Oxygen

| Symbol | O |
| Atomic Number | 8 |
| Atomic Mass | 15.999 g.mol-1 |
| Discovered by | Joseph Priestly in 1774 |
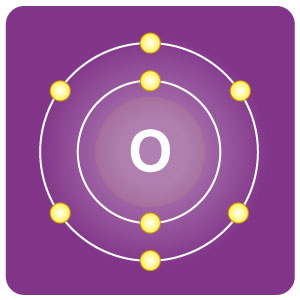
Table of Contents
- Chemical Properties of Oxygen
- What is Oxygen?
- Uses of Oxygen
- Physical Properties of Oxygen
- Other Important Information
- Recommended Videos
Chemical Properties of Oxygen
| Group | 16 | Melting point | -219 °c |
| Period | 2 | Boiling point | -183 °c |
| Block | p | Density (g cm−3) | 0.001308 |
| Atomic number | 8 | Relative atomic mass | 15.999 |
| State at 20°C | Gas | Key isotopes | 16O |
| Electron configuration | [He]2s2 2p4 | CAS number | 7782-44-7 |
| ChemSpider ID | 140526 | ChemSpider is a free chemical structure database | |
What is Oxygen?
- Oxygen is a member of the chalcogen group on the periodic table. It is an essential element in most combustion processes.
- It is one of the most abundant elements in the Earth’s crust.
Uses of Oxygen
- It is used in the production and manufacturing of glass and stone products, and in mining.
- Special oxygen chambers are used in case of high pressure to increase the partial pressure of oxygen around the patient.
- The primary applications of oxygen include melting, refining, and manufacturing of steel along with other metals.
Physical Properties of Oxygen
- The gas is colourless, odourless and insipid in a normal state. Liquid oxygen is slightly paramagnetic. It is reactive and forms oxides with every element except helium, neon, krypton, and argon. It is moderately soluble in water.
- Dioxygen is one of the common allotropes of oxygen.
- Trioxygen is the most reactive allotrope of oxygen that would cause damage to lung tissue. This allotrope is termed ozone.
Other Important Information
- O-16, O-17, and O-18 are the three naturally occurring stable isotopes of Oxygen.
- Oxygen is characterised by a paramagnetic property.
Recommended Videos


It’s very good to see that we have such a wonderful learning programme in our INDIA. I’m very proud to see this, that’s what I want to say. That’s all