 21 percent in NFHS-4 and stunting has also declined by approx 3 percent since the last survey.
- There has also been improvement in areas of institutional delivery and vaccination of infants in 12-23 months age group.
- Health insurance coverage has increased from 28.7% to 41%.
- Gender ratio has, for the first time, recorded more women per 1,000 men.
Areas of concern
- The gains in areas of child nutrition are marginal and require urgent action.
- Also, the sex ratio at birth is still a cause of concern.
- The incidence of anaemia has increased among men, women, and children from the last survey.
- There is a marked increase in obesity among women and men, especially urban women.
Importance of NFHS and Census.
- NFHS is conducted at the district level and uses a sample population whereas Census is nationwide and covers every single household.
- Census is decennial whereas NFHS started in 1992 and is conducted at shorter intervals making it very useful for improving the development indicators.
Category: ENVIRONMENT & ECOLOGY
1. Setting the tone at Glasgow, the job ahead in Delhi
Context
India’s pledge to reach ‘net zero’ emissions by 2070 at CoP26 in Glasgow.
India needs to focus on sustainable well-being amid lofty promises and pledges
- India’s per capita emissions are less than 50% of the global average.
- India’s commitment to reach ‘net zero’ emissions by 2070 has cemented India’s position as a global leader.
- However, India should not succumb to external or internal pressures to become equal among the unequal emitters.
“Carbon colonialism” and beyond
- Undoubtedly it should be the common goal to limit emissions but the treatment for different nations must also be mindful of historical, geographical, and economic disparities.
- The commitments from the large developing nations like India and China lately has forced influential world groupings such as G7 to make a retraction in goal setting for others.
- Climate justice and financial constraints are like partners which cannot be divorced to achieve much-needed harmony.
Making investments not incurring costs
- To uphold and respect the pledges India will have to make transformational changes at almost every level.
- The western civilization and industrialization pattern has to be relooked for their cost-benefit analysis.
- The expenditures for renewable energy, e-mobility, waste to energy, etc. should be taken as a long-term investment rather than costly affairs for now.
Need vs Greed
- The sustainable development goals categorically vouch for ensuring sustainable production and consumption-based social order.
- We have enough resources to fulfil our needs but not anyone’s greed.
- The consumption patterns of the west and also across the globe need to be shifted away from resource and carbon-intensive goods and services from diet to mobility.
- The distribution of wealth and prosperity and affordable energy for all is needed.
Way forward
- While India has always shown the bigger heart in dealing with the issues concerning environmental sustainability and humanity, it must not forget to address the grassroots problems amicably. The constitutional powers and obligations on the society should be adhered to while framing any disrupting legislation or making any commitment, that can affect the lives and dreams of the billions.
F. Prelims Facts
1. Scorpene class submarine INS Vela joins Navy
- The fourth Scorpene class conventional submarine, INS Vela, part of the Indian Navy’s Project-75, has been commissioned into the Navy.
- Six Scorpene submarines are being built under Project-75 by Mazagaon Dock Ltd. under technology transfer from Naval Group of France.
- The first three submarines of the scorpene class include INS Kalvari, INS Khanderi and INS Karanj. The yet to be inducted scorpene class submarines include Vagir and Vagsheer.
- Currently, the Navy has 16 conventional and one nuclear submarine (INS Arihant) in service.
2. Russia puts into orbit classified military satellite
- Russia has successfully placed into orbit a military satellite believed to be part of its early warning anti-missile system.
- The Soyuz rocket carried what is believed to be a Tundra satellite, part of Russia’s missile warning system named Kupol or dome.
- Kupol is designed to detect launches of ballistic missiles and track them to their landing site.
- The system has been designed as a replacement for the current system of early warning satellites called Oko.
G. Tidbits
1. ‘Bring in three-rate GST structure’
- As per a National Institute of Public Finance and Policy (NIPFP) study, the Government can rationalise the GST rate structure without losing revenues by rejigging the four major rates of 5%, 12%, 18% and 28% with a three-rate framework of 8%, 15% and 30%.
- Currently, the GST regime levies eight different rates, including zero for essential goods and special rates of 0.25% on diamonds, precious stones and 3% on gems and jewellery.
- Multiple rate changes since the introduction of the GST regime in July 2017 have brought the effective GST rate to 11.6% from the original revenue-neutral rate of 15.5%.
2. India flays raising bilateral issues at SCO
- Speaking at the 20th meeting of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Council of Heads of Government, the Indian External Affairs Minister has criticized the attempts by member countries of SCO to raise bilateral issues in the forum.
- These attempts the minister argued violates the well-established principles and norms of the SCO Charter and would also be counterproductive to the spirit of consensus and cooperation of the SCO.
- The SCO Charter calls for a “peaceful settlement” of conflicts and disputes among member states.
- India joined the SCO at the Astana summit in 2017.
H. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions
Q1. Which of the given statements is/are INCORRECT with respect to the ASEM Process?
- ASEM is a platform for the countries in Asia and Europe to exchange views on regional and global issues and strengthen cooperation.
- The grouping comprises members of the European Union and ASEAN only.
- The latest summit marked the 25th anniversary of the ASEM process and was chaired by India.
Options:
- 1 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- None of the above
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: c
Explanation:
- The Asia-Europe Meeting (ASEM) is an informal forum for dialogue and cooperation, bringing together partners from across Europe and Asia. Its main purpose is to provide a platform for fostering political dialogue, strengthening economic cooperation and tackling together global challenges. ASEM is conducted as an informal and flexible process on the basis of equal partnership, mutual respect and benefit.
- Currently, ASEM comprises 51 partner countries: the 28 Member States of the European Union plus Norway and Switzerland on the European side and the 10 ASEAN countries plus Australia, Bangladesh, China, India, Japan, Kazakhstan, Republic of Korea, Mongolia, New Zealand, Pakistan and Russia on the Asian side. It also includes two institutional partners: the European Union and the ASEAN Secretariat.
- 2021 marks the 25th anniversary of the ASEM process. Cambodia currently holds the rotating ASEM presidency.
Q2. Consider the following statements with respect to INS Vela:
- It is the first of the Indian Navy’s six submarines under Project 75.
- It is a Stealth Scorpene-Class Submarine.
- It is a diesel-electric attack submarine of Kalvari-class.
Which of the given statements is/are INCORRECT?
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 only
- 3 only
- None of the above
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: b
Explanation:
- INS Vela is the fourth of the Indian Navy’s six submarines under Project 75.
- It is a Scorpene-Class Submarine. It is a diesel-electric attack submarine of Kalvari-class.
Q3. The herb “Withania somnifera” is often seen in News as:
- It is a widely used herb in traditional Indian Medicine.
- It is an invasive species present in the Kole Wetlands in Kerala.
- Its extract is widely used in making pesticides.
- It is a herb that contains a dangerous amount of Iodine which can cause goitre, high thyroid-stimulating hormone levels, and hypothyroidism.
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: a
Explanation:
- Withania somnifera, known commonly as ashwagandha is an annual evergreen shrub in the Solanaceae or nightshade family that grows in India, the Middle East, and parts of Africa. It is a very revered herb of the Indian Ayurvedic system of medicine as a Rasayana (tonic).
Q4. Which of the given statements with repsect to Rashtriya Gokul Mission is/are correct?
- It is a component of the National Programme for Bovine Breeding and Dairy Development.
- It was initiated in 2018 with a focus on the conservation and development of indigenous breeds and improve their genetic makeup.
- Its components include the establishment of integrated indigenous cattle centres (Gokul Gram) and breeder’s societies (Gopalan Sangh).
Options:
- 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: c
Explanation:
- Rashtriya Gokul Mission is one of the components of the National Programme for Bovine Breeding and Dairy Development.
- Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM) was launched in 2014 for the development and conservation of indigenous breeds through selective breeding in the breeding tract and genetic up-gradation of non-descript breeds.
- The mission envisages the establishment of integrated cattle development centres, Gokul Grams and breeder’s societies (Gopalan Sangh) to develop indigenous breeds.
Q5. In the Constitution of India, promotion of international peace and security is included in the: (UPSC-2014)
- Preamble to the Constitution
- Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP)
- Fundamental Duties
- Ninth Schedule
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: b
Explanation:
- Article 51 of the Indian Constitution deals with the promotion of international peace and security. It states that the State shall endeavour to—
- promote international peace and security;
- maintain just and honourable relations between nations;
- foster respect for international law and treaty obligations in the dealings of organized peoples with one another; and
- encourage settlement of international disputes by arbitration.
I. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
- Will the idea of designating three capitals for the State promote ‘distributed development’? Critically examine. (15 Marks, 250 Words)[GS-2, Polity and Governance]
- The rising tide of criminalization in Indian politics threatens the survival of true democracy. Discuss. (15 Marks, 250 Words)[GS-2, Polity and Governance]
Read the previous CNA here.
CNA 26 Nov 2021:- Download PDF Here

Comments